Dopamine D1-Like Receptor Family Signaling Pathways
Click on each of the dopamine receptor families below to see the signaling pathways activated by receptors in that family. Click on DARPP-32 to view the phosphorylation sites on DARPP-32 with the respective kinases.
Ca2+
Channel
Ca2+
Channel
Receptor Family
Receptor Family
D5 R/DRD5
D5 R/DRD5
D1 R/DRD1
D1 R/DRD1
D2 R/DRD2
D2 R/DRD2
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Family
Kinase
Family
Kinase
Internalization
Internalization
Cyclase
Cyclase
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Increase Activity- NMDA Receptors
- AMPA Receptors
- L-Type Ca2+
Channels
Channels
Increase Activity- NMDA Receptors
- AMPA Receptors
- L-Type Ca2+
Channels
Channels
Decrease Activity- Nav Channels
- Kir Channels
- N-, P/Q-Type Ca2+
Channels
Channels
Decrease Activity- Nav Channels
- Kir Channels
- N-, P/Q-Type Ca2+
Channels
Channels
Nuclear Translocation
Nuclear Translocation
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
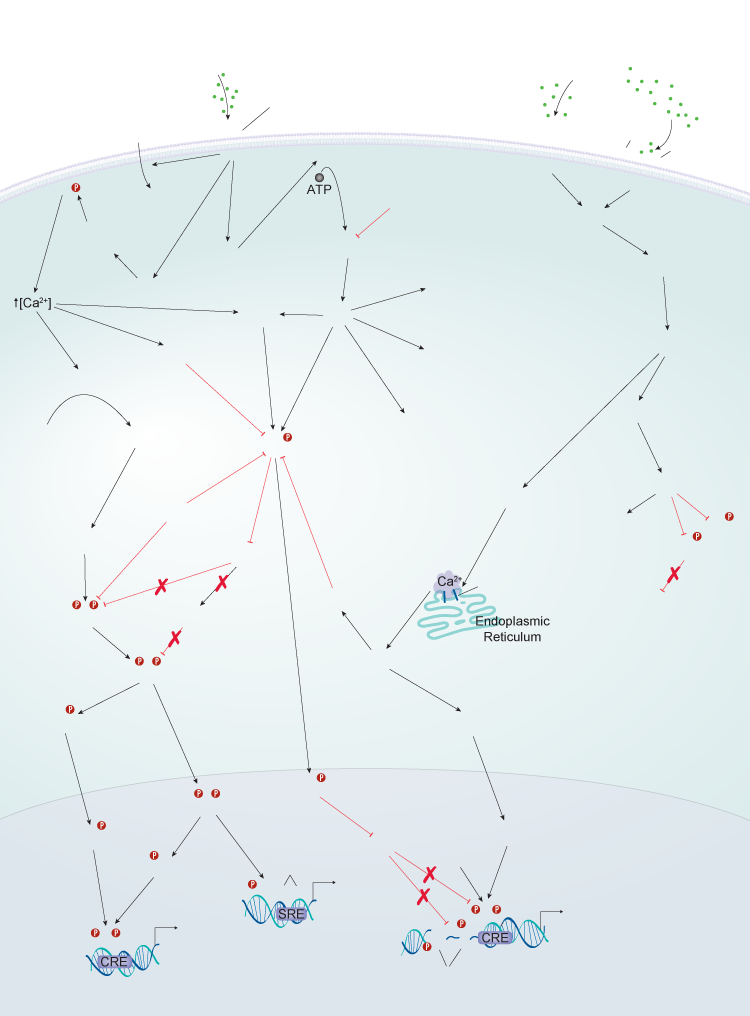
Dopamine (DA) is the dominate catecholamine neurotransmitter in the brain. It participates in a number of functions such as locomotion, memory, emotional and motivated behaviors, and neuroendocrine regulation. DA levels have been implicated in numerous neurological and psychiatric disorders including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington's disease, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and Tourette's syndrome.
DA exerts its effects through five G protein-coupled receptors that are divided into two families based on structure and biological response: D1- and D2-like receptor families. The D1-like receptors, Dopamine D1 Receptor/DRD1 and Dopamine D5 Receptor/DRD5, share 80% amino acid (aa) sequence homology in their transmembrane domains, while the D2-like receptors, Dopamine D2 Receptor/DRD2, Dopamine D3 Receptor/DRD3, and Dopamine D4 Receptor/DRD4, are less homologous. The transmembrane regions of the D2 receptor share 75% and 53% aa sequence homology with the transmembrane domains of the D3 and D4 receptors, respectively. The D1 and D2 receptors are the most abundant dopamine receptor subtypes in the brain and exhibit broad expression patterns. The highest expression levels of the D1 receptor are observed in the caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, olfactory bulb, amygdala, and frontal cortex. The highest levels of the D2 receptor are found in the caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle, substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, hypothalamus, septum, amygdala, hippocampus, and cortical areas.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway

