Human/Canine NGFR/TNFRSF16 Antibody Summary
Lys29-Asn250
Accession # P08138
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human NGF R/TNFRSF16 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of SW480 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human/Canine NGF R/TNFRSF16 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB367) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for NGF R/TNFRSF16 at approximately 65 kDa (as indicated). GAPDH (Catalog # MAB5718) is shown as a loading control. This experiment was conducted under non-reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of NGF R/TNFRSF16 in SH‑SY5Y Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human NGF R/TNFRSF16 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB367, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram) followed by anti-Mouse IgG PE-conjugated Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
NGF R/TNFRSF16 in Canine Mesenchymal Stem Cells. NGF R/TNFRSF16 was detected in immersion fixed canine mesenchymal stem cells using Mouse Anti-Human/Canine NGF R/TNFRSF16 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB367) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
NGF R/TNFRSF16 in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. NGF R/TNFRSF16 was detected in immersion fixed human mesenchymal stem cells using Mouse Anti-Human/Canine NGF R/TNFRSF16 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB367) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
NGF R/TNFRSF16 in Human Brain. NGF R/TNFRSF16 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human brain (cortex) using 25 µg/mL Mouse Anti-Human/Canine NGF R/TNFRSF16 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB367) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Mouse HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS002) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
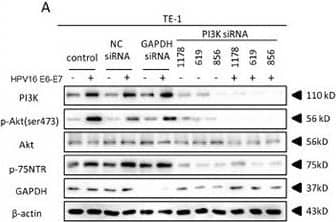
Detection of NGFR/TNFRSF16 by Western Blot HPV16 E6-E7 increased p75NTR expression through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in TE-1 cellsA. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. TE-1 cells were treated by negative control RNA, GAPDH RNA, PI3K siRNA, respectively. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. “-” means HPV16 E6-E7 negative which represents TE-1-control cells, “+” means HPV16 E6-E7 positive which represents TE-1-psb cells. B. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. TE-1 cells were treated by negative control RNA, GAPDH RNA, Akt siRNA, respectively. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. “-” means HPV16 E6-E7 negative which represents TE-1-control cells, “+” means HPV16 E6-E7 positive which represents TE-1-psb cells. C. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure A were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells in control siRNA group. ###P<0.001, relative to TE-1-psb cell in control siRNA group. D. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure B were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells in control siRNA group or Akt siRNA group. ###P<0.001, relative to TE-1-psb cell in control siRNA group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27489353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
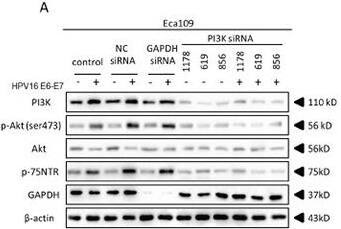
Detection of NGFR/TNFRSF16 by Western Blot HPV16 E6-E7 increased p75NTR expression through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in Eca109 cellsA. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. Eca109 cells were treated by negative control RNA, GAPDH RNA, PI3K siRNA, respectively. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. “-” means HPV16 E6-E7 negative which represents Eca109-control cells, “+”means HPV16 E6-E7 positive which represents Eca109-psb cells. B. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. Eca109 cells were treated by negative control RNA, GAPDH RNA, Akt siRNA, respectively. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. “-”means HPV16 E6-E7 negative which represents Eca109-control cells, “+”means HPV16 E6-E7 positive which represents Eca109-psb cells. C. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure A were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells in control siRNA group. ###P<0.001, relative to Eca109-psb cell in control siRNA group. D. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure B were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells in control siRNA group or Akt siRNA group. ###P<0.001, relative to Eca109-psb cell in control siRNA group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27489353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
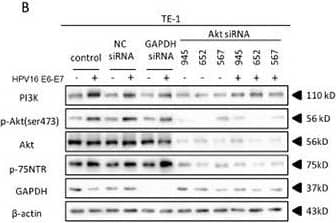
Detection of NGFR/TNFRSF16 by Western Blot HPV16 E6-E7 increased p75NTR expression through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in TE-1 cellsA. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. TE-1 cells were treated by negative control RNA, GAPDH RNA, PI3K siRNA, respectively. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. “-” means HPV16 E6-E7 negative which represents TE-1-control cells, “+” means HPV16 E6-E7 positive which represents TE-1-psb cells. B. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. TE-1 cells were treated by negative control RNA, GAPDH RNA, Akt siRNA, respectively. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. “-” means HPV16 E6-E7 negative which represents TE-1-control cells, “+” means HPV16 E6-E7 positive which represents TE-1-psb cells. C. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure A were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells in control siRNA group. ###P<0.001, relative to TE-1-psb cell in control siRNA group. D. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure B were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells in control siRNA group or Akt siRNA group. ###P<0.001, relative to TE-1-psb cell in control siRNA group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27489353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
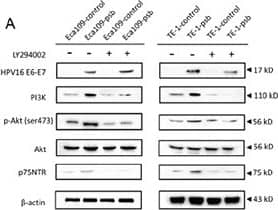
Detection of NGFR/TNFRSF16 by Western Blot PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation and increased p75NTR expression induced by HPV16 E6-E7 were inhibited by LY294002 in ESCC cellsA. Proteins involved in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and p75NTR protein were analysed by western blotting. Cells were treated with LY294002 (10μmol/L) for 24h. Equal protein loading was evaluated by beta -actin. B. Densitometric of western blotting bands in Figure A were analyzed and expressed relative to the loading control, beta -actin. Data are typical of three experiments and the histogram values are mean ± S.D. **P<0.01,***P<0.001, relative to control cells without LY294002 treatment. ###P<0.001, relative to psb cells without LY294002 treatment. C. p-Akt, PI3K and p75NTR proteins of ESCC cells were detected by immunofluorescence. D. PI3K and p75NTR proteins of spheres formed from ESCC cells were detected by immunofluorescence. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27489353), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
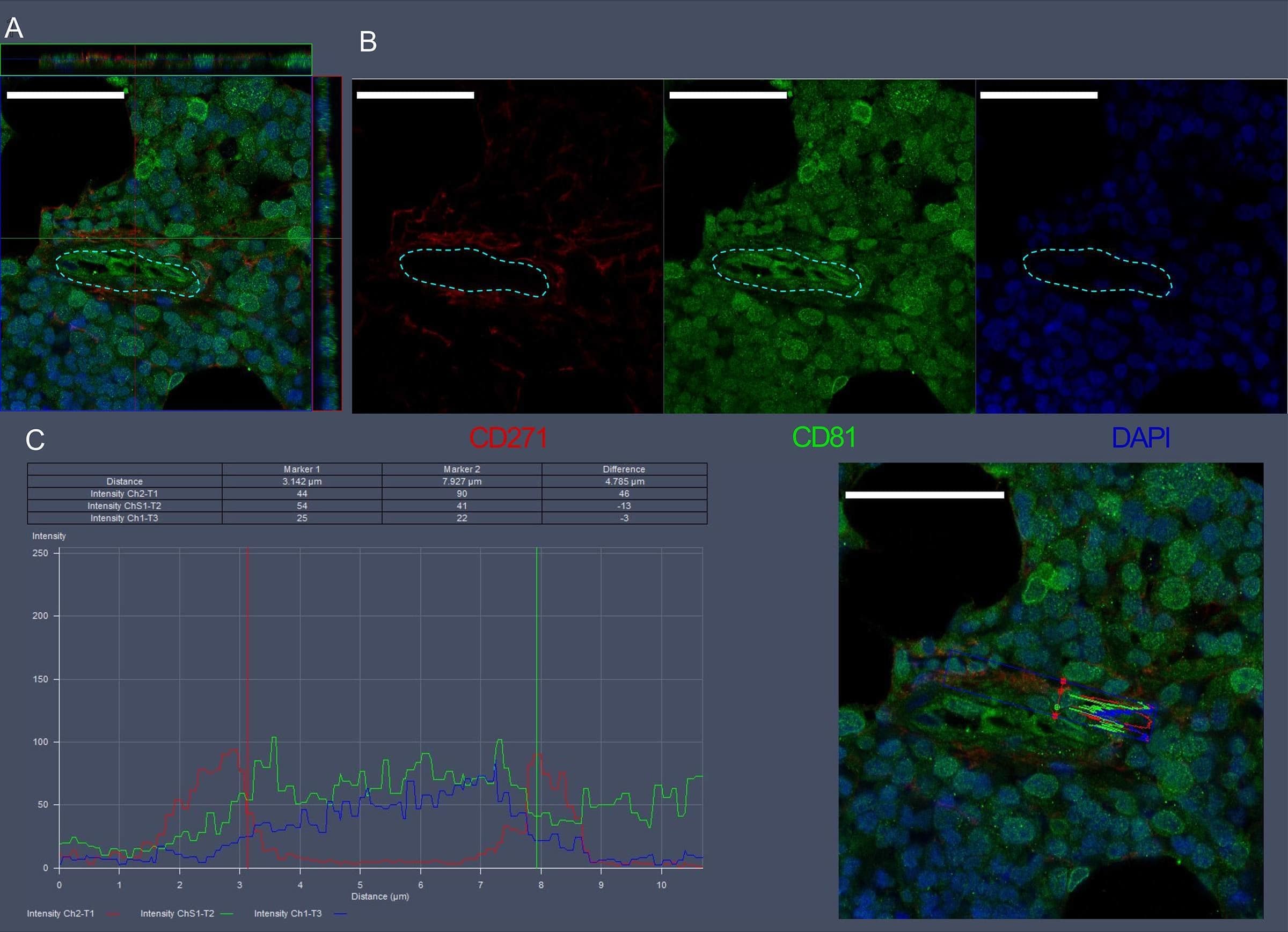
Detection of NGFR/TNFRSF16 by Immunohistochemistry Visualization of CD271 and CD81 expression in bone marrow vascular regions by confocal microscopy.(A) Confocal scan of vascular region in BM biopsies with 3D orthographic cross-section view, co-stained with mouse anti-CD271, rabbit anti-CD81, and DAPI. (B) Single channel data for the florescent markers in A. (C) Intensity profile for all channels in A across a cell of interest in a representative z plane. Scale bars represent 50 μm. Yellow dashed lines indicated vessel surface. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36876630), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
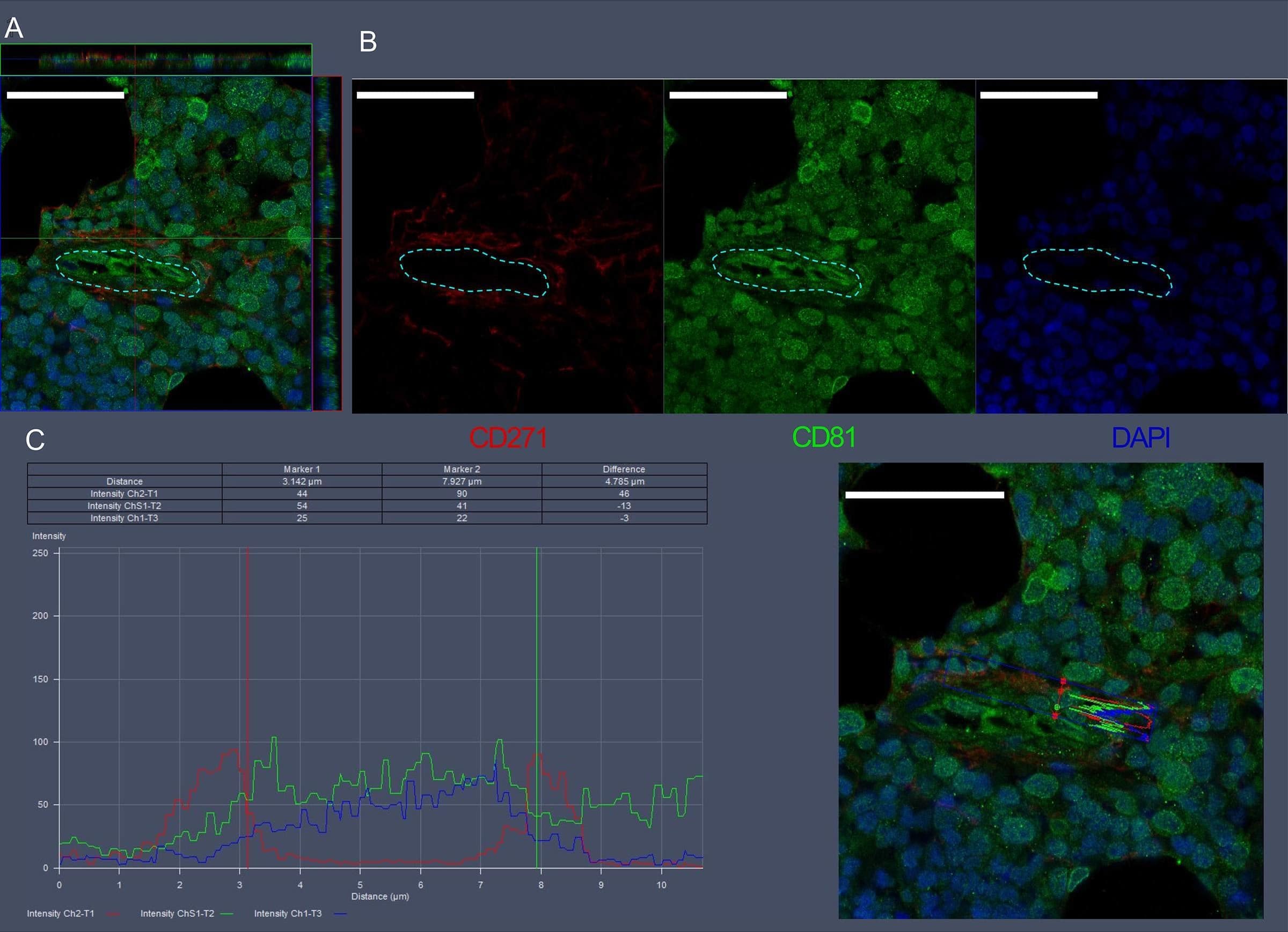
Detection of NGFR/TNFRSF16 by Immunohistochemistry Visualization of CD271 and CD81 expression in bone marrow vascular regions by confocal microscopy.(A) Confocal scan of vascular region in BM biopsies with 3D orthographic cross-section view, co-stained with mouse anti-CD271, rabbit anti-CD81, and DAPI. (B) Single channel data for the florescent markers in A. (C) Intensity profile for all channels in A across a cell of interest in a representative z plane. Scale bars represent 50 μm. Yellow dashed lines indicated vessel surface. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36876630), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: NGFR/TNFRSF16
NGF R is a type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor family (1) and has been designated TNFRSF16. This receptor is also known as p75 NTR (neurotrophin receptor) because of its ability to bind at low affinity not only to NGF, but also other neurotrophins including Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), Neurotrophin-3 and Neurotrophin-4/5. NGF R is a 75 kDa protein that is expressed in neuronal axons, Schwann’s cells and perineural cells of peripheral nerves (1). Neural crest stem cells have been isolated based on their surface expression of NGF R (2, 3). In addition, neuroepithelial-derived NGF R positive cells have also been demonstrated to be able to differentiate into neurons, smooth muscle and Schwann cells in culture (4). NGF R has been used as a marker to identify mesenchymal precursors as well as hepatic stellate cells (5, 6).
- Barker, P.A. et al. (1992) Mol. Cell Biochem. 110:1.
- Stemple, D.L. et al. (1992) Cell 71:973.
- Morrison, S.J. et al. (1999) Cell 96:737.
- Mujtaba, T. et al. (1998) Dev. Biol. 200:1.
- Campagnolo, L. et al. (2001) Biol. Reprod. 64:464.
- Cassiman, D. et al. (2001) Hepatology 33:148.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Canine NGFR/TNFRSF16 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
11
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Visual Sequences Drive Experience-Dependent Plasticity in Mouse Anterior Cingulate Cortex
Authors: Sidorov MS, Kim H, Rougie M et al.
Cell Reports
-
A Single Injection of NTG-101 Reduces the Expression of Pain-Related Neurotrophins in a Canine Model of Degenerative Disc Disease
Authors: Ajay Matta, Muhammad Zia Karim, Hoda Gerami, Bettina Zoe Benigno, Ivan Cheng, Arne Mehrkens et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
-
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor localization and activation effects on ganglion response properties.
Authors: Strang CE, Renna JM, Amthor FR, Keyser KT.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci
-
Identification of phenotypically, functionally, and anatomically distinct stromal niche populations in human bone marrow based on single-cell RNA sequencing
Authors: Li H, Bräunig S, Dhapolar P et al.
eLife
-
Visual Sequences Drive Experience-Dependent Plasticity in Mouse Anterior Cingulate Cortex
Authors: Sidorov MS, Kim H, Rougie M et al.
Cell Reports
-
Tracking extracellular vesicle phenotypic changes enables treatment monitoring in melanoma
Authors: J Wang, A Wuethrich, AA Sina, RE Lane, LL Lin, Y Wang, J Cebon, A Behren, M Trau
Sci Adv, 2020-02-26;6(9):eaax3223.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
An initial investigation into endothelial CC chemokine expression in the human rheumatoid synovium.
Authors: Rump L, Mattey D, Kehoe O, Middleton J
Cytokine, 2017-09-01;97(0):133-140.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Decreased demand for olfactory periglomerular cells impacts on neural precursor cell viability in the rostral migratory stream
Sci Rep, 2016-08-30;6(0):32203.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Human papillomavirus 16 infection predicts poor outcome in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Authors: Xi R, Zhang X, Chen X, Pan S, Hui B, Zhang L, Fu S, Li X, Zhang X, Gong T, Guo J, Che S
Onco Targets Ther, 2015-03-05;8(0):573-81.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
BDNF and its receptors in human myasthenic thymus: implications for cell fate in thymic pathology.
Authors: Berzi A, Ayata CK, Cavalcante P, Falcone C, Candiago E, Motta T, Bernasconi P, Hohlfeld R, Mantegazza R, Meinl E, Farina C
J. Neuroimmunol., 2008-06-13;197(2):128-39.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC-Fr -
Mesenchymal stem cell abnormalities in patients with multiple myeloma.
Authors: Garderet L, Mazurier C, Chapel A, Ernou I, Boutin L, Holy X, Gorin NC, Lopez M, Doucet C, Lataillade JJ
Leuk. Lymphoma, 2007-10-01;48(10):2032-41.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Canine NGFR/TNFRSF16 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human/Canine NGFR/TNFRSF16 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:




