Human GDF-15 DuoSet ELISA Summary
* Provided that the recommended microplates, buffers, diluents, substrates and solutions are used, and the assay is run as summarized in the Assay Procedure provided.
This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human GDF-15. The suggested diluent is suitable for the analysis of most cell culture supernate samples. Diluents for complex matrices, such as serum and plasma, should be evaluated prior to use in this DuoSet.
Product Features
- Optimized capture and detection antibody pairings with recommended concentrations save lengthy development time
- Development protocols are provided to guide further assay optimization
- Assay can be customized to your specific needs
- Economical alternative to complete kits
Kit Content
- Capture Antibody
- Detection Antibody
- Recombinant Standard
- Streptavidin conjugated to horseradish-peroxidase (Streptavidin-HRP)
Other Reagents Required
DuoSet Ancillary Reagent Kit 2 (5 plates): (Catalog # DY008) containing 96 well microplates, plate sealers, substrate solution, stop solution, plate coating buffer (PBS), wash buffer, and Reagent Diluent Concentrate 2.
The components listed above may be purchased separately:
PBS: (Catalog # DY006), or 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8.1 mM Na2HPO4, 1.5 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.2 - 7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Wash Buffer: (Catalog # WA126), or 0.05% Tween® 20 in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4
Reagent Diluent: (Catalog # DY995), or 1% BSA in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Substrate Solution: 1:1 mixture of Color Reagent A (H2O2) and Color Reagent B (Tetramethylbenzidine) (Catalog # DY999)
Stop Solution: 2 N H2SO4 (Catalog # DY994)
Microplates: R&D Systems (Catalog # DY990)
Plate Sealers: ELISA Plate Sealers (Catalog # DY992)
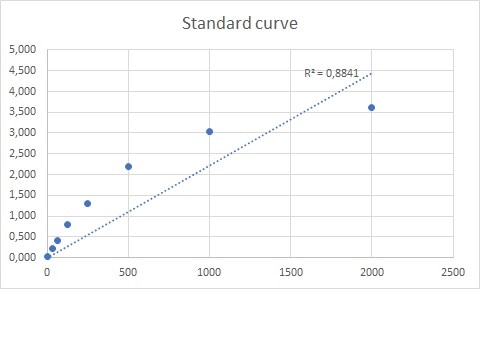
Scientific Data
Product Datasheets
Preparation and Storage
Background: GDF-15
Growth/differentiation factors (GDF-1 to GDF-15) are members of the BMP family of TGF-beta superfamily proteins. They are produced as inactive preproproteins which are then cleaved and assembled into active secreted homodimers. GDF dimers are disulfide-linked with the exception of GDF-3 and -9. GDF proteins are important during embryonic development, particularly in the skeletal, nervous, and muscular systems.
Assay Procedure
GENERAL ELISA PROTOCOL
Plate Preparation
- Dilute the Capture Antibody to the working concentration in PBS without carrier protein. Immediately coat a 96-well microplate with 100 μL per well of the diluted Capture Antibody. Seal the plate and incubate overnight at room temperature.
- Aspirate each well and wash with Wash Buffer, repeating the process two times for a total of three washes. Wash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (400 μL) using a squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, or autowasher. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essential for good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining Wash Buffer by aspirating or by inverting the plate and blotting it against clean paper towels.
- Block plates by adding 300 μL Reagent Diluent to each well. Incubate at room temperature for a minimum of 1 hour.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2. The plates are now ready for sample addition.
Assay Procedure
- Add 100 μL of sample or standards in Reagent Diluent, or an appropriate diluent, per well. Cover with an adhesive strip and incubate 2 hours at room temperature.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2 of Plate Preparation.
- Add 100 μL of the Detection Antibody, diluted in Reagent Diluent, to each well. Cover with a new adhesive strip and incubate 2 hours at room temperature.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2 of Plate Preparation.
- Add 100 μL of the working dilution of Streptavidin-HRP to each well. Cover the plate and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2.
- Add 100 μL of Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
- Add 50 μL of Stop Solution to each well. Gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing.
- Determine the optical density of each well immediately, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm. If wavelength correction is available, set to 540 nm or 570 nm. If wavelength correction is not available, subtract readings at 540 nm or 570 nm from the readings at 450 nm. This subtraction will correct for optical imperfections in the plate. Readings made directly at 450 nm without correction may be higher and less accurate.
Citations for Human GDF-15 DuoSet ELISA
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
47
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and hepatocyte stress increase GDF-15 throughout development of obesity to MASH
Authors: L'homme, L;Sermikli, BP;Haas, JT;Fleury, S;Quemener, S;Guinot, V;Barreby, E;Esser, N;Caiazzo, R;Verkindt, H;Legendre, B;Raverdy, V;Cheval, L;Paquot, N;Piette, J;Legrand-Poels, S;Aouadi, M;Pattou, F;Staels, B;Dombrowicz, D;
Nature communications
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Total and H-specific GDF-15 levels increase in caloric deprivation independently of leptin in humans
Authors: Chrysafi, P;Valenzuela-Vallejo, L;Stefanakis, K;Kelesidis, T;Connelly, MA;Mantzoros, CS;
Nature communications
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Relationships between Circulating Biomarkers and Body Composition Parameters in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Community-Based Study
Authors: Tarabeih, N;Kalinkovich, A;Ashkenazi, S;Cherny, SS;Shalata, A;Livshits, G;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
GDF15 linked to maternal risk of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
Authors: Fejzo, M;Rocha, N;Cimino, I;Lockhart, SM;Petry, CJ;Kay, RG;Burling, K;Barker, P;George, AL;Yasara, N;Premawardhena, A;Gong, S;Cook, E;Rimmington, D;Rainbow, K;Withers, DJ;Cortessis, V;Mullin, PM;MacGibbon, KW;Jin, E;Kam, A;Campbell, A;Polasek, O;Tzoneva, G;Gribble, FM;Yeo, GSH;Lam, BYH;Saudek, V;Hughes, IA;Ong, KK;Perry, JRB;Sutton Cole, A;Baumgarten, M;Welsh, P;Sattar, N;Smith, GCS;Charnock-Jones, DS;Coll, AP;Meek, CL;Mettananda, S;Hayward, C;Mancuso, N;O'Rahilly, S;
Nature
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: Mass Spectometry -
GDF15 promotes weight loss by enhancing energy expenditure in muscle
Authors: Wang, D;Townsend, LK;DesOrmeaux, GJ;Frangos, SM;Batchuluun, B;Dumont, L;Kuhre, RE;Ahmadi, E;Hu, S;Rebalka, IA;Gautam, J;Jabile, MJT;Pileggi, CA;Rehal, S;Desjardins, EM;Tsakiridis, EE;Lally, JSV;Juracic, ES;Tupling, AR;Gerstein, HC;Paré, G;Tsakiridis, T;Harper, ME;Hawke, TJ;Speakman, JR;Blondin, DP;Holloway, GP;Jørgensen, SB;Steinberg, GR;
Nature
Species: Mouse, Human
Sample Types: Plasma, Serum
-
Fetally-encoded GDF15 and maternal GDF15 sensitivity are major determinants of nausea and vomiting in human pregnancy
Authors: Fejzo, M;Rocha, N;Cimino, I;Lockhart, SM;Petry, C;Kay, RG;Burling, K;Barker, P;George, AL;Yasara, N;Premawardhena, A;Gong, S;Cook, E;Rainbow, K;Withers, DJ;Cortessis, V;Mullin, PM;MacGibbon, KW;Jin, E;Kam, A;Campbell, A;Polasek, O;Tzoneva, G;Gribble, FM;Yeo, G;Lam, B;Saudek, V;Hughes, IA;Ong, KK;Perry, J;Sutton Cole, A;Baumgarten, M;Welsh, P;Sattar, N;Smith, G;Charnock Jones, DS;Coll, AP;Meek, CL;Mettananda, S;Hayward, C;Mancuso, N;O'Rahilly, S;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Plasma
-
A Story of PA/BSA and Biomarkers to Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis-The Rise of IGF-BP2 and GDF-15
Authors: J Kletzer, S Hecht, S Ramsauer, B Scharinger, R Kaufmann, J Kammler, J Kellermair, K Akbari, H Blessberge, C Steinwende, K Hergan, UC Hoppe, M Lichtenaue, E Boxhammer
Journal of cardiovascular development and disease, 2023-01-05;10(1):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Intermittent fasting increases growth differentiation factor 15 in females with overweight or obesity but not associated with food intake
Authors: K Liu, B Liu, GA Wittert, CH Thompson, AT Hutchison, LK Heilbronn
Obesity research & clinical practice, 2022-12-09;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
The fatal trajectory of pulmonary COVID-19 is driven by lobular ischemia and fibrotic remodelling
Authors: M Ackermann, JC Kamp, C Werlein, CL Walsh, H Stark, V Prade, R Surabattul, WL Wagner, C Disney, AJ Bodey, T Illig, DJ Leeming, MA Karsdal, A Tzankov, P Boor, MP Kühnel, FP Länger, SE Verleden, HM Kvasnicka, HH Kreipe, A Haverich, SM Black, A Walch, P Tafforeau, PD Lee, MM Hoeper, T Welte, B Seeliger, S David, D Schuppan, SJ Mentzer, DD Jonigk
EBioMedicine, 2022-10-04;85(0):104296.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
CT-Diagnosed Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Biomarkers in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: Is It Possible to Predict Muscle Loss Based on Laboratory Tests?-A Multicentric Retrospective Analysis
Authors: S Hecht, E Boxhammer, R Kaufmann, B Scharinger, C Reiter, J Kammler, J Kellermair, M Hammerer, H Blessberge, C Steinwende, UC Hoppe, K Hergan, M Lichtenaue
Journal of personalized medicine, 2022-09-04;12(9):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Combined genetic deletion of GDF15 and FGF21 has modest effects on body weight, hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in high fat fed mice
Authors: S Patel, A Haider, A Alvarez-Gu, G Bidault, JS El-Sayed M, E Guiu-Jurad, JA Tadross, J Warner, J Harrison, S Virtue, F Scurria, I Zvetkova, M Blüher, KS Small, S O'Rahilly, DB Savage
Molecular Metabolism, 2022-09-02;65(0):101589.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
A TGFbetaR inhibitor represses keratin-7 expression in 3D cultures of human salivary gland progenitor cells
Authors: EW Fowler, EJ van Venroo, RL Witt, X Jia
Scientific Reports, 2022-09-02;12(1):15008.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
The Upregulation of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester on Growth Differentiation Factor 15 Inhibits Transforming Growth Factor beta/Smad Signaling in Bladder Carcinoma Cells
Authors: CP Hou, KH Tsui, ST Chen, KS Chang, HC Sung, SY Hsu, YH Lin, TH Feng, HH Juang
Biomedicines, 2022-07-07;10(7):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Metabolomic Profiling in Patients with Heart Failure and Exercise Intolerance: Kynurenine as a Potential Biomarker
Authors: T Bekfani, M Bekhite, S Neugebauer, S Derlien, A Hamadanchi, J Nisser, MS Hilse, D Haase, T Kretzschma, MF Wu, M Lichtenaue, M Kiehntopf, S von Haehli, P Schlattman, G Lehmann, M Franz, S Möbius-Win, C Schulze
Cells, 2022-05-18;11(10):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Elevated Levels of Growth/Differentiation Factor-15 in the Aqueous Humor and Serum of Glaucoma Patients
Authors: R Maddala, LTY Ho, S Karnam, I Navarro, A Osterwald, SS Stinnett, C Ullmer, RR Vann, P Challa, PV Rao
Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2022-01-29;11(3):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Aqueous Humor
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits the growth of bladder carcinoma cells by upregulating growth differentiation factor 15
Authors: CP Hou, KH Tsui, KS Chang, HC Sung, SY Hsu, YH Lin, PS Yang, CL Chen, TH Feng, HH Juang
Biomedical journal, 2021-10-15;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Longitudinal association of the anti-inflammatory serum marker GDF-15 with serum IgA and IgG in apparently healthy children
Authors: G Carreras-B, A Gómez-Vila, B Mas-Parés, S Xargay-Tor, A Prats-Puig, E Puerto-Car, F de Zegher, L Ibáñez, J Bassols, A López-Berm
Scientific Reports, 2021-09-14;11(1):18215.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
GDF-15 Deficiency Reduces Autophagic Activity in Human Macrophages In Vitro and Decreases p62-Accumulation in Atherosclerotic Lesions in Mice
Authors: A Heduschke, K Ackermann, B Wilhelm, L Mey, GA Bonaterra, R Kinscherf, A Schwarz
Cells, 2021-09-07;10(9):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
-
The dynamics of human bone marrow adipose tissue in response to feeding and fasting
Authors: PK Fazeli, MA Bredella, OG Pachon-Peñ, W Zhao, X Zhang, AT Faje, M Resulaj, SP Polineni, TM Holmes, H Lee, EK O'Donnell, OA MacDougald, MC Horowitz, CJ Rosen, A Klibanski
JCI Insight, 2021-06-22;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Plasma biomarkers of the amyloid pathway are associated with geographic atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration
Authors: K Lashkari, GC Teague, U Beattie, J Betts, S Kumar, MM McLaughlin, FJ López
PLoS ONE, 2020-08-07;15(8):e0236283.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Prognostic Value of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Kidney Donors and Recipients
Authors: U Jehn, K Schütte-Nü, U Henke, J Bautz, H Pavenstädt, B Suwelack, S Reuter
J Clin Med, 2020-05-03;9(5):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Expression of the Novel Cardiac Biomarkers sST2, GDF-15, suPAR, and H-FABP in HFpEF Patients Compared to ICM, DCM, and Controls
Authors: P Jirak, R Pistulli, M Lichtenaue, B Wernly, V Paar, LJ Motloch, R Rezar, C Jung, UC Hoppe, PC Schulze, D Kretzschma, RC Braun-Dull, T Bekfani
J Clin Med, 2020-04-15;9(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Effect of a ketogenic diet on hepatic steatosis and hepatic mitochondrial metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Authors: PK Luukkonen, S Dufour, K Lyu, XM Zhang, A Hakkaraine, TE Lehtimäki, GW Cline, KF Petersen, GI Shulman, H Yki-Järvin
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2020-03-16;117(13):7347-7354.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
The myokine GDF-15 is a potential biomarker for myositis and associates with the protein aggregates of sporadic inclusion body myositis
Authors: B De Paepe, F Verhamme, JL De Bleecke
Cytokine, 2020-01-02;127(0):154966.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Circulating growth/differentiation factor 15 is associated with human CD56bright natural killer cell dysfunction and nosocomial infection in severe systemic inflammation
Authors: H Kleinertz, M Hepner-Sch, S Ehnert, M Claus, R Halbgebaue, L Boller, M Huber-Lang, P Cinelli, C Kirschning, S Flohé, A Sander, C Waydhas, S Vonderhage, M Jäger, M Dudda, C Watzl, SB Flohé
EBioMedicine, 2019-04-13;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
A multiplex immunoassay of serum biomarkers for the detection of uveal melanoma
Authors: J Song, SL Merbs, LJ Sokoll, DW Chan, Z Zhang
Clin Proteomics, 2019-03-05;16(0):10.
-
Potential relation between soluble growth differentiation factor-15 and testosterone deficiency in male patients with coronary artery disease
Authors: H Liu, Y Lyu, D Li, Y Cui, Y Huang, W Dai, Y Li
Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2019-02-28;18(1):21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Growth and differentiation factor 15 is a biomarker for low back pain-associated disability
Authors: N Tarabeih, A Shalata, S Trofimov, A Kalinkovic, G Livshits
Cytokine, 2019-02-15;117(0):8-14.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Association of serum level of growth differentiation factor 15 with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Authors: Liu X, Chi X, Gong Q, Gao L, Niu Y, Chi X, Cheng M, Si Y, Wang M, Zhong J, Niu J, Yang W
PLoS ONE, 2015-05-21;10(5):e0127518.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Growth differentiating factor 15 enhances the tumor-initiating and self-renewal potential of multiple myeloma cells.
Authors: Tanno, Toshihik, Lim, Yiting, Wang, Qiuju, Chesi, Marta, Bergsagel, P Leif, Matthews, Geoff, Johnstone, Ricky W, Ghosh, Nilanjan, Borrello, Ivan, Huff, Carol An, Matsui, William
Blood, 2013-12-17;123(5):725-33.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Inappropriately low hepcidin levels in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome carrying a somatic mutation of SF3B1.
Authors: Ambaglio I, Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E, Laarakkers C, Della Porta M, Galli A, Da Via M, Bono E, Ubezio M, Travaglino E, Albertini R, Campbell P, Swinkels D, Cazzola M
Haematologica, 2013-01-08;98(3):420-3.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Wild-type p53 attenuates cancer cell motility by inducing growth differentiation factor-15 expression.
Authors: Cheng JC, Chang HM, Leung PC
Endocrinology, 2011-05-17;152(8):2987-95.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Plasma markers for identifying patients with metastatic melanoma.
Authors: Kluger HM, Hoyt K, Bacchiocchi A, Mayer T, Kirsch J, Kluger Y, Sznol M, Ariyan S, Molinaro A, Halaban R
Clin. Cancer Res., 2011-04-12;17(8):2417-25.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Transferrin receptor 2 is a component of the erythropoietin receptor complex and is required for efficient erythropoiesis.
Authors: Forejtnikova H, Vieillevoye M, Zermati Y, Lambert M, Pellegrino RM, Guihard S, Gaudry M, Camaschella C, Lacombe C, Roetto A, Mayeux P, Verdier F
Blood, 2010-09-08;116(24):5357-67.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
GDF-15 contributes to proliferation and immune escape of malignant gliomas.
Authors: Roth P, Junker M, Tritschler I, Mittelbronn M, Dombrowski Y, Breit SN, Tabatabai G, Wick W, Weller M, Wischhusen J
Clin. Cancer Res., 2010-06-09;16(15):3851-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 regulates melanoma vascular development.
Authors: Huh SJ, Chung CY, Sharma A
Am. J. Pathol., 2010-04-29;176(6):2948-57.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Progressive postnatal motoneuron loss in mice lacking GDF-15.
Authors: Strelau J, Strzelczyk A, Rusu P, Bendner G, Wiese S, Diella F, Altick AL, von Bartheld CS, Klein R, Sendtner M, Unsicker K
J. Neurosci., 2009-10-28;29(43):13640-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Regulation of iron metabolism through GDF15 and hepcidin in pyruvate kinase deficiency.
Authors: Finkenstedt A, Bianchi P, Theurl I, Vogel W, Witcher DR, Wroblewski VJ, Murphy AT, Zanella A, Zoller H
Br. J. Haematol., 2008-12-20;144(5):789-93.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Identification of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in adipose tissue and its secretion as an adipokine by human adipocytes.
Authors: Ding Q, Mracek T, Gonzalez-Muniesa P, Kos K, Wilding J, Trayhurn P, Bing C
Endocrinology, 2008-12-12;150(4):1688-96.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Regulation of growth differentiation factor 15 expression by intracellular iron.
Authors: Lakhal S, Talbot NP, Crosby A, Stoepker C, Townsend AR, Robbins PA, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Mole DR
Blood, 2008-12-01;113(7):1555-63.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Growth differentiation factor 15 production is necessary for normal erythroid differentiation and is increased in refractory anaemia with ring-sideroblasts.
Authors: Ramirez JM, Schaad O, Durual S, Cossali D, Docquier M, Beris P, Descombes P, Matthes T
Br. J. Haematol., 2008-11-19;144(2):251-62.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Iron metabolism in heterozygotes for hemoglobin E (HbE), alpha-thalassemia 1, or beta-thalassemia and in compound heterozygotes for HbE/beta-thalassemia.
Authors: Zimmermann MB, Fucharoen S, Winichagoon P, Sirankapracha P, Zeder C, Gowachirapant S, Judprasong K, Tanno T, Miller JL, Hurrell RF
Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2008-10-01;88(4):1026-31.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Elevated growth differentiation factor 15 expression in patients with congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type I.
Authors: Tamary H, Shalev H, Perez-Avraham G, Zoldan M, Levi I, Swinkels DW, Tanno T, Miller JL
Blood, 2008-09-29;112(13):5241-4.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Differential effects of chemotherapeutic drugs versus the MDM-2 antagonist nutlin-3 on cell cycle progression and induction of apoptosis in SKW6.4 lymphoblastoid B-cells.
Authors: Barbarotto E, Corallini F, Rimondi E, Fadda R, Mischiati C, Grill V, Vaccarezza M, Celeghini C
J. Cell. Biochem., 2008-05-15;104(2):595-605.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Activation of the p53 pathway down-regulates the osteoprotegerin expression and release by vascular endothelial cells.
Authors: Secchiero P, Corallini F, Rimondi E, Chiaruttini C, di Iasio MG, Rustighi A, Del Sal G, Zauli G
Blood, 2007-11-13;111(3):1287-94.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
MDM2 antagonist Nutlin-3 suppresses the proliferation and differentiation of human pre-osteoclasts through a p53-dependent pathway.
Authors: Zauli G, Rimondi E, Corallini F, Fadda R, Capitani S, Secchiero P
J. Bone Miner. Res., 2007-10-01;22(10):1621-30.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
High levels of GDF15 in thalassemia suppress expression of the iron regulatory protein hepcidin.
Authors: Tanno T, Bhanu NV, Oneal PA, Goh SH, Staker P, Lee YT, Moroney JW, Reed CH, Luban NL, Wang RH, Eling TE, Childs R, Ganz T, Leitman SF, Fucharoen S, Miller JL
Nat. Med., 2007-08-26;13(9):1096-101.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all ELISA FAQsReviews for Human GDF-15 DuoSet ELISA
Average Rating: 4.8 (Based on 4 Reviews)
Have you used Human GDF-15 DuoSet ELISA?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
We used this kit for quantifying GDF15 in human serum and plasma samples and it worked very well
Very good, reliable reasults. Samples diluted 1/20, some needed dilution 1/40 as signal was too strong for the standard curve we applied. It may be ok with just 1/20 if the full standard curve is applied
Excellent kit, work very well for healthy controls and patients samples at 1:5 dilution