Mouse CCL5/RANTES Antibody Summary
Ser24-Ser91
Accession # P30882
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
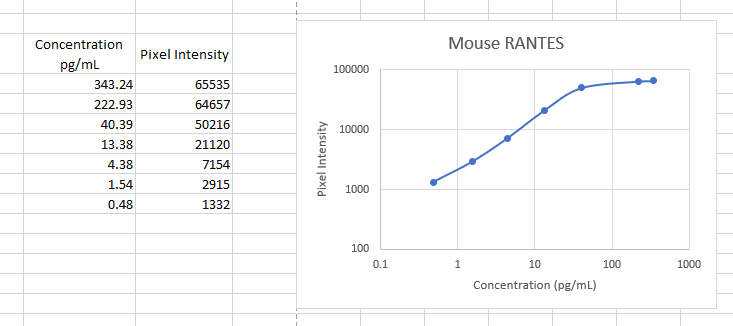
 View Larger
View Larger
CCL5/RANTES in Mouse Splenocytes. CCL5/RANTES was detected in immersion fixed mouse splenocytes using Mouse CCL5/RANTES Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB478) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL013) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
Chemotaxis Induced by CCL5/RANTES and Neutralization by Mouse CCL5/RANTES Antibody. Recombinant Mouse CCL5/RANTES (Catalog # 478-MR) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CCR5 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (Catalog # AR002). Chemotaxis elicited by Recombinant Mouse CCL5/RANTES (0.025 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse CCL5/RANTES Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB478). The ND50 is typically 0.1-0.5 µg/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CCL5/RANTES by Immunohistochemistry Antagonizing RANTES within CNS extends the survival of mice after TBEV infection. Mice were treated with Met-RANTES, vehicle, anti-RANTES mAb, or isotype-matched control Ab daily from day 2 to 8 after a primary TBEV infection. a Met-RANTES-treated mice exhibited a delay in mortality following lethal TBEV challenge. Mortality in each group was monitored daily for 14 days. Data were pooled from three independent experiments (total of approximately 18 mice per group). Statistical differences were evaluated using the Kaplan–Meier test for mortality. *P < 0.05, compared to vehicle-treated mice. b Anti-RANTES mAb-treated mice exhibited a delay in mortality following lethal TBEV challenge. Mortality in each group was monitored daily for 14 days. Data were pooled from three independent experiments (total of approximately 18 mice per group). *P < 0.05, compared to isotype Ab-treated mice. c, d Body weight changes of mice were monitored daily. For each time point, the measured values are the average of the surviving mice. Bars represent the means ± the standard deviations of three independent experiments (total of approximately 18 mice per group). e Infectious virus in brain tissues. No significant difference in virus titers was observed at day 2, 5, or 8 between Met-RANTES-treated mice and vehicle-injected mice or anti-RANTES mAb-treated and isotype Ab-injected mice. Bars represent the means ± the standard deviations of three independent experiments (n = 4 mice per group). NS not significant. f Met-RANTES or anti-RANTES mAb treatment reduced inflammatory cell accumulation (indicated by black arrows) in cerebral cortex sections, compared to results for vehicle- or isotype Ab-treated mice, respectively. The histopathological changes of PFA-fixed sections in cerebral cortex were examined by HE staining on day 8 p.i. The photomicrographs demonstrate representative images obtained from three independent experiments (n = 4 mice per group). Bars, 100 μm Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://jneuroinflammation.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12974-016-0665-9), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CCL5/RANTES
CCL5, also known as RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed and presumably Secreted), is an 8 kDa beta -chemokine that plays a primary role in the inflammatory immune response by means of its ability to attract and activate leukocytes (1-3). Human and mouse RANTES exhibit cross-species activity on human and mouse cells (4). Mature mouse CCL5 shares 100% amino acid (aa) sequence identity with rat CCL5 and 75-88% with canine, cotton rat, feline, and human CCL5 (5). CCL5 is secreted by many cell types at inflammatory sites, and it exerts a wide range of activities through the receptors CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CCR5 (6, 7). Inflammatory responses can be impaired by the sequestration of CCL5 by the cytomegalovirus protein US28 (8). In humans, CCR5 binding to CCL5 inhibits the infectivity of R5 (M-tropic) but not X4 (T-tropic) strains of HIV-1 (9). The two N-terminal residues of CCL5 can be removed by CD26/DPPIV, generating a protein that functions as a chemotaxis inhibitor and more effectively blocks M-tropic HIV-1 infection of monocytes (10). Oligomerization of CCL5 on glycosaminoglycans is required for CCR1-mediated leukocyte adhesion and activation as well as CCL5’s interaction with the chemokine CXCL4/PF4 (11-13). The deposition of CCL5 on activated vascular endothelial cells is crucial for monocyte adhesion to damaged vasculature, but CCL5 oligomerization is not required for the extravasation of adherent leukocytes (14-16). CCL5 is upregulated in breast cancer and promotes tumor progression through the attraction of pro-inflammatory macrophages in addition to its actions on tumor cells, stromal cells, and the vasculature (17).
- Schall, T.J. et al. (1990) Nature 347:669.
- Bacon, K.B. et al. (1995) Science 269:1727.
- Fischer, F.R. et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 167:1637.
- Schall, T.J. et al. (1992) Eur. J. Immunol. 22:1477.
- Heeger, P. et al. (1992) Kidney Int. 41:220.
- Appay, V. and S.L. Rowland-Jones (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:83.
- Levy, J.A. (2009) J. Immunol. 182:3945.
- Randolph-Habecker, J.R. et al. (2002) Cytokine 19:37.
- DeVico, A.L. and R.C. Gallo (2004) Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:401.
- Proost, P. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:7222.
- Appay, V. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:27505.
- Proudfoot, A.E.I. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:1885.
- von Hundelshausen, P. et al. (2005) Blood 105:924.
- von Hundelshausen, P. et al. (2001) Circulation 103:1772.
- Zernecke, A. et al. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:1897.
- Baltus, T. et al. (2003) Blood 102:1985.
- Soria, G. and A. Ben-Baruch (2008) Cancer Lett. 267:271.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse CCL5/RANTES Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
29
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
High mobility group box-1 protein promotes astrocytic CCL5 production through the MAPK/NF-?B pathway following spinal cord injury
Authors: Chi, G;Lu, J;He, T;Wang, Y;Zhou, X;Zhang, Y;Qiu, L;
Scientific reports
Species: Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In vivo assay -
Transcriptional control of pancreatic cancer immunosuppression by metabolic enzyme CD73 in a tumor-autonomous and -autocrine manner
Authors: Tang, T;Huang, X;Lu, M;Zhang, G;Han, X;Liang, T;
Nature communications
Species: Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
IL-3 orchestrates ulcerative colitis pathogenesis by controlling the development and the recruitment of splenic reservoir neutrophils
Authors: Bénard, A;Mittelstädt, A;Klösch, B;Glanz, K;Müller, J;Schoen, J;Nüse, B;Brunner, M;Naschberger, E;Stürzl, M;Mattner, J;Muñoz, LE;Sohn, K;Grützmann, R;Weber, GF;
Cell reports
Species: Mouse
Sample Types:
Applications: In Vivo -
Pericyte stem cells induce Ly6G + cell accumulation and immunotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer
Authors: Zhichong Wu, Kevin Thierry, Sophie Bachy, Xinyi Zhang, Pia Gamradt, Hector Hernandez‐Vargas et al.
EMBO reports
-
Intramyocardial injected human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (HucMSCs) contribute to the recovery of cardiac function and the migration of CD4+ T cells into the infarcted heart via CCL5/CCR5 signaling
Authors: Jing Liu, Xiaoting Liang, Mimi Li, Fang Lin, Xiaoxue Ma, Yuanfeng Xin et al.
Stem Cell Research & Therapy
-
Intratumoral gamma δ T‐Cell Infiltrates, Chemokine (C‐C Motif) Ligand 4/Chemokine (C‐C Motif) Ligand 5 Protein Expression and Survival in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Authors: Na Zhao, Hien Dang, Lichun Ma, Sean P. Martin, Marshonna Forgues, Kris Ylaya et al.
Hepatology
-
MYC inhibition reprograms tumor immune microenvironment by recruiting T lymphocytes and activating the CD40/CD40L system in osteosarcoma
Authors: Kuo Jiang, Qianfeng Zhang, Yong Fan, Jia Li, Jitao Zhang, Wentao Wang et al.
Cell Death Discovery
-
Immune deconvolution and temporal mapping identifies stromal targets and developmental intervals for abrogating murine low-grade optic glioma formation
Authors: Amanda de Andrade Costa, Jit Chatterjee, Olivia Cobb, Elizabeth Cordell, Astoria Chao, Suzanne Schaeffer et al.
Neuro-Oncology Advances
-
Runx-mediated regulation of CCL5 via antagonizing two enhancers influences immune cell function and anti-tumor immunity
Authors: W Seo, K Shimizu, S Kojo, A Okeke, T Kohwi-Shig, SI Fujii, I Taniuchi
Nat Commun, 2020-03-26;11(1):1562.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Hepatospecific ablation of p38alpha MAPK governs liver regeneration through modulation of inflammatory response to CCl4-induced acute injury
Authors: M Fortier, M Cadoux, N Boussetta, S Pham, R Donné, JP Couty, C Desdouets, S Celton-Mor
Sci Rep, 2019-10-10;9(1):14614.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Nitrosporeusine analogue ameliorates Chandipura virus induced inflammatory response in CNS via NF?b inactivation in microglia
Authors: AK Verma, TS Waghmare, GR Jachak, SC Philkhana, DS Reddy, A Basu
PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2018-07-12;12(7):e0006648.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development (Capture) -
NK Cells Stimulate Recruitment of cDC1 into the Tumor Microenvironment Promoting Cancer Immune Control
Authors: JP Böttcher, E Bonavita, P Chakravart, H Blees, M Cabeza-Cab, S Sammicheli, NC Rogers, E Sahai, S Zelenay, C Reis E Sou
Cell, 2018-02-08;172(5):1022-1037.e14.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
The HIV co-receptor CCR5 regulates osteoclast function
Authors: JW Lee, A Hoshino, K Inoue, T Saitou, S Uehara, Y Kobayashi, S Ueha, K Matsushima, A Yamaguchi, Y Imai, T Iimura
Nat Commun, 2017-12-20;8(1):2226.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
CCL5 Promotes Resolution-Phase Macrophage Reprogramming in Concert with the Atypical Chemokine Receptor D6 and Apoptotic Polymorphonuclear Cells
Authors: M Aswad, S Assi, S Schif-Zuck, A Ariel
J. Immunol., 2017-07-03;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Tick-borne encephalitis virus induces chemokine RANTES expression via activation of IRF-3 pathway
J Neuroinflammation, 2016-08-30;13(1):209.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay, Neutralization -
Non-redundant requirement for CXCR3 signalling during tumoricidal T-cell trafficking across tumour vascular checkpoints
Authors: M. E. Mikucki, D. T. Fisher, J. Matsuzaki, J. J. Skitzki, N. B. Gaulin, J. B. Muhitch et al.
Nature Communications
-
Tumor-induced pressure in the bone microenvironment causes osteocytes to promote the growth of prostate cancer bone metastases.
Authors: Sottnik J, Dai J, Zhang H, Campbell B, Keller E
Cancer Res, 2015-04-08;75(11):2151-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
The Inflammatory Preatherosclerotic Remodeling Induced by Intermittent Hypoxia Is Attenuated by RANTES/CCL5 Inhibition
Authors: Claire Arnaud, Pauline C. Beguin, Sylvie Lantuejoul, Jean-Louis Pepin, Christiane Guillermet, Graziano Pelli et al.
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
-
T Cell-, Interleukin-12-, and Gamma Interferon-Driven Viral Clearance in Measles Virus-Infected Brain Tissue
Authors: Samantha R. Stubblefield Park, Mi Widness, Alan D. Levine, Catherine E. Patterson
Journal of Virology
-
Acid sphingomyelinase is a key regulator of cytotoxic granule secretion by primary T lymphocytes.
Authors: Herz J, Pardo J, Kashkar H, Schramm M, Kuzmenkina E, Bos E, Wiegmann K, Wallich R, Peters PJ, Herzig S, Schmelzer E, Kronke M, Simon MM, Utermohlen O
Nat. Immunol., 2009-06-14;10(7):761-8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Rapid dendritic cell mobilization to the large intestinal epithelium is associated with resistance to Trichuris muris infection.
Authors: Cruickshank SM, Deschoolmeester ML, Svensson M, Howell G, Bazakou A, Logunova L, Little MC, English N, Mack M, Grencis RK, Else KJ, Carding SR
J. Immunol., 2009-03-01;182(5):3055-62.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Role of the chemokine decoy receptor D6 in balancing inflammation, immune activation, and antimicrobial resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
Authors: Di Liberto D, Locati M, Caccamo N, Vecchi A, Meraviglia S, Salerno A, Sireci G, Nebuloni M, Caceres N, Cardona PJ, Dieli F, Mantovani A
J. Exp. Med., 2008-08-11;205(9):2075-84.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Joint capsule treatment with enkephalin-encoding HSV-1 recombinant vector reduces inflammatory damage and behavioural sequelae in rat CFA monoarthritis.
Authors: Lu Y, McNearney TA, Wilson SP, Yeomans DC, Westlund KN
Eur. J. Neurosci., 2008-03-01;27(5):1153-65.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
The direct action of 1alpha,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 on purified mouse Langerhans cells.
Authors: Fujita H, Asahina A, Komine M, Tamaki K
Cell. Immunol., 2007-05-15;245(2):70-9.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Protection against inflammation- and autoantibody-caused fetal loss by the chemokine decoy receptor D6.
Authors: Martinez de la Torre Y, Buracchi C, Borroni EM, Dupor J, Bonecchi R, Nebuloni M, Pasqualini F, Doni A, Lauri E, Agostinis C, Bulla R, Cook DN, Haribabu B, Meroni P, Rukavina D, Vago L, Tedesco F, Vecchi A, Lira SA, Locati M, Mantovani A
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2007-02-05;104(7):2319-24.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Synthesis of several chemokines but few cytokines by primed uncommitted precursor CD4 T cells suggests that these cells recruit other immune cells without exerting direct effector functions.
Authors: Mosmann T
Eur. J. Immunol., 2004-06-01;34(6):1617-26.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
NKT cell-derived RANTES recruits APCs and CD8+ T cells to the spleen during the generation of regulatory T cells in tolerance.
Authors: Faunce DE, Stein-Streilein J
J. Immunol., 2002-07-01;169(1):31-8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Stat3-dependent acute Rantes production in vascular smooth muscle cells modulates inflammation following arterial injury in mice.
Authors: Kovacic JC, Gupta R, Lee AC, Ma M, Fang F, Tolbert CN, Walts AD, Beltran LE, San H, Chen G, St Hilaire C, Boehm M
J. Clin. Invest., 2009-12-28;120(1):303-14.
-
A new HIF-1alpha/RANTES driven pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma mediated by germline haploinsufficiency of SART1/HAF.
Authors: Koh MY, Gagea M, Sargis T et al.
Hepatology.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse CCL5/RANTES Antibody
Average Rating: 4.7 (Based on 3 Reviews)
Have you used Mouse CCL5/RANTES Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Worked as capture IgG