Mouse HGFR/c-MET Antibody Summary
Glu25-Asn929
Accession # P16056
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
HGF R/c‑MET in HT‑29 and U937 Human Cell Lines. HGF R/c-MET was detected in immersion fixed HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cell line (positive control, left panel) and U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (negative control, right panel) using Goat Anti-Mouse HGF R/c-MET Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF527) at 5 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
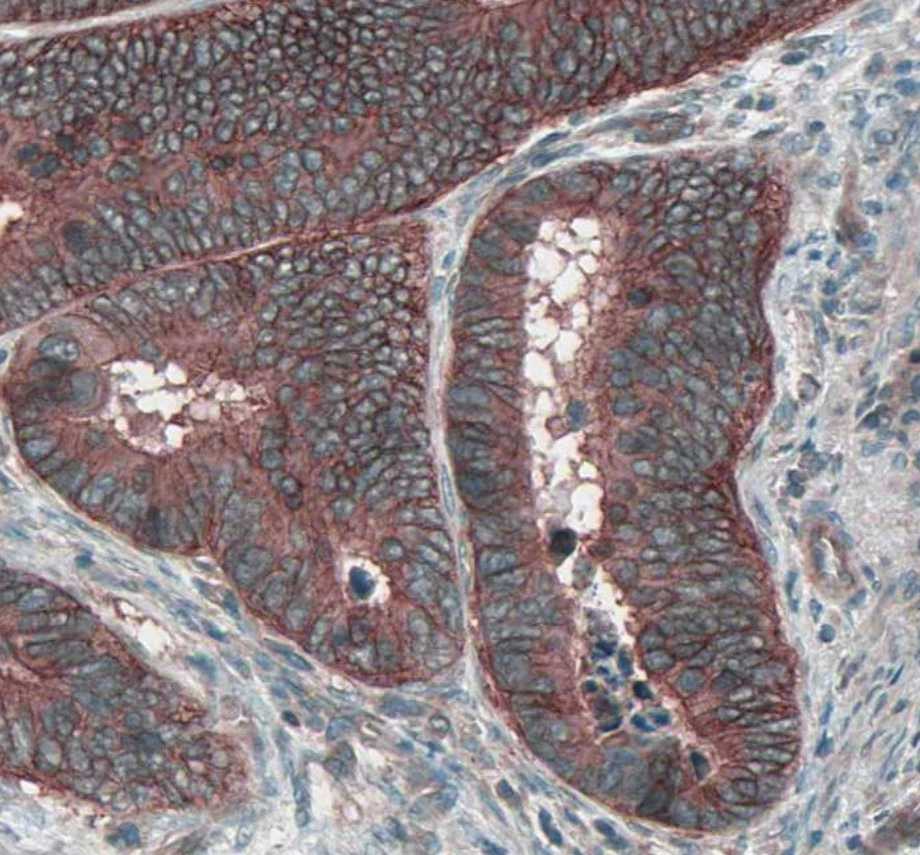
 View Larger
View Larger
HGF R/c‑MET in Mouse Embryo. HGF R/c-MET was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (15 d.p.c.) using Goat Anti-Mouse HGF R/c-MET Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF527) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in muscle cells. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: HGFR/c-MET
HGF R, also known as Met (from N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced), is a glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in epithelial morphogenesis and cancer development. HGF R is synthesized as a single chain precursor which undergoes cotranslational proteolytic cleavage. This generates a mature HGF R that is a disulfide-linked dimer composed of a 50 kDa extracellular alpha chain and a 145 kDa transmembrane beta chain (1, 2). The extracellular domain (ECD) contains a seven bladed beta -propeller sema domain, a cysteine-rich PSI/MRS, and four Ig-like E-set domains, while the cytoplasmic region includes the tyrosine kinase domain (3, 4). An alternately spliced form of mouse HGF R lacks a cytoplasmic juxtamembrane region important for regulation of signal transduction (5, 6). The sema domain, which is formed by both the alpha and beta chains of HGF R, mediates both ligand binding and receptor dimerization (3, 7). Ligand-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in the cytoplasmic region activates the kinase domain and provides docking sites for multiple SH2-containing molecules (8, 9). HGF stimulation induces HGF R downregulation via internalization and proteasome-dependent degradation (10). In the absence of ligand, HGF R forms non-covalent complexes with a variety of membrane proteins including CD44v6, CD151, EGF R, Fas, integrin alpha 6/ beta 4, plexins B1, 2, 3, and MSP R/Ron (11-18). Ligation of one complex component triggers activation of the other, followed by cooperative signaling effects (11-18). Formation of some of these heteromeric complexes is a requirement for epithelial cell morphogenesis and tumor cell invasion (11, 15, 16). Paracrine induction of epithelial cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis results from the stimulation of HGF R on undifferentiated epithelium by HGF released from neighboring mesenchymal cells (19). Genetic polymorphisms, chromosomal translocation,
over-expression, and additional splicing and proteolytic cleavage of HGF R have been described in a wide range of cancers (1). Within the ECD, mouse HGF R shares 87%, 87%, and 94% amino acid sequence identity with canine, human, and rat HGF R, respectively.
- Birchmeier, C. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:915.
- Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
- Gherardi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:12039.
- Chan, A.M. et al. (1988) Oncogene 2:593.
- Lee, C.-C. and K.M. Yamada (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:19457.
- Lee, C.-C., et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:507.
- Kong-Beltran, M. et al. (2004) Cancer Cell 6:75.
- Naldini, L. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1793.
- Ponzetto, C. et al. (1994) Cell 77:261.
- Jeffers, M. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:799.
- Orian-Rousseau, V. et al. (2002) Genes Dev. 16:3074.
- Klosek, S.K. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336:408.
- Jo, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:8806.
- Wang, X. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell 9:411.
- Trusolino, L. et al. (2001) Cell 107:643.
- Giordano, S. et al. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4:720.
- Conrotto, P. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:5131.
- Follenzi, A. et al. (2000) Oncogene 19:3041.
- Sonnenberg, E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 123:223.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse HGFR/c-MET Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
35
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Hepatocyte Growth Factor and MET Support Mouse Enteric Nervous System Development, the Peristaltic Response, and Intestinal Epithelial Proliferation in Response to Injury
Authors: Marina Avetisyan, Hongtao Wang, Ellen Merrick Schill, Saya Bery, John R. Grider, John A. Hassell et al.
The Journal of Neuroscience
-
Specific Connectivity and Unique Molecular Identity of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Expressing Serotonergic Neurons in the Caudal Dorsal Raphe Nuclei
Authors: Ryan J. Kast, Hsiao-Huei Wu, Piper Williams, Patricia Gaspar, Pat Levitt
ACS Chemical Neuroscience
-
Prenatal Expression of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in the Fetal Mouse Dorsal Raphe Nuclei and the Visceral Motor/Sensory Brainstem
Authors: Hsiao-Huei Wu, Pat Levitt
Developmental Neuroscience
-
SOX9-positive pituitary stem cells differ according to their position in the gland and maintenance of their progeny depends on context
Authors: Rizzoti, K;Chakravarty, P;Sheridan, D;Lovell-Badge, R;
Science advances
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Novel rAAV vector mediated intrathecal HGF delivery has an impact on neuroimmune modulation in the ALS motor cortex with TDP-43 pathology
Authors: B Genç, B Nho, H Seung, B Helmold, H Park, Ö Gözütok, S Kim, J Park, S Ye, H Lee, N Lee, SS Yu, S Kim, J Lee, H Özdinler
Gene Therapy, 2023-02-24;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Fibroblast-derived Hgf controls recruitment and expansion of muscle during morphogenesis of the mammalian diaphragm
Authors: EM Sefton, M Gallardo, CE Tobin, BC Collins, MP Colasanto, AJ Merrell, G Kardon
Elife, 2022-09-26;11(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
The study of direct and indirect effects of radiofrequency ablation on tumor microenvironment in liver tumor animal model
Authors: AN Jiang, B Wang, S Wang, K Zhao, H Wu, K Yan, W Wu, W Yang
BMC Cancer, 2022-06-17;22(1):663.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Two-Chains Tissue Plasminogen Activator Unifies Met and NMDA Receptor Signalling to Control Neuronal Survival
Authors: E Hedou, S Douceau, A Chevilley, A Varangot, AM Thiebaut, H Triniac, I Bardou, C Ali, M Maillasson, T Crepaldi, P Comoglio, E Lemarchand, V Agin, BD Roussel, D Vivien
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021-12-15;22(24):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot -
Wnt signaling enhances macrophage responses to IL-4 and promotes resolution of atherosclerosis
Authors: A Weinstock, K Rahman, O Yaacov, H Nishi, P Menon, CA Nikain, ML Garabedian, S Pena, N Akbar, BE Sansbury, SP Heffron, J Liu, G Marecki, D Fernandez, EJ Brown, KV Ruggles, SA Ramsey, C Giannarell, M Spite, RP Choudhury, P Loke, EA Fisher
Elife, 2021-03-15;10(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Aberrant activation of hepatocyte growth factor/MET signaling promotes beta-catenin-mediated prostatic tumorigenesis
Authors: J Aldahl, J Mi, A Pineda, WK Kim, A Olson, E Hooker, Y He, EJ Yu, V Le, DH Lee, J Geradts, Z Sun
J. Biol. Chem., 2019-12-09;295(2):631-644.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Activation of hepatocyte growth factor/MET signaling initiates oncogenic transformation and enhances tumoraggressiveness in the murine prostate
Authors: J Mi, E Hooker, S Balog, H Zeng, DT Johnson, Y He, EJ Yu, H Wu, V Le, DH Lee, J Aldahl, ML Gonzalgo, Z Sun
J. Biol. Chem., 2018-11-06;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Pulmonary pericytes regulate lung morphogenesis
Authors: K Kato, R Diéguez-Hu, DY Park, SP Hong, S Kato-Azuma, S Adams, M Stehling, B Trappmann, JL Wrana, GY Koh, RH Adams
Nat Commun, 2018-06-22;9(1):2448.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Hepatocyte Growth Factor-c-MET Signaling Mediates the Development of Nonsensory Structures of the Mammalian Cochlea and Hearing
J Neurosci, 2016-08-03;36(31):8200-9.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Beta 1-integrin-c-Met cooperation reveals an inside-in survival signalling on autophagy-related endomembranes
Authors: Rachel Barrow-McG
Nat Commun, 2016-06-23;7(0):11942.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Met Promotes Cell Survival via Kinase-Independent Maintenance of Integrin ?3?1
Authors: Lia Tesfay
Mol Biol Cell, 2016-06-15;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: IHC-Fr, Western Blot -
MET is required for the recruitment of anti-tumoural neutrophils.
Authors: Finisguerra V, Di Conza G, Di Matteo M, Serneels J, Costa S, Thompson A, Wauters E, Walmsley S, Prenen H, Granot Z, Casazza A, Mazzone M
Nature, 2015-05-18;522(7556):349-53.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: ELISA Development (Capture) -
Regulation of hepatocyte growth factor in mice with pneumonia by peptidases and trans-alveolar flux.
Authors: Raymond W, Xu X, Nimishakavi S, Le C, McDonald D, Caughey G
PLoS ONE, 2015-05-04;10(5):e0125797.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Targeting matriptase in breast cancer abrogates tumour progression via impairment of stromal-epithelial growth factor signalling.
Authors: Zoratti G, Tanabe L, Varela F, Murray A, Bergum C, Colombo E, Lang J, Molinolo A, Leduc R, Marsault E, Boerner J, List K
Nat Commun, 2015-04-15;6(0):6776.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Recombinant insulin-like growth factor-1 activates satellite cells in the mouse urethral rhabdosphincter.
Authors: Wei W, Howard P, Macarak E
BMC Urol, 2013-11-26;13(0):62.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
c-Met and its ligand hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor regulate mature B cell survival in a pathway induced by CD74.
Authors: Gordin M, Tesio M, Cohen S
J. Immunol., 2010-07-16;185(4):2020-31.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Western Blot -
Enhanced c-Met activity promotes G-CSF-induced mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells via ROS signaling.
Authors: Tesio M, Golan K, Corso S
Blood, 2010-06-28;117(2):419-28.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, In Vivo, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Neutralization, Western Blot -
Expression of the HGF receptor c-met by macrophages in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Authors: Moransard M, Sawitzky M, Fontana A, Suter T
Glia, 2010-04-01;58(5):559-71.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot -
High concentrations of HGF inhibit skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation in vitro by inducing expression of myostatin: a possible mechanism for reestablishing satellite cell quiescence in vivo.
Authors: Yamada M, Tatsumi R, Yamanouchi K, Hosoyama T, Shiratsuchi S, Sato A, Mizunoya W, Ikeuchi Y, Furuse M, Allen RE
Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 2009-12-09;298(3):C465-76.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Possible implication of satellite cells in regenerative motoneuritogenesis: HGF upregulates neural chemorepellent Sema3A during myogenic differentiation.
Authors: Tatsumi R, Sankoda Y, Anderson JE, Sato Y, Mizunoya W, Shimizu N, Suzuki T, Yamada M, Rhoads RP, Ikeuchi Y, Allen RE
Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 2009-06-10;297(2):C238-52.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
A role for calcium-calmodulin in regulating nitric oxide production during skeletal muscle satellite cell activation.
Authors: Tatsumi R, Wuollet AL, Tabata K, Nishimura S, Tabata S, Mizunoya W, Ikeuchi Y, Allen RE
Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 2009-01-21;296(4):C922-9.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
Purification and characterization of mouse lacrimal gland epithelial cells and reconstruction of an acinarlike structure in three-dimensional culture.
Authors: Ueda Y, Karasawa Y, Satoh Y, Nishikawa S, Imaki J, Ito M
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 2008-12-20;50(5):1978-87.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Ets-1 triggers and orchestrates the malignant phenotype of mammary cancer cells within their matrix environment.
Authors: Furlan A, Vercamer C, Desbiens X, Pourtier A
J. Cell. Physiol., 2008-06-01;215(3):782-93.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
A selective small molecule inhibitor of c-Met, PHA-665752, reverses lung premalignancy induced by mutant K-ras.
Authors: Yang Y, Wislez M, Fujimoto N, Prudkin L, Izzo JG, Uno F, Ji L, Hanna AE, Langley RR, Liu D, Johnson FM, Wistuba I, Kurie JM
Mol. Cancer Ther., 2008-04-01;7(4):952-60.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Gastrointestinal hormones cause rapid c-Met receptor down-regulation by a novel mechanism involving clathrin-mediated endocytosis and a lysosome-dependent mechanism.
Authors: Hoffmann KM, Tapia JA, Berna MJ, Thill M, Braunschweig T, Mantey SA, Moody TW, Jensen RT
J. Biol. Chem., 2006-10-10;281(49):37705-19.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
A recombinant single-chain IL-7/HGFbeta hybrid cytokine induces juxtacrine interactions of the IL-7 and HGF (c-Met) receptors and stimulates the proliferation of CFU-S12, CLPs, and pre-pro-B cells.
Authors: Lai L, Zeff RA, Goldschneider I
Blood, 2005-11-22;107(5):1776-84.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Neutralization, Western Blot -
Distinct projection targets define subpopulations of mouse brainstem vagal neurons that express the autism-associated MET receptor tyrosine kinase
Authors: Anna Kamitakahara, Hsiao-Huei Wu, Pat Levitt
Journal of Comparative Neurology
-
cMET inhibitor crizotinib impairs angiogenesis and reduces tumor burden in the C3(1)-Tag model of basal-like breast cancer
Authors: Alyssa J. Cozzo, Sneha Sundaram, Ottavia Zattra, Yuanyuan Qin, Alex J. Freemerman, Luma Essaid et al.
SpringerPlus
-
MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Regulates Lifespan Ultrasonic Vocalization and Vagal Motor Neuron Development
Authors: Anna K. Kamitakahara, Ramin Ali Marandi Ghoddousi, Alexandra L. Lanjewar, Valerie M. Magalong, Hsiao-Huei Wu, Pat Levitt
Frontiers in Neuroscience
-
Failure to ubiquitinate c-Met leads to hyperactivation of mTOR signaling in a mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Authors: Shan Qin, Mary Taglienti, Surya M. Nauli, Leah Contrino, Ayumi Takakura, Jing Zhou et al.
Journal of Clinical Investigation
-
Tumour growth stimulation following partial hepatectomy in mice is associated with increased upregulation of c-Met
Authors: Nadia Harun, Patricia Costa, C. Christophi
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse HGFR/c-MET Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse HGFR/c-MET Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: