Mouse Cathepsin D Biotinylated Antibody Summary
Ile21-Leu410
Accession # Q3UCD9
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
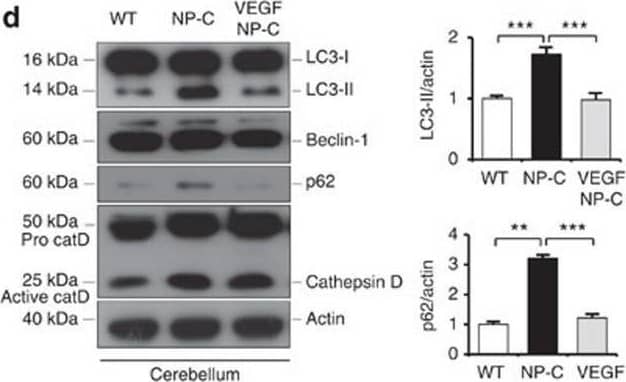 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Cathepsin D by Western Blot VEGF replenishment reverses defective autophagy in NP–C mice.(a) Western blot analysis of LC3, beclin-1, p62 and cathepsin D in primary cultured PNs derived from WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C mice (WT, n=5; NP–C, n=6; and VEGF/NP–C, n=6). (b) Immunocytochemistry of LC3 in WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C PNs (n=6 per group; scale bar, 20 μm). (c) Cathepsin D activity in primary cultured PNs (WT, n=5; NP–C, n=6; and VEGF/NP–C, n=6). (d) Western blot analysis of LC3, beclin-1, p62 and cathepsin D in the cerebellums of 6-week-old WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C mice (WT, n=6; NP–C, n=7; and VEGF/NP–C, n=7). (e) Cathepsin D activity in the cerebellums of WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C mice (WT, n=5; NP–C, n=6; and VEGF/NP–C, n=6). (f) EM images and quantification data of the cerebellum (n=5 per group; low-magnification scale bar, 1 μm; high-magnification scale bar, 200 nm). Arrow indicates autophagic vacuole. (g) Western blot analysis of Rab5 and Rab7 levels in the cerebellum (n=6 per group). (h) Cerebellar sections were immunostained with anti-active caspase-3 and the number of active caspase-3-positive cells in PCL was quantified (n=5 per group; scale bar, 50 μm). a–g, one-way analysis of variance, Tukey’s post hoc test. h, Student’s t-test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. All error bars indicate s.e.m. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25417698), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
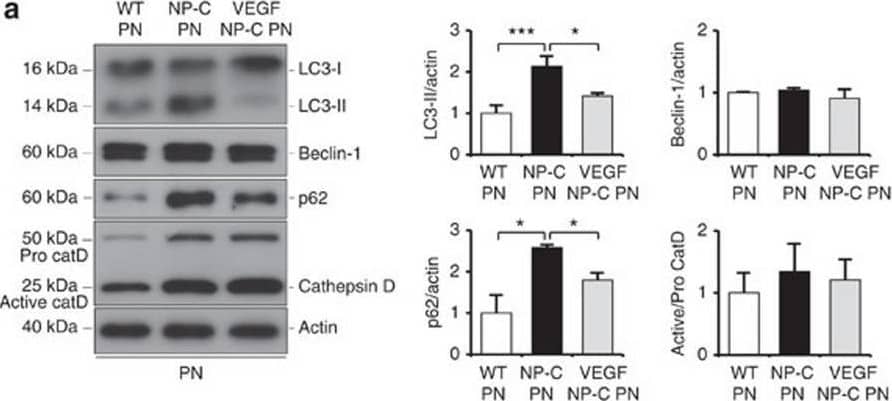 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Cathepsin D by Western Blot VEGF replenishment reverses defective autophagy in NP–C mice.(a) Western blot analysis of LC3, beclin-1, p62 and cathepsin D in primary cultured PNs derived from WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C mice (WT, n=5; NP–C, n=6; and VEGF/NP–C, n=6). (b) Immunocytochemistry of LC3 in WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C PNs (n=6 per group; scale bar, 20 μm). (c) Cathepsin D activity in primary cultured PNs (WT, n=5; NP–C, n=6; and VEGF/NP–C, n=6). (d) Western blot analysis of LC3, beclin-1, p62 and cathepsin D in the cerebellums of 6-week-old WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C mice (WT, n=6; NP–C, n=7; and VEGF/NP–C, n=7). (e) Cathepsin D activity in the cerebellums of WT, NP–C and VEGF/NP–C mice (WT, n=5; NP–C, n=6; and VEGF/NP–C, n=6). (f) EM images and quantification data of the cerebellum (n=5 per group; low-magnification scale bar, 1 μm; high-magnification scale bar, 200 nm). Arrow indicates autophagic vacuole. (g) Western blot analysis of Rab5 and Rab7 levels in the cerebellum (n=6 per group). (h) Cerebellar sections were immunostained with anti-active caspase-3 and the number of active caspase-3-positive cells in PCL was quantified (n=5 per group; scale bar, 50 μm). a–g, one-way analysis of variance, Tukey’s post hoc test. h, Student’s t-test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. All error bars indicate s.e.m. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25417698), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Cathepsin D
Cathepsin D is a lysosomal aspartic protease of the pepsin family (4). Mouse Cathepsin D is synthesized as a precursor protein, consisting of a signal peptide (residues 1‑20), a propeptide (residues 21‑64), and a mature chain (residues 65‑410) (1‑3). It is expressed in most cells and overexpressed in breast cancer cells (5). It is a major enzyme in protein degradation in lysosomes, and also involved in the presentation of antigenic peptides. Mice deficient in this enzyme showed a progressive atrophy of the intestinal mucosa, a massive destruction of lymphoid organs, and a profound neuronal ceroid lipofucinosis, indicating that Cathepsin D is essential for proteolysis of proteins regulating cell growth and tissue homeostasis (6). Cathepsin D secreted from human prostate carcinoma cells is responsible for the generation of angiostatin, a potent endogeneous inhibitor of angiogenesis (6).
- Diedrich, et al. (1990) Nucl. Acid Res. 18:7184.
- Grusby, et al. (1990) Nucl. Acid Res. 18:4008.
- Hetman, et al. (1994) DNA Cell Biol. 13:419.
- Conner (2004) in Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes (Barrett, et al. eds) Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, p. 43.
- Rochefort, et al. (2000) Clin. Chim. Acta. 291:157.
- Tsukuba, et al. (2000) Mol. Cells 10:601.
Product Datasheets
Citation for Mouse Cathepsin D Biotinylated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
1 Citation: Showing 1 - 1
-
Pathological roles of the VEGF/SphK pathway in niemann-Pick type C neurons.
Authors: Lee H, Lee Jk, Park Mh et al.
Nat Commun.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse Cathepsin D Biotinylated Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse Cathepsin D Biotinylated Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse Cathepsin D Biotinylated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

