Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody Summary
Glu18-Lys590
Accession # Q08481
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
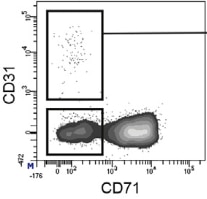
Detection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Mouse splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3628G, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108G, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Rat Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Rat splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3628G, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108G, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
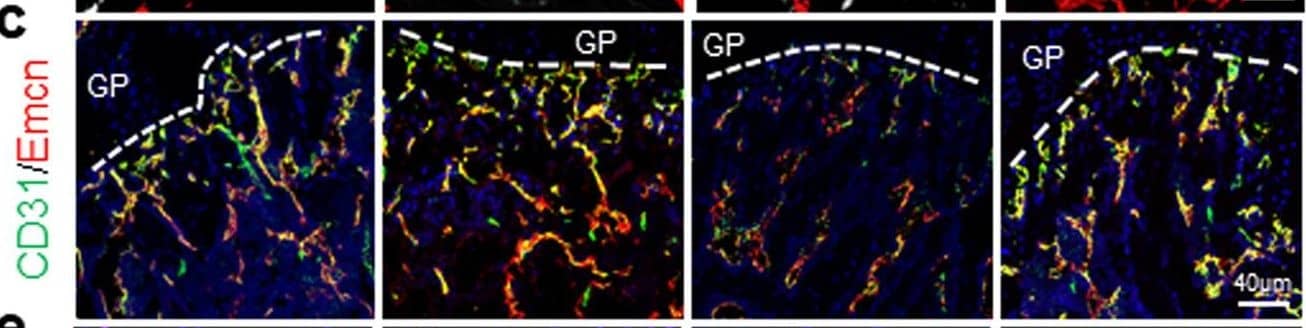
Detection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence LIMB and immunofluorescence analysis indicate possible mechanisms of vascular morphological changes deep in the femoral bone marrow, during regeneration, and in steady-state homeostasis. a Immunofluorescence analysis shows that type H vessels, characterized by CD31hiEmcnhi-expressing endothelial cells, are induced and present around the implant at day 3 after LIMB implantation. Their presence may vary individually but normalizes within 28 days post-surgery. Sinusoidal and type H vessel morphology adjacent to the wc is irregular in the first week and completely reorganizes to an appearance comparable to vessels found at endosteal areas distant from the injury site (n = 3 mice). bm bone marrow, cb cortical bone. Scale bar = 500 µm (left panels). b Immunofluorescence analysis after EdU pulse-chase experiments indicates similar EdU-uptake in the bone marrow of LIMB-implanted femurs and contralateral bones. Proliferating endothelial cells were rarely present at late time points after implantation. This result also supports the conclusion that 28 days after LIMB implantation both the bone and the bone marrow reach homeostasis (n = 3 mice in each cohort). c 3D fluorescence image (300 × 300 × 66 µm3, left and right panel) acquired by LIMB 26 days post-surgery, in a paGFP mouse with the vasculature labeled by Qdots. Photoactivation was performed within a volume of 100 × 100 × 9 µm3 in the center of the image. The fluorescence image was acquired 2 h post activation. Scale bar = 50 µm. The middle panel shows time-lapse 3D images of the inset from the left panel, indicating that paGFP fluorescent cells outside the initial photoactivation volume are present 3 h after photoactivation and that they fluctuate in number and position within the tissue. Passive displacement of the relatively immobile stromal and vascular compartments by continuous proliferation and movement of hematopoietic cells is a possible mechanism of tissue and vascular re-localization during homeostasis (see Supplementary Movies 10, 11) Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29255233), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunohistochemistry Recombinant human ANG (rhANG) rescues GC-impaired bone growth and mineral acquisition.Three-week-old BALB/c mice were treated with vehicle, MPS alone at 10 mg/m2/day or MPS plus rhANG (1 µg/day) by daily intraperitoneal injection for 4 weeks. Representative images of SA-beta Gal staining (white) and immunofluorescence staining of Endomucin (Emcn, red) in primary spongiosa of femoral bone in (a). Percentage of SA-beta Gal-expressing vessels were quantified in (b). Double immunofluorescence staining of Emcn (red) and CD31 (green) in metaphysis of femoral bone in (c). DAPI-stained nuclei blue. Relative yellow fluorescence intensity in primary spongiosa was measured in (d). Immunofluorescence staining of femoral metaphysis sections were performed using antibody against Osx (red) in (e). DAPI stains nuclei blue. Numbers of Osx+ cells per mm2 tissue area (N. Osx+ cells/Ar) were quantified in (f). Representative μCT images of distal femur in mice were shown in (g, longitudinal sections) and (h, cross sections). Quantitative analyses of trabecular bone volume fraction (BV/TV) (i), trabecular thickness (Tb. Th) (j), trabecular number (Tb. N) (k), and trabecular separation (Tb.Sp) (l). Trichrome staining of the metaphyseal trabecular bone at distal femora in (m). Osteoid stains red and mineralized bone stains green. Osteoid surface per bone surface (OS/BS) was measured in (n). Representative images of calcein double labeling (o) and quantification of bone formation rate per bone surface (BFR/BS) (p) of the metaphyseal trabecular bone at distal femora. GP growth plate. n = 6-10 mice. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. **p < 0.01 as determined by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33758201), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
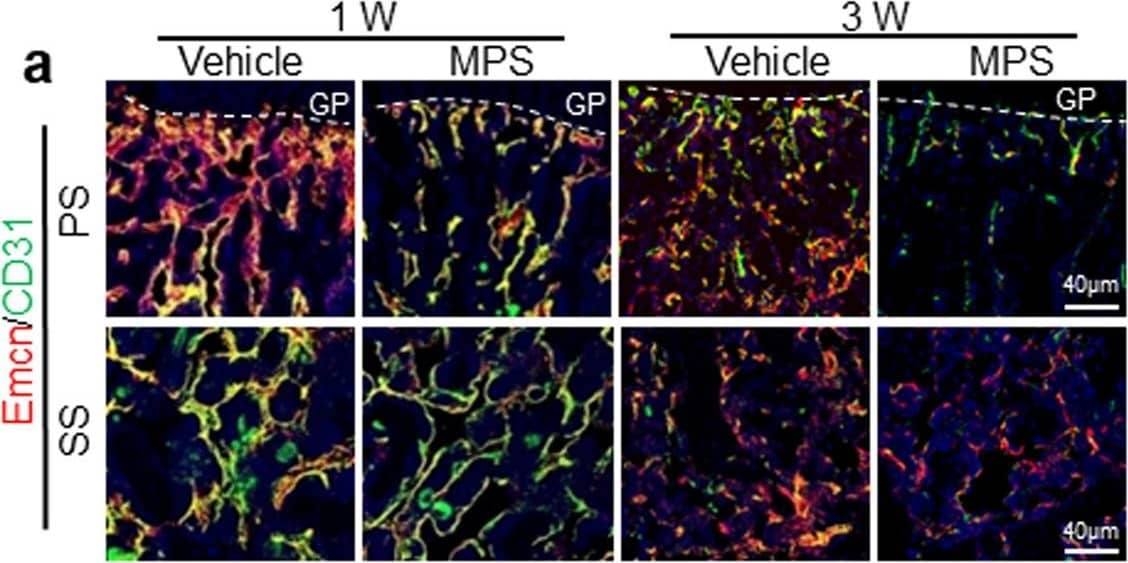
Detection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Antagonizing endothelial cell senescence improves GC-impaired bone angiogenesis and osteogenesis.a–i Three-week-old BALB/c mice were treated with MPS at 10 mg/m2/day or vehicle by daily intraperitoneal injection for 1 or 3 weeks. Double-immunofluorescence staining of femur metaphysis sections was performed using antibodies against Emcn (red) and CD31 (green) in (a). DAPI stains nuclei blue. Relative yellow fluorescence intensity (vessels expressing both Emcn and CD31) in primary spongiosa (b) and secondary spongiosa (c) was measured. Cells isolated from femoral metaphysis of MPS-treated or vehicle-treated mice were subjected to flow cytometry analysis. Representative images are shown in (d). Black circle: type-H vessels; Brown circle: type-L vascular cells. The percentages of the CD31hiEmcnhi cells and CD31loEmcnlo cells are shown in (e) and (f), respectively. Immunofluorescence staining of femoral metaphysis sections was performed using antibody against Osteocalcin (OCN, green) in (g). DAPI stains nuclei blue. Quantified numbers of OCN+ cells per mm2 tissue area (N. OCN+ cells/Ar) in primary spongiosa and secondary spongiosa are shown in (h) and (i), respectively. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33758201), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: CD31/PECAM-1
PECAM-1 (Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1), also known as CD31, is a 130 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein adhesion molecule in the immunoglobulin superfamily (1, 2). Expression is restricted to cells involved in circulation, especially endothelial cells, platelets, monocytes, neutrophils and lymphocyte subsets. PECAM-1 is concentrated at cell-cell junctions and is required for Transendothelial Migration (TEM) (1-3). The Extracellular Domain (ECD) of PECAM-1 has ten potential N-linked glycosylation sites and six C2-type Ig-like domains, the first of which is critical for adhesion and extravasation (3, 4). The cytoplasmic domain contains Immunoregulatory Tyrosine-based Inhibitory and Switch Motifs (ITIM, ITSM) that mediate both inhibition and activation via phosphotyrosine-mediated engagement of SH2-containing signaling molecules (1, 5). Metalloproteinase-mediated ectodomain shedding occurs during apoptosis (6) but increased serum PECAM-1 ectodomain in HIV and active multiple sclerosis occurs independent of apoptosis (7, 8). In humans, expression of six isoforms with exon deletions in the cytoplasmic domain is tissue- and stage-specific, but full-length PECAM-1 is predominant. A form lacking the ITSM predominates in mouse (9). Mouse PECAM-1 ECD shows 77%, 63%, 63%, 63%, and 61% amino acid (aa) identity with rat, human, canine, porcine, and bovine PECAM-1, respectively. PECAM-1 participates with other adhesion molecules in some functions, but is the critical molecule for TEM. Homotypic PECAM-1 adhesion in trans, combined with cycling of PECAM-1 to and from surface-connected endothelial cell vesicles, leads leukocytes across endothelial tight junctions (3, 10). Homotypic adhesion and signaling functions also strongly suppress mitochondria-dependent apoptosis (11). In platelets, PECAM-1 is necessary for limiting thrombus formation (12) and promoting integrin-mediated clot retraction and platelet spreading (13), but mechanisms for these phenomena are unclear. PECAM-/- mice are deficient in chemokine-mediated chemotaxis (14).
- Ilan, N. and J.A. Madri (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:515.
- Xie, Y. and W.A. Muller (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5569.
- Liao, F. et al. (1997) J. Exp. Med. 185:1349.
- Nakada, M.T. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 164:452.
- Chemnitz, J.M. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:945.
- Ilan, N. et al. (2001) FASEB J. 15:362.
- Eugenin, E.A. et al. (2006) J. Leukoc. Biol. 79:444.
- Losy, J. et al. (1999) J. Neuroimmunol. 99:169.
- Wang, Y. et al. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284:H1008.
- Mamdouh, Z. et al. (2003) Nature 421:748.
- Gao, C. et al. (2003) Blood 102:169.
- Falati, S. et al. (2006) Blood 107:535.
- Wee, J.L. and D.E. Jackson (2005) Blood 106:3816.
- Wu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:3484.
Product Datasheets
Product Specific Notices
This product is provided under an agreement between Life Technologies Corporation and R&D Systems, Inc, and the manufacture, use, sale or import of this product is subject to one or more US patents and corresponding non-US equivalents, owned by Life Technologies Corporation and its affiliates. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer the non-transferable right to use the purchased amount of the product and components of the product only in research conducted by the buyer (whether the buyer is an academic or for-profit entity). The sale of this product is expressly conditioned on the buyer not using the product or its components (1) in manufacturing; (2) to provide a service, information, or data to an unaffiliated third party for payment; (3) for therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic purposes; (4) to resell, sell, or otherwise transfer this product or its components to any third party, or for any other commercial purpose. Life Technologies Corporation will not assert a claim against the buyer of the infringement of the above patents based on the manufacture, use or sale of a commercial product developed in research by the buyer in which this product or its components was employed, provided that neither this product nor any of its components was used in the manufacture of such product. For information on purchasing a license to this product for purposes other than research, contact Life Technologies Corporation, Cell Analysis Business Unit, Business Development, 29851 Willow Creek Road, Eugene, OR 97402, Tel: (541) 465-8300. Fax: (541) 335-0354.
Citations for Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
38
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Region-specific sympatho-adrenergic regulation of specialized vasculature in bone homeostasis and regeneration
Authors: Hao-Kun Xu, Jie-Xi Liu, Chen-Xi Zheng, Lu Liu, Chao Ma, Jiong-Yi Tian et al.
iScience
-
Distinct Bone Marrow Sources of Pleiotrophin Control Hematopoietic Stem Cell Maintenance and Regeneration
Authors: HA Himburg, CM Termini, L Schlussel, J Kan, M Li, L Zhao, T Fang, JP Sasine, VY Chang, JP Chute
Cell Stem Cell, 2018-08-09;0(0):.
-
Alteration of m6A epitranscriptomic tagging of ribonucleic acids after spinal cord injury in mice
Authors: Shuangfei Ni, Zixiang Luo, Yonggang Fan, Weixin Zhang, Wei Peng, Huafeng Zhang
Frontiers in Neuroscience
-
Metformin accelerates bone fracture healing by promoting type H vessel formation through inhibition of YAP1/TAZ expression
Authors: Zhe Ruan, Hao Yin, Teng-Fei Wan, Zhi-Rou Lin, Shu-Shan Zhao, Hai-Tao Long et al.
Bone Research
-
Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys Promote Angio‐Osteogenesis to Enhance Bone Repair
Authors: Hyung‐Seop Han, Indong Jun, Hyun‐Kwang Seok, Kang‐Sik Lee, Kyungwoo Lee, Frank Witte et al.
Advanced Science
-
SHED aggregate exosomes shuttled miR‐26a promote angiogenesis in pulp regeneration via TGF‐ beta /SMAD2/3 signalling
Authors: Meiling Wu, Xuemei Liu, Zihan Li, Xiaoyao Huang, Hao Guo, Xiaohe Guo et al.
Cell Proliferation
-
Glucocorticoids Disrupt Skeletal Angiogenesis Through Transrepression of NF‐ kappa B–Mediated Preosteoclast Pdgfb Transcription in Young Mice
Authors: Yi Peng, Shan Lv, Yusheng Li, Jianxi Zhu, Shijie Chen, Gehua Zhen et al.
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research
-
Mechanosensing by Gli1 + cells contributes to the orthodontic force‐induced bone remodelling
Authors: An‐Qi Liu, Li‐Shu Zhang, Ji Chen, Bing‐Dong Sui, Jin Liu, Qi‐Ming Zhai et al.
Cell Proliferation
-
The protective role of adipogenic lineage precursors in maintaining bone marrow redox homeostasis in a mouse model of prenatal dexamethasone exposure
Authors: Su, J;Ma, S;Yang, M;Wu, J;Chen, Y;Jin, M;Shi, Q;Zhang, X;
Redox biology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Localization of Both CD31- and Endomucin-Expressing Vessels in Mouse Dental Pulp
Authors: Kambe, R;Mitomo, K;Ikarashi, T;Haketa, M;Tashiro, K;Furusawa, M;Muramatsu, T;
Acta histochemica et cytochemica
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Promoting diabetic oral mucosa wound healing with a light-responsive hydrogel adaptive to the microenvironment
Authors: Ding, S;Zhang, X;Wang, G;Shi, J;Zhu, J;Yan, J;Wang, J;Wu, J;
Heliyon
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
MCT1-mediated endothelial cell lactate shuttle as a target for promoting axon regeneration after spinal cord injury
Authors: Shi, C;Xu, J;Ding, Y;Chen, X;Yuan, F;Zhu, F;Duan, C;Hu, J;Lu, H;Wu, T;Jiang, L;
Theranostics
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Tanshinone IIA attenuates osteoarthritis via inhibiting aberrant angiogenesis in subchondral bone
Authors: Li, HZ;Han, D;Ao, RF;Cai, ZH;Zhu, GZ;Wu, DZ;Gao, JW;Zhuang, JS;Tu, C;Zhao, K;Wu, ZY;Zhong, ZM;
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
11 beta -Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Facilitates Osteoporosis by Turning on Osteoclastogenesis through Hippo Signaling
Authors: Li, H;Hu, S;Wu, R;Zhou, H;Zhang, K;Li, K;Lin, W;Shi, Q;Chen, H;Lv, S;
International journal of biological sciences
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
HA-g-CS Implant and Moderate-intensity Exercise Stimulate Subchondral Bone Remodeling and Promote Repair of Osteochondral Defects in Mice
Authors: K Shen, X Liu, H Qin, Y Chai, L Wang, B Yu
International Journal of Medical Sciences, 2021-10-22;18(16):3808-3820.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Targeting local lymphatics to ameliorate heterotopic ossification via FGFR3-BMPR1a pathway
Authors: D Zhang, J Huang, X Sun, H Chen, S Huang, J Yang, X Du, Q Tan, F Luo, R Zhang, S Zhou, W Jiang, Z Ni, Z Wang, M Jin, M Xu, F Li, L Chen, M Liu, N Su, X Luo, L Yin, Y Zhu, JQ Feng, D Chen, H Qi, L Chen, Y Xie
Nature Communications, 2021-07-19;12(1):4391.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
SHED aggregate exosomes shuttled miR‐26a promote angiogenesis in pulp regeneration via TGF‐ beta /SMAD2/3 signalling
Authors: Meiling Wu, Xuemei Liu, Zihan Li, Xiaoyao Huang, Hao Guo, Xiaohe Guo et al.
Cell Proliferation
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Post-myocardial infarction heart failure dysregulates the bone vascular niche
Authors: J Hoffmann, G Luxán, WT Abplanalp, SF Glaser, T Rasper, A Fischer, M Muhly-Rein, M Potente, B Assmus, D John, AM Zeiher, S Dimmeler
Nature Communications, 2021-06-25;12(1):3964.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Mechanosensitive Piezo1 in endothelial cells promotes angiogenesis to support bone fracture repair
Authors: P Chen, G Zhang, S Jiang, Y Ning, B Deng, X Pan, S Liu, Y He, L Zhang, R Wan, Z Wu, Q He, J Yin, H Wang, J Li
Cell Calcium, 2021-06-07;97(0):102431.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Osteoclasts protect bone blood vessels against senescence through the angiogenin/plexin-B2 axis
Authors: X Liu, Y Chai, G Liu, W Su, Q Guo, X Lv, P Gao, B Yu, G Ferbeyre, X Cao, M Wan
Nature Communications, 2021-03-23;12(1):1832.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Gli1+ Cells Couple with Type H Vessels and Are Required for Type H Vessel Formation
Authors: J Chen, M Li, AQ Liu, CX Zheng, LH Bao, K Chen, XL Xu, JT Guan, M Bai, T Zhou, BD Sui, DH Li, Y Jin, CH Hu
Stem Cell Reports, 2020-07-14;15(1):110-124.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Cellular senescence mediates the detrimental effect of prenatal dexamethasone exposure on postnatal long bone growth in mouse offspring
Authors: J Su, Y Chai, Z Ji, Y Xie, B Yu, X Zhang
Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020-07-06;11(1):270.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissues
Applications: IHC -
Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis
Authors: R Fu, WC Lv, Y Xu, MY Gong, XJ Chen, N Jiang, Y Xu, QQ Yao, L Di, T Lu, LM Wang, R Mo, ZQ Wu
Nat Commun, 2020-01-23;11(1):460.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Angiocrine signals regulate quiescence and therapy resistance in bone metastasis
Authors: A Singh, V Veeriah, P Xi, R Labella, J Chen, SG Romeo, SK Ramasamy, AP Kusumbe
JCI Insight, 2019-07-11;4(13):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Nidogen-1 Contributes to the Interaction Network Involved in Pro-B Cell Retention in the Peri-sinusoidal Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche
Authors: M Balzano, M De Grandis, TP Vu Manh, L Chasson, F Bardin, A Farina, A Sergé, G Bidaut, P Charbord, L Hérault, AL Bailly, A Cartier-Mi, A Boned, M Dalod, E Duprez, P Genever, M Coles, M Bajenoff, L Xerri, M Aurrand-Li, C Schiff, SJC Mancini
Cell Rep, 2019-03-19;26(12):3257-3271.e8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Programmed cell senescence in skeleton during late puberty
Authors: C Li, Y Chai, L Wang, B Gao, H Chen, P Gao, FQ Zhou, X Luo, JL Crane, B Yu, X Cao, M Wan
Nat Commun, 2017-11-03;8(1):1312.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Synergistic protection of bone vasculature and bone mass by desferrioxamine in osteoporotic mice
Authors: L Wang, P Jia, Y Shan, Y Hao, X Wang, Y Jiang, Y Yuan, Q Du, H Zhang, F Yang, W Zhang, M Sheng, Y Xu
Mol Med Rep, 2017-09-08;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Intimal hyperplasia induced by vascular intervention causes lipoprotein retention and accelerated atherosclerosis
Authors: S Kijani, AM Vázquez, M Levin, J Borén, P Fogelstran
Physiol Rep, 2017-07-01;5(14):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Cell-matrix signals specify bone endothelial cells during developmental osteogenesis
Authors: UH Langen, ME Pitulescu, JM Kim, R Enriquez-G, KK Sivaraj, AP Kusumbe, A Singh, J Di Russo, MG Bixel, B Zhou, L Sorokin, JM Vaquerizas, RH Adams
Nat. Cell Biol, 2017-02-20;19(3):189-201.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC -
Oral mucosa harbors a high frequency of endothelial cells - a novel postnatal cell source for angiogenic regeneration
Stem Cells Dev., 2016-12-22;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Blood flow controls bone vascular function and osteogenesis
Nat Commun, 2016-12-06;7(0):13601.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC -
Age-dependent modulation of vascular niches for haematopoietic stem cells
Authors: AP Kusumbe, SK Ramasamy, T Itkin, MA Mäe, UH Langen, C Betsholtz, T Lapidot, RH Adams
Nature, 2016-04-13;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Filter-Dense Multicolor Microscopy.
Authors: Kijani S, Yrlid U, Heyden M, Levin M, Boren J, Fogelstrand P
PLoS ONE, 2015-03-04;10(3):e0119499.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone.
Authors: Kusumbe A, Ramasamy S, Adams R
Nature, 2014-03-12;507(7492):323-8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC-Fr -
Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone.
Authors: Ramasamy S, Kusumbe A, Wang L, Adams R
Nature, 2014-03-12;507(7492):376-80.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC-Fr -
Vascular endothelial growth factor pathway promotes osseointegration and CD31hiEMCNhi endothelium expansion in a mouse tibial implant model: an animal study
Authors: G. Ji, R. Xu, Y. Niu, N. Li, L. Ivashkiv, M. P. G. Bostrom et al.
The Bone & Joint Journal
-
Longitudinal intravital imaging of the femoral bone marrow reveals plasticity within marrow vasculature
Authors: D Reismann, J Stefanowsk, R Günther, A Rakhymzhan, R Matthys, R Nützi, S Zehentmeie, K Schmidt-Bl, G Petkau, HD Chang, S Naundorf, Y Winter, F Melchers, G Duda, AE Hauser, RA Niesner
Nat Commun, 2017-12-18;8(1):2153.
-
Neuropilin 1 regulates bone marrow vascular regeneration and hematopoietic reconstitution
Authors: CM Termini, A Pang, T Fang, M Roos, VY Chang, Y Zhang, NJ Setiawan, L Signaevska, M Li, MM Kim, O Tabibi, PK Lin, JP Sasine, A Chatterjee, R Murali, HA Himburg, JP Chute
Nature Communications, 2021-11-30;12(1):6990.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: