Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody Summary
Val615-Val855
Accession # Q9Y5Y6
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain in PC‑3 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line was stained with Sheep Anti-Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3946, filled histogram) or control antibody (5-001-A, open histogram), followed by NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (NL010). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with saponin.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta -actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta -actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta -actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta -actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta -actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Matriptase/ST14
Human matriptase, encoded by the ST14 (suppression of tumorogenicity 14) gene, is also known as tumor associated differentially expressed gene 15 protein/TADG‑15), epithin, and membrane-type serine protease 1/MT-SP1 (1). Predicted to have a significant role in tumor biology, matriptase may be a novel target for anti-cancer therapy (2). However, expressed in most human epithelia, matriptase is also important in several physiological processes (1). For example, it activates prostasin to initiate a protease cascade that is essential for epidermal differentiation (3), and it converts a single-chain IGFBP-rp1 into the two-chain form (4).
Matriptase is a type II transmembrane serine protease with a complex modular structure (1). The 855 amino acid (aa) sequence of human matriptase consists of a cytoplasmic tail (aa 1-55), a transmembrane domain (aa 56-76), and an extracellular portion (aa 77-855). The latter contains the following domains: SEA (aa 86-201), two CUBs (aa 214-334 and 340-447), four LDLRAs (aa 452-486, 487-523, 524-560, and 566-603), and a serine protease (aa 615-855). The physiological activation of the single-chain zymogen requires the cleavage at the SEA domain within the ER or Golgi, association with HAI-1, which facilitates the transport of the protease to the cell surface, and auto-cleavage at QAR-V(615)VGG (1). The activated matriptase is inhibited by HAI-1, and the resulting HAI-1 complex can be shed from the cell surface (1). R&D Systems rhST14 corresponds to the catalytic domain, and is inhibited effectively by rhHAI-1 and rhHAI-2A (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1048-PI and 1106-PI).
- List, K. et al. (2006) Mol. Med. 12:1.
- Uhland, K. (2006) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63:2968.
- Netzel-Arnett, S. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:32941.
- Ahmed, S. et al. (2006) FEBS J. 273:615.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
18
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Kidney-Specific Membrane-Bound Serine Proteases CAP1/Prss8 and CAP3/St14 Affect ENaC Subunit Abundances but Not Its Activity
Authors: Ehret, E;Stroh, S;Auberson, M;Ino, F;Jäger, Y;Maillard, M;Szabo, R;Bugge, TH;Frateschi, S;Hummler, E;
Cells
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Exosome-Mediated Activation of the Prostasin-Matriptase Serine Protease Cascade in B Lymphoma Cells
Authors: Li-Mei Chen, Karl X. Chai
Cancers (Basel)
-
Zymogen‐locked mutant prostasin (Prss8) leads to incomplete proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) and severely compromises triamterene tolerance in mice
Authors: Daniel Essigke, Alexandr V. Ilyaskin, Matthias Wörn, Bernhard N. Bohnert, Mengyun Xiao, Christoph Daniel et al.
Acta Physiol (Oxf)
-
Matriptase Cleaves EpCAM and TROP2 in Keratinocytes, Destabilizing Both Proteins and Associated Claudins
Authors: CJ Wu, M Lu, X Feng, G Nakato, MC Udey
Cells, 2020-04-21;9(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Conserved function of the matriptase-prostasin proteolytic cascade during epithelial morphogenesis
Authors: L Drees, T Königsmann, MHJ Jaspers, R Pflanz, D Riedel, R Schuh
PLoS Genet., 2019-01-02;15(1):e1007882.
Species: Drosophila
Sample Types: Whole Embryo
Applications: IHC -
Matriptase zymogen supports epithelial development, homeostasis and regeneration
Authors: S Friis, D Tadeo, SM Le-Gall, HJ Jürgensen, KU Sales, E Camerer, TH Bugge
BMC Biol., 2017-06-01;15(1):46.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
Inflammatory cytokines down-regulate the barrier protective prostasin-matriptase proteolytic cascade early in experimental colitis
Authors: MS Buzza, TA Johnson, GD Conway, EW Martin, S Mukhopadhy, T Shea-Donoh, TM Antalis
J. Biol. Chem., 2017-05-10;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM destabilizes claudins and dysregulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis
Authors: Chuan-Jin Wu, Xu Feng, Michael Lu, Sohshi Morimura, Mark C. Udey
Journal of Clinical Investigation
-
Distinct Developmental Functions of Prostasin (CAP1/PRSS8) Zymogen and Activated Prostasin
Authors: S Friis, DH Madsen, TH Bugge
J. Biol. Chem, 2015-12-30;291(6):2577-82.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Simple Western, Western Blot -
Targeting matriptase in breast cancer abrogates tumour progression via impairment of stromal-epithelial growth factor signalling.
Authors: Zoratti G, Tanabe L, Varela F, Murray A, Bergum C, Colombo E, Lang J, Molinolo A, Leduc R, Marsault E, Boerner J, List K
Nat Commun, 2015-04-15;6(0):6776.
Species: Human, Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Matriptase promotes inflammatory cell accumulation and progression of established epidermal tumors.
Authors: Sales K, Friis S, Abusleme L, Moutsopoulos N, Bugge T
Oncogene, 2014-12-08;34(35):4664-72.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Regulation of feto-maternal barrier by matriptase- and PAR-2-mediated signaling is required for placental morphogenesis and mouse embryonic survival.
Authors: Szabo R, Peters D, Kosa P, Camerer E, Bugge T
PLoS Genet, 2014-07-31;10(7):e1004470.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Matriptase proteolytically activates influenza virus and promotes multicycle replication in the human airway epithelium.
Authors: Beaulieu A, Gravel E, Cloutier A, Marois I, Colombo E, Desilets A, Verreault C, Leduc R, Marsault E, Richter M
J Virol, 2013-01-30;87(8):4237-51.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Reduced prostasin (CAP1/PRSS8) activity eliminates HAI-1 and HAI-2 deficiency-associated developmental defects by preventing matriptase activation.
Authors: Szabo, Roman, Uzzun Sales, Katiuchi, Kosa, Peter, Shylo, Natalia, Godiksen, Sine, Hansen, Karina K, Friis, Stine, Gutkind, J Silvio, Vogel, Lotte K, Hummler, Edith, Camerer, Eric, Bugge, Thomas H
PLoS Genet, 2012-08-30;8(8):e1002937.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
c-Met-induced epithelial carcinogenesis is initiated by the serine protease matriptase.
Authors: Szabo R, Rasmussen AL, Moyer AB
Oncogene, 2011-01-10;30(17):2003-16.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Endogenous expression of matriptase in neural progenitor cells promotes cell migration and neuron differentiation.
Authors: Fang JD, Chou HC, Tung HH
J. Biol. Chem., 2010-12-13;286(7):5667-79.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC-P, Western Blot -
Matriptase initiates activation of epidermal pro-kallikrein and disease onset in a mouse model of Netherton syndrome.
Authors: Sales KU, Masedunskas A, Bey AL
Nat. Genet., 2010-07-25;42(8):676-83.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Loss of matriptase suppression underlies spint1 mutation-associated ichthyosis and postnatal lethality.
Authors: Szabo R, Kosa P, List K, Bugge TH
Am. J. Pathol., 2009-04-23;174(6):2015-22.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
-
Why is intracellular flow staining performed with Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody (Catalog #s MAB3946 and AF3946) when Human Matripase is a type II transmembrane serine protease?
We have performed intracellular staining with Catalog #s MAB3946 and AF3946 because when PC-3 and some other cell lines were tested using the surface staining protocol, the results were negative. It is possible that the level of expression of this protein is too low to be detected on the surface. Furthermore, with optimization of staining, one may be able to detect protein on the surface.
Reviews for Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
0.44 ug recombinant matriptase catalytic domain (R&D; Catalog Number: 3946-SEB) were used in a biochemical cleavage assay. Samples were analyzed under denaturing/reducing conditions by SDS-PAGE/western blot and stained using this matriptase catalytic domain antibody (0.1 ug/ml; blocking 1x supplemented with 10 % milk). I would recommend this antibody.
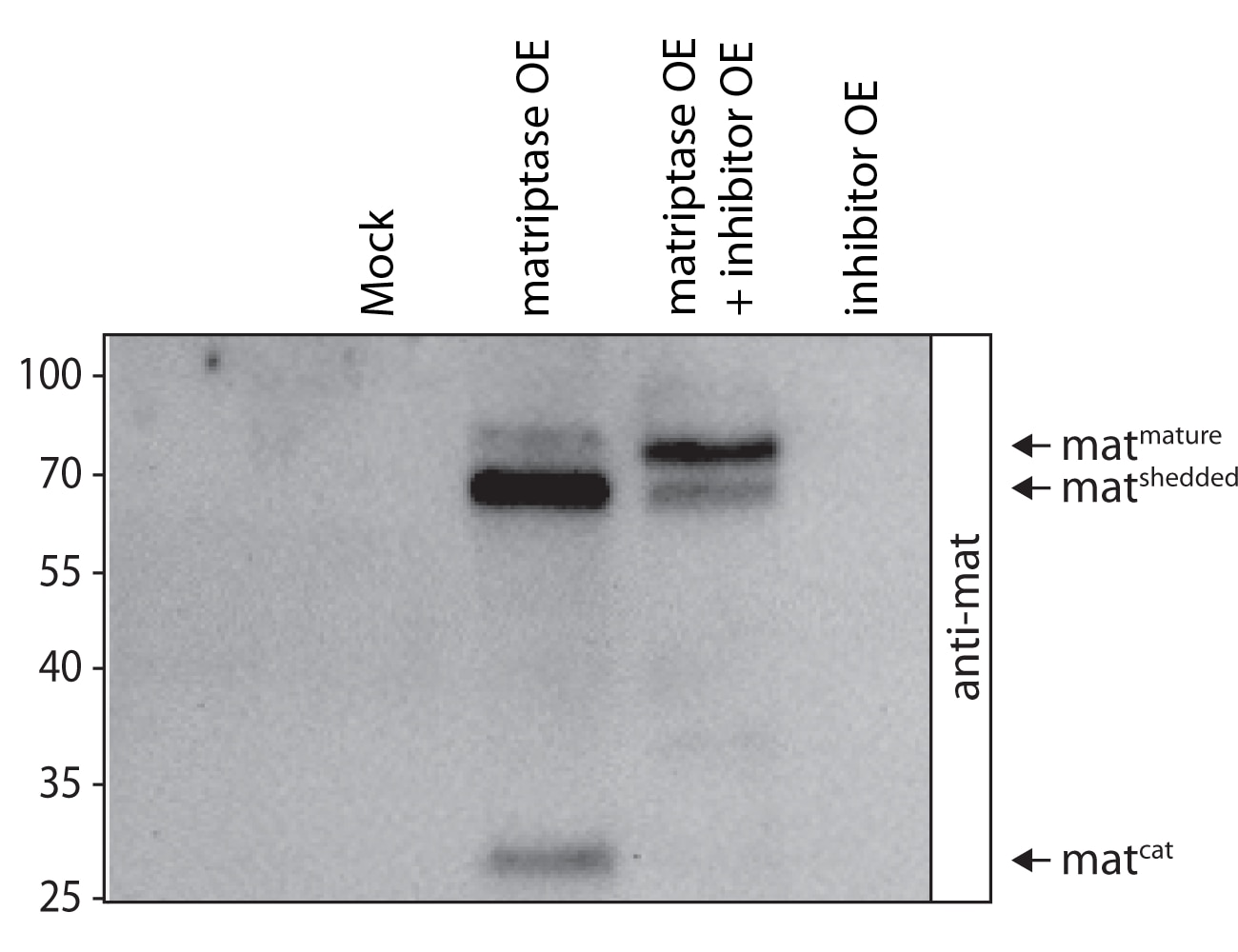
Full length matriptase was overexpressed exclusively or co-overexpressed with its human inhibitor in Drosophila S2R+ cells. After three days incubation, supernatants of cells were examined under denaturing/reducing conditions using SDS-PAGE/western blot and antibody staining. The antibody stains three forms of matriptase: the mature and shedded matriptase as well as the catalytic domain.