Natural Killer Cell Markers
Click on one of the ILC subsets shown in the buttons below to see the markers that are commonly used to identify each cell type.
Recommended Products
Overview
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphoid cells with both intrinsic cytotoxic potential and cytokine-producing capabilities that have been classified as group 1 ILCs. NK cells activation occurs following the detection of abnormalities in target cells, including cells infected with certain bacteria, virally infected cells and cancer. While NK cells share many features with ILC1s including expression of the transcription factor T-bet and activation-induced production of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, they also express the transcription factor, eomesodermin (Eomes), along with granzyme B and perforin, which ILC1s do not. Accordingly, NK cells have been suggested to be the innate counterpart of CD8+ T cells.
Mouse Cell Surface Markers
In mice, NK cells are defined as CD3-NK1.1+ or CD3-NKp46+ cells that also typically express Integrin alpha 2/CD49b, Integrin alpha M/CD11b, CD27, T-bet, and Eomes, and lack expression of CD127/IL-7 R alpha. Three subsets of mouse NK cells have been characterized based on the differential expression of Integrin alpha M/CD11b and CD27.
These include:
- CD11dimCD27bright NK cells
- CD11bbrightCD27dim NK cells
- CD11bbrightCD27bright NK cells
| Table 1. Markers Used to Identify Mouse NK Cells - Antibodies by Molecule | |||||
| CD3 | CD11b/Integrin alpha M | CD27 | CD122/IL-2 R beta | CD127/IL-7 R alpha | CD161/NK1.1 |
| Eomes | Integrin alpha 2/CD49b | NKG2D | NKp46 | T-bet | |
Human Cell Surface Markers
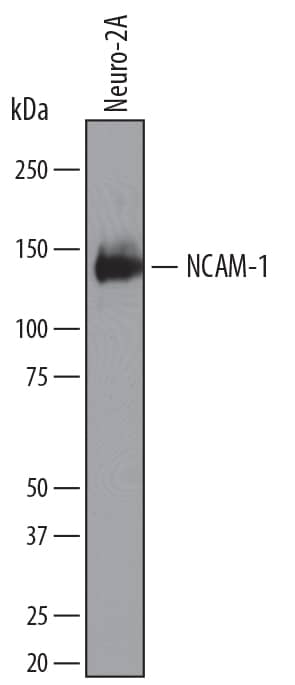
In humans, NK cells are typically defined as CD3-CD56+ cells that are also CD7+CD127-NKp46+T-bet+Eomes+. Different subtypes of human NK cells have been identified that are either CD3-CD56dimCD16+ or CD3-CD56brightCD16-. The CD56dimCD16+ subset of NK cells is predominantly found in the blood and is highly cytotoxic, while the CD56brightCD16- subset is the main subtype found in the lymph nodes and has only weak cytotoxic potential. Some studies have suggested that CD56< sup>brightCD16- subset are immature precursors of mature CD56dimCD16+ NK cells.
| Table 2. Markers Used to Identify Human NK Cells - Antibodies by Molecule | |||||
| CD3 | CD56/NCAM-1 | CD94 | CD122/IL-2 R beta | CD127/IL-7 R alpha | Eomes |
| Fc gamma RIII/CD16 | NKG2A | NKG2D | NKp30 | NKp44 | NKp46 |
| NKp80 | T-bet | ||||
NK cell activation markers
In addition to the markers which are commonly used to identify mouse and human NK cells by flow cytometry, NK cells also express multiple cell surface receptors that regulate their activation. These include the human killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) and mouse Ly49 family receptors, CD94-NKG2 heterodimeric receptors, NKG2D, natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs).
| Table 3. Antibodies to Detect Receptors that Regulate NK Cell Activation | |||||
| 2B4/CD244 | CD27 | CD94 | CD96 | CD100/Semaphorin 4D | CD160 |
| CEACAM-1 | CRACC/SLAMF7 | CRTAM | DNAM-1/CD226 | Fc gamma RIIIA/CD16 | KIR2DL1 |
| KIR2DL2 | KIR2DL3 | KIR2DL4 | KIR2DL5 | KIR3DL1 | KIR3DL2 |
| KIR3DL3 | KIR2DS1 | KIR2DS4 | KIR2DS5 | KIR3DS1 | KLRG1 |
| LAIR1 | LILRB1/ILT2 | NKG2A | NKG2C | NKG2D | NKp30 |
| NKp44 | NKp46 | NKp80 | NTB-A/SLAMF6 | ||
Additional Products for NK Cell Culture and Analysis
| Table 4. Cytokines for Natural Killer (NK) Cell Culture and Differentiation - Proteins by Molecule | |||||
| IL-2*† | IL-12 | IL-15*† | IL-18/IL-1F4 | IL-21*† | |
| * GMP-grade proteins are available for these molecules. | |||||
| † Liquid formulations for GMP and Animal-free Preclinical grades of this cytokine are now available. | |||||
| Table 5. Select ELISAs for Detecting Molecules Secreted by NK Cells - Products by Molecule | |||||
| GM-CSF | Granzyme B | IFN-gamma | IL-10 | Perforin | TNF-alpha |
Featured Product

Fluorokines™ for Cell Marker Research
- Direct Detection
- Reduced processing Time
- High Levels of Bioactivity
Featured Literature

Cell Markers Guide to Human Immune Cell Characterization
Order Your Poster TodayFeatured Pathway