Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2/HDM2 Antibody Summary
Asn3-Pro491
Accession # Q00987
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
MDM2/HDM2 in Human Kidney. MDM2/HDM2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using Rabbit Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2/HDM2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1244) at 3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Rabbit IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC003). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and nuclei for epithelial cells in convoluted tubules. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
MDM2 in Mouse Kidney. MDM2 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse kidney using Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1244) at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rabbit HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS005) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human MDM2 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of U2OS human osteosarcoma cell line, MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line, and CEM human T-lymphoblastoid cell line untreated (-) or treated (+) with 5 µM LLnV for 1 hour. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1244), followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF008). A specific band was detected for MDM2 at approximately 95 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
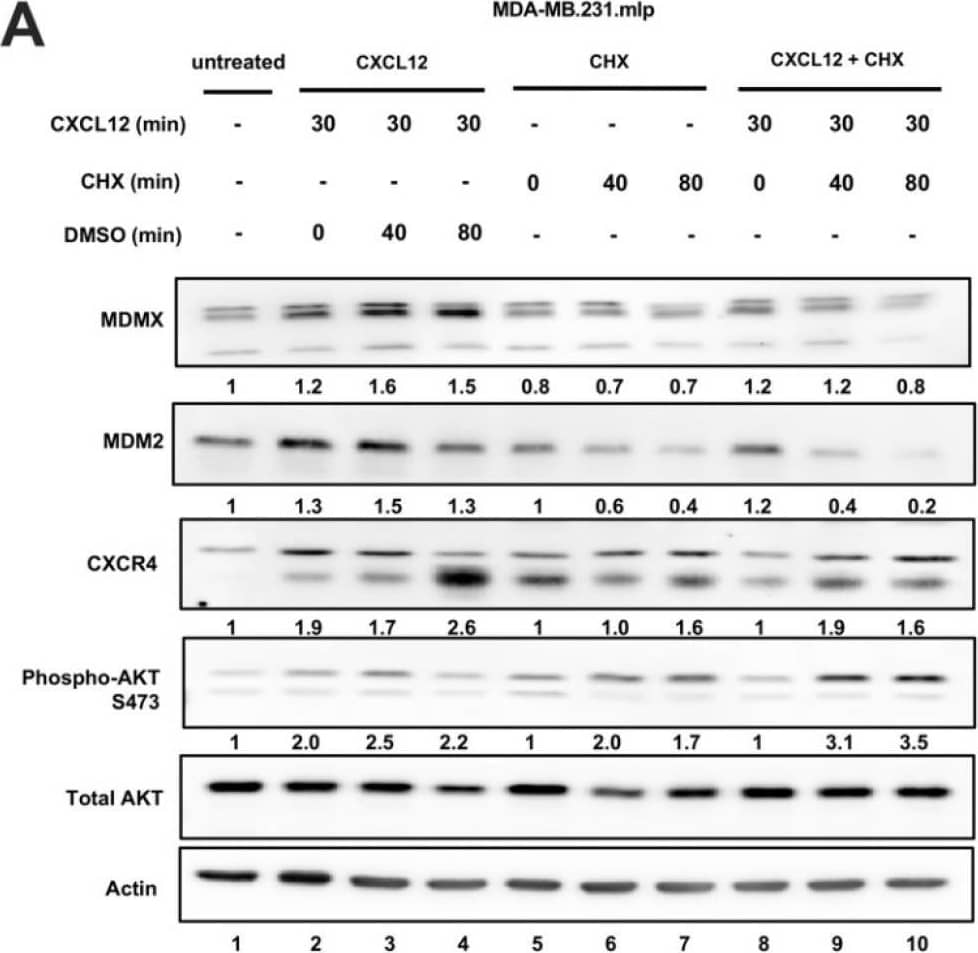
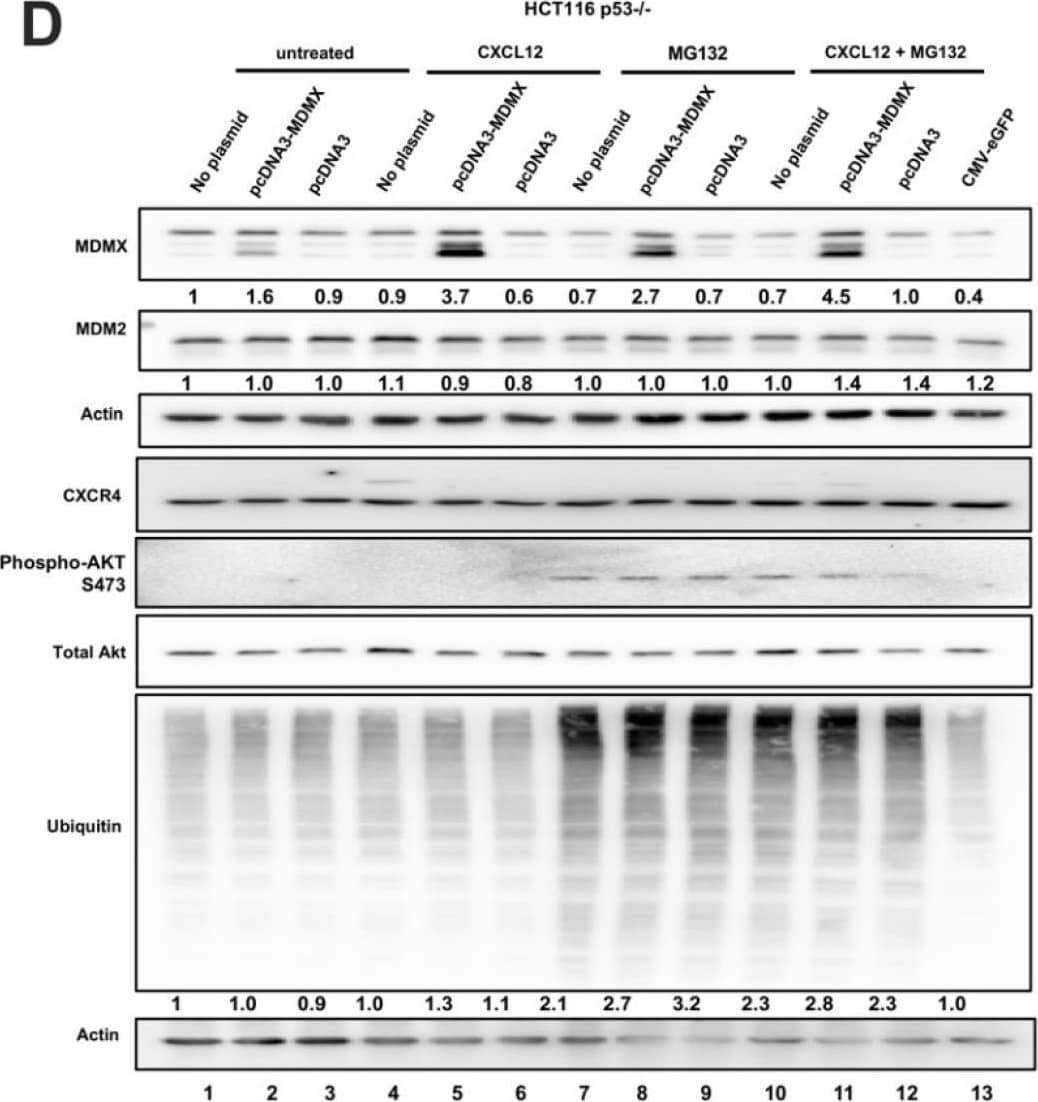
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot CXCL12 addition does not increase MDMX protein half-life following cycloheximide or MG132 treatment. (A) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by cycloheximide (CHX) or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2 and MDMX. Actin was probed as a loading control. (B,C) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. (D) HCT116 p53-/- cells were transfected with pcDNA3-MDMX for 24 h and then treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by MG132 or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2, MDMX, and Ubiquitin. Actin was probed as a loading control. (E,F) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism 10 software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot The MDM2 antagonist RG7112 concomitant with CEP-1347 effectively activates p53 and inhibits the growth of malignant brain tumor cells expressing wild-type p53. (A) IMR90 normal human fibroblasts, IOMM-Lee cells, and A172 cells treated with the indicated drugs (CEP-1347, 250 nM; RG7112, 500 nM) for 3 days were subjected to the trypan blue dye exclusion assay. (B) IOMM-Lee, A172, and T98G cells treated with the indicated drugs (CEP-1347, 250 nM; RG7112, 500 nM) for 2 days were subjected to a Western blot analysis. (C) Cells treated with the indicated drugs (CEP-1347, 250 nM; RG7112, 500 nM) for 3 days were cultured for another 5 days in the absence of any drugs for the colony formation assay. Representative images (left panels) and the number of colonies (right graphs) are shown. Values represent means + SD from triplicate samples of a representative experiment. * p < 0.05. † p < 0.05 vs. cells treated without any drugs. Similar results were obtained from more than two independent biological replicates. Original blot images can be found in Figure S4. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37686602), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot CEP-1347-induced MDM2 overexpression counteracts the CEP-1347-induced activation of p53. IOMM-Lee and A172 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated siRNA against MDM2 (#1 and #3) or with control siRNA (siCt). After being cultured for 1 day, cells treated without or with 250 nM CEP-1347 for 2 and 3 additional days were subjected to a Western blot analysis (A) and the trypan blue dye exclusion assay (B), respectively. Values represent the means + SD of triplicate samples of a representative experiment. * p < 0.05. † p < 0.05 vs. siCt-transfected cells treated without CEP-1347. Similar results were obtained from more than three independent biological replicates. Original blot images can be found in Figure S3. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37686602), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot Endogenous expression of MDM2 contributes to p53 inactivation. (A) IOMM-Lee and A172 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated siRNA against MDM2 (#1 and #3) or with control siRNA (siCt). After being cultured for 3 days, cells were subjected to a Western blot analysis. (B) Cells were transiently transfected as in (A). After 3 days, transfected cells were subjected to the trypan blue dye exclusion assay to measure the number of viable cells. Values represent means + SD from triplicate samples of a representative experiment. * p < 0.05 vs. siCt-transfected cells. Similar results were obtained from more than two independent biological replicates. Original blot images can be found in Figure S2. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37686602), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
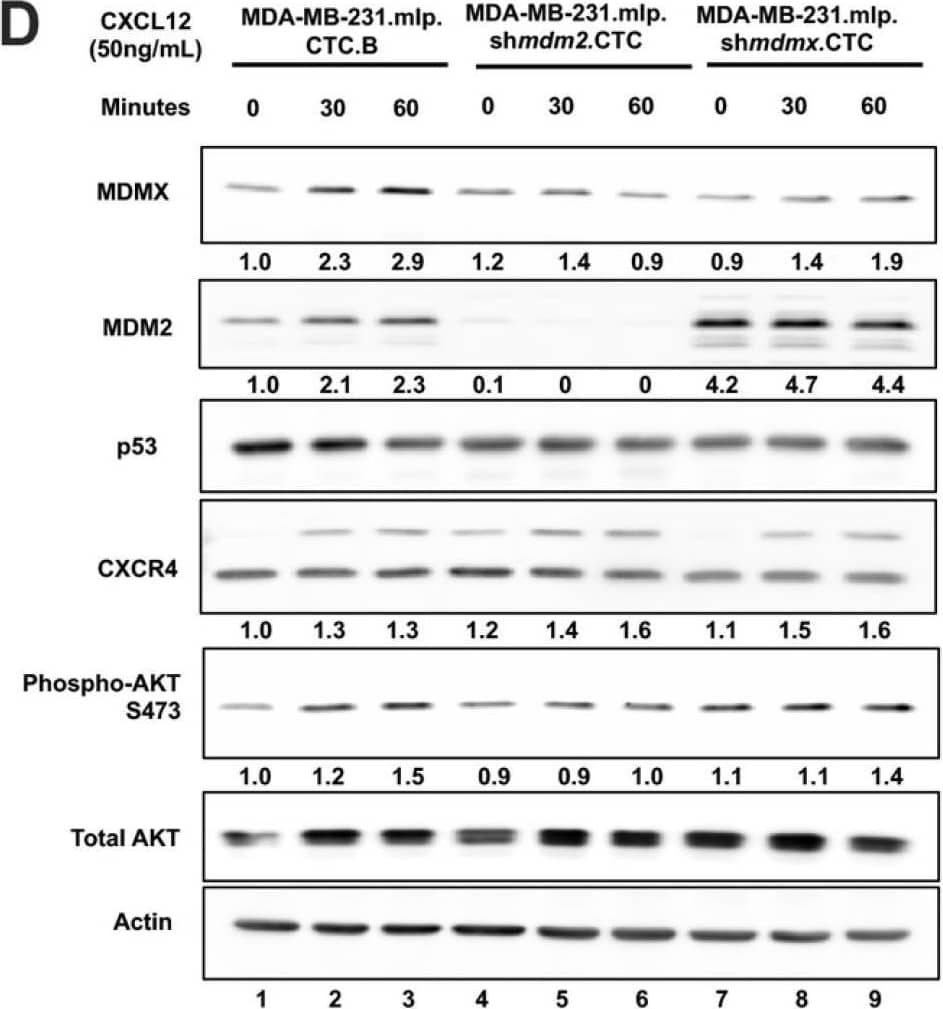
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines compared to MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC maintain increased migratory compacity but have reduced response to CXCL12. (A) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp, MDA-MB-231.shmdm2, and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx (lanes 1–3) and MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC A and B (lanes 4 and 5), MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC (lane 6), and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC (lane 7) cell lines probed for MDMX (top) and MDM2 (middle). The loading control was actin (bottom) (B) Representative images of MDA-MB-231-derived CTC lines in wound healing assay. Black lines denote the borders of the scratch made. (C) Graph of % wound closure at 12 h time point. Error bars represent SD. *** p < 0.001, NS = nonsignificant. The p value was calculated using two-tailed unpaired t tests on Prism software (D) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines treated with CXCL12 at a final concentration of 50 ng/mL for 30 and 60 min. (E) MDMX and MDM2 protein expression was compared using ImageJ quantitation relative to actin, respectively, as a loading control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines compared to MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC maintain increased migratory compacity but have reduced response to CXCL12. (A) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp, MDA-MB-231.shmdm2, and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx (lanes 1–3) and MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC A and B (lanes 4 and 5), MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC (lane 6), and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC (lane 7) cell lines probed for MDMX (top) and MDM2 (middle). The loading control was actin (bottom) (B) Representative images of MDA-MB-231-derived CTC lines in wound healing assay. Black lines denote the borders of the scratch made. (C) Graph of % wound closure at 12 h time point. Error bars represent SD. *** p < 0.001, NS = nonsignificant. The p value was calculated using two-tailed unpaired t tests on Prism software (D) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines treated with CXCL12 at a final concentration of 50 ng/mL for 30 and 60 min. (E) MDMX and MDM2 protein expression was compared using ImageJ quantitation relative to actin, respectively, as a loading control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot CXCL12 addition does not increase MDMX protein half-life following cycloheximide or MG132 treatment. (A) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by cycloheximide (CHX) or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2 and MDMX. Actin was probed as a loading control. (B,C) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. (D) HCT116 p53-/- cells were transfected with pcDNA3-MDMX for 24 h and then treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by MG132 or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2, MDMX, and Ubiquitin. Actin was probed as a loading control. (E,F) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism 10 software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
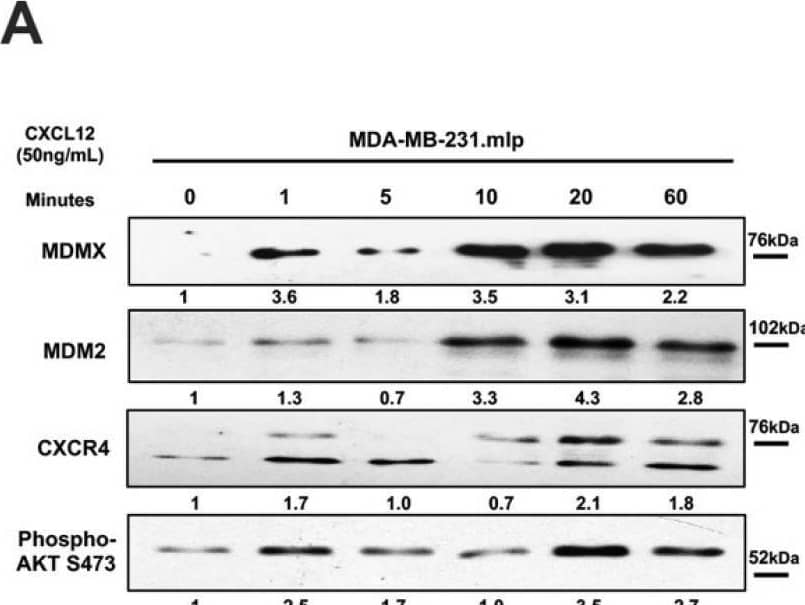
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot Chemokine CXCL12 addition to cell culture increases CXCR4, activates PI3K/AKT, and MDMX and MDM2 protein levels. (A) Panels show immunoblot analysis for MDMX, MDM2, CXCR4, and phospho-AKT S473, total AKT, and actin in MDA-MB-231.mlp cells after treatment for up to 60 min with CXCL12 at 50 ng/mL for 0, 1, 5, 10, 20, and 60 min, lanes 1–6. Total AKT and actin were used as loading controls. The proteins were derived from the same samples run on different gels/membranes at the same time and their molecular weights are shown. (B) Untreated cells and those following the 20 min treatments were compared for the MDMX and MDM2 protein levels evaluated (using actin as a normalizer control for loading) using ImageJ and graphs were created with Prism 10 software, with the untreated value set as 1 and the ratio reported for CXCL12-treated samples (20 min) used to report the fold change. (C) Untreated and 20 min treatments were compared for CXCR4 and phospho-AKT S473 protein levels quantified via ImageJ relative to total AKT as a loading control with the untreated value set as 1 and the ratio reported for CXCL12-treated samples (20 min) used to report the fold change. Images were analyzed using ImageJ and graphs were created with Prism software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, NS = non-significant (N = 4 biological replicates). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
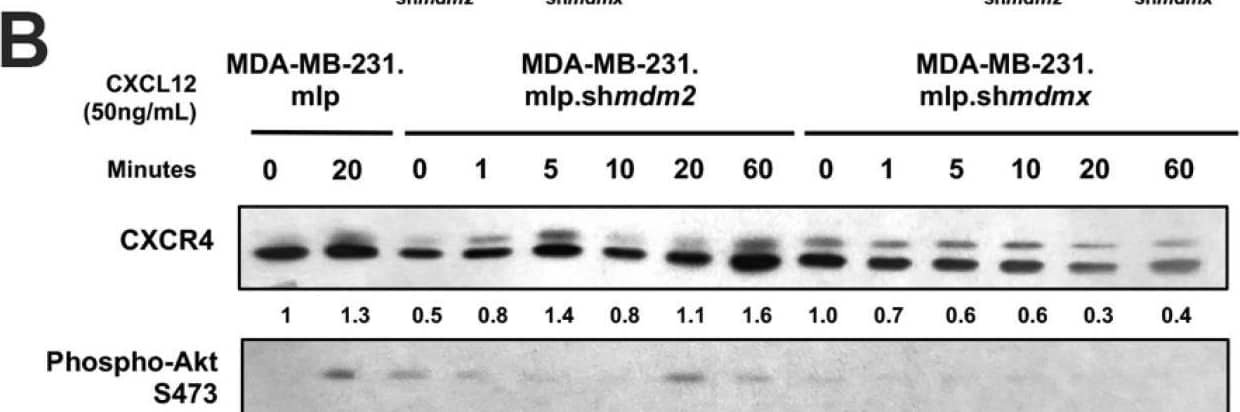
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot Knockdown of MDMX in MDA-MB-231 cells disrupts CXCL12 signaling to upregulate CXCR4, MDM2, and AKT activation. MDA-MB-231.mlp, MDA-MB-231.mlp.shmdm2, and MDA-MB-231.mlp.shmdmx cells treated in cell culture with the addition of CXCL12 at a final concentration of 50 ng/mL in cell culture for up to 60 min. (A) CXCR4 and phospho-AKT S473 protein levels were semi-quantified at 20 min via ImageJ relative to actin as a loading control. Protein level analysis was carried out using Western blot results using Image J and Prism software and densitometries were measured as a ratio relative to the actin band density. Fold change was calculated relative to protein levels in the untreated 231.mlp vector control cells. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant (N = 3 biological replicates). (B) Immunoblot analysis for CXCR4, phospho-AKT, MDMX, and MDM2 protein levels in MDA-MB-231 or knockdown cells after the addition of CXCL12. (C) MDMX and MDM2 protein levels were semi-quantified at 20 min post addition of CXCL12 to the cell culture. Protein levels were normalized to actin and fold change was calculated relative to untreated 231.mlp vector control cells. MDM2 or MDMX knockdown were confirmed for each respective cell line. Protein level analysis was carried out from Western blot results using Image J and Prism software and expression scores were normalized to actin. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant (N = 3 biological replicates). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: MDM2/HDM2
MDM2 is a key regulator of p53 tumor suppressor protein activity and stability. MDM2 binds to and inhibits the transactivation domain of p53. In addition, MDM2 controls p53 stability by functioning as its E3 ligase in ubiquitination and by shuttling p53 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for subsequent degradation. The importance of the p53/MDM2 relationship is underscored by the existence of an autoregulatory feedback loop whereby activated p53 transcriptionally up‑regulates the expression of its own inhibitor, MDM2.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2/HDM2 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
22
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The MDM2-p53 Axis Represents a Therapeutic Vulnerability Unique to Glioma Stem Cells
Authors: Nakagawa-Saito, Y;Mitobe, Y;Togashi, K;Suzuki, S;Sugai, A;Takenouchi, S;Nakamura, K;Sonoda, Y;Kitanaka, C;Okada, M;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
A CANCER PERSISTENT DNA REPAIR CIRCUIT DRIVEN BY MDM2, MDM4 (MDMX), AND MUTANT P53 FOR RECRUITMENT OF MDC1 AND 53BP1 TO CHROMATIN
Authors: Ellison, V;Polotskaia, A;Xiao, G;Leybengrub, P;Qiu, W;Lee, R;Hendrickson, R;Hu, W;Bargonetti, J;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Antagonizing MDM2 Overexpression Induced by MDM4 Inhibitor CEP-1347 Effectively Reactivates Wild-Type p53 in Malignant Brain Tumor Cells
Authors: Yuta Mitobe, Shuhei Suzuki, Yurika Nakagawa-Saito, Keita Togashi, Asuka Sugai, Yukihiko Sonoda et al.
Cancers (Basel)
-
Single-Cell Spatial MIST for Versatile, Scalable Detection of Protein Markers
Authors: Meah, A;Vedarethinam, V;Bronstein, R;Gujarati, N;Jain, T;Mallipattu, SK;Li, Y;Wang, J;
Biosensors
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Complex Sample Type
Applications: IHC -
The Novel MDM4 Inhibitor CEP-1347 Activates the p53 Pathway and Blocks Malignant Meningioma Growth In Vitro and In Vivo
Authors: Mitobe, Y;Suzuki, S;Nakagawa-Saito, Y;Togashi, K;Sugai, A;Sonoda, Y;Kitanaka, C;Okada, M;
Biomedicines
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysate
Applications: Western Blot -
Cardiac GRK2 Protein Levels Show Sexual Dimorphism during Aging and Are Regulated by Ovarian Hormones
Authors: AC Arcones, MR Martínez-C, R Vila-Bedma, C Yáñez, I Lladó, AM Proenza, F Mayor, C Murga
Cells, 2021-03-17;10(3):.
Species: Mouse, Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Targeting Triple Negative Breast Cancer with a Nucleus-Directed p53 Tetramerization Domain Peptide
Authors: Gu Xiao, George K. Annor, Kimberly Fung, Outi Keinänen, Brian M. Zeglis, Jill Bargonetti
Molecular Pharmaceutics
-
Molecular Targeting of H/MDM-2 Oncoprotein in Human Colon Cancer Cells and Stem-like Colonic Epithelial-derived Progenitor Cells
Authors: ANUSHA THADI, WILLIAM F. MORANO, MARIAN KHALILI, BLAKE D. BABCOCK, MOHAMMAD F. SHAIKH, DESHKA S. FOSTER et al.
Anticancer Research
-
Identification of VRK1 as a New Neuroblastoma Tumor Progression Marker Regulating Cell Proliferation
Authors: A Colmenero-, MA Gómez-Muño, I Rodríguez-, A Amador-Álv, KO Henrich, D Pascual-Va, K Okonechnik, E Rivas, F Westermann, R Pardal, FM Vega
Cancers (Basel), 2020-11-20;12(11):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Targeting Membrane HDM-2 by PNC-27 Induces Necrosis in Leukemia Cells But Not in Normal Hematopoietic Cells
Authors: ANUSHA THADI, LAUREN LEWIS, EVE GOLDSTEIN, ANSHU AGGARWAL, MARIAN KHALILI, LINDSAY STEELE et al.
Anticancer Research
-
Dual Antagonist of cIAP/XIAP ASTX660 Sensitizes HPV(−) and HPV(+) Head and Neck Cancers To TNF alpha, TRAIL, and Radiation Therapy
Authors: Roy Xiao, Yi An, Wenda Ye, Adeeb Derakhshan, Hui Cheng, Xinping Yang et al.
Clinical Cancer Research
-
The transcription factors TFE3 and TFEB amplify p53 dependent transcriptional programs in response to DNA damage
Authors: Eutteum Jeong, Eutteum Brady, José A Martina, Mehdi Pirooznia, Ilker Tunc, Rosa Puertollano
eLife
-
A novel mouse model of rhabdomyosarcoma underscores the dichotomy of MDM2-ALT1 function in vivo
Authors: Daniel F. Comiskey Jr, Aishwarya G. Jacob, Brianne L. Sanford, Matías Montes, Andrew K. Goodwin, Haley Steiner et al.
Oncogene
-
Adverse Effects on ?-Adrenergic Receptor Coupling: Ischemic Postconditioning Failed to Preserve Long-Term Cardiac Function
Authors: R Schreckenb, P Bencsik, M Weber, Y Abdallah, C Csonka, K Gömöri, K Kiss, J Pálóczi, J Pipis, M Sárközy, P Ferdinandy, R Schulz, KD Schlüter
J Am Heart Assoc, 2017-12-22;6(12):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Multicolor quantitative confocal imaging cytometry
Authors: DL Coutu, KD Kokkaliari, L Kunz, T Schroeder
Nat. Methods, 2017-11-13;15(1):39-46.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Endogenous c-Myc is essential for p53-induced apoptosis in response to DNA damage in vivo.
Authors: Phesse, T J, Myant, K B, Cole, A M, Ridgway, R A, Pearson, H, Muncan, V, van den Brink, G R, Vousden, K H, Sears, R, Vassilev, L T, Clarke, A R, Sansom, O J
Cell Death Differ, 2014-02-28;21(6):956-66.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
HDM2 antagonist MI-219 (spiro-oxindole), but not Nutlin-3 (cis-imidazoline), regulates p53 through enhanced HDM2 autoubiquitination and degradation in human malignant B-cell lymphomas.
J Hematol Oncol, 2012-09-18;5(0):57.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Cell death via DR5, but not DR4, is regulated by p53 in myeloma cells.
Authors: Surget S, Chiron D, Gomez-Bougie P, Descamps G, Menoret E, Bataille R, Moreau P, Le Gouill S, Amiot M, Pellat-Deceunynck C
Cancer Res, 2012-06-27;72(17):4562-73.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Sudemycins, Novel Small Molecule Analogues of FR901464, Induce Alternative Gene Splicing
Authors: Liying Fan, Chandraiah Lagisetti, Carol C. Edwards, Thomas R. Webb, Philip M. Potter
ACS Chemical Biology
-
Anoikis triggers Mdm2-dependent p53 degradation
Authors: Abhijit Ghosh, Tina Chunyuan Chen, Yvonne L. Kapila
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry
-
A high-frequency regulatory polymorphism in the p53 pathway accelerates tumor development.
Authors: Post SM, Quintas-Cardama A, Pant V, Iwakuma T, Hamir A, Jackson JG, Maccio DR, Bond GL, Johnson DG, Levine AJ, Lozano G
Cancer Cell, 2010-09-14;18(3):220-30.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
CARPs are ubiquitin ligases that promote MDM2-independent p53 and phospho-p53ser20 degradation.
Authors: Rozan LM, McDonald ER, Navaraj A, Matthew EM, Dicker DT, El-Deiry WS
J. Biol. Chem., 2006-11-22;282(5):3273-81.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2/HDM2 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2/HDM2 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human/Mouse/Rat MDM2/HDM2 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


