Mouse RGM-B Antibody Summary
Gly49-Ser414
Accession # Q7TQ33
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
RGM-B in Mouse Brain. RGM-B was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse brain (trigeminal ganglia) using 1.7 µg/mL Sheep Anti-Mouse RGM-B Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3597) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Sheep HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS019) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
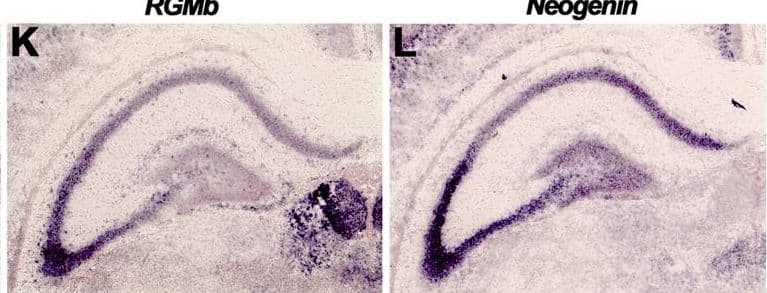
Detection of RGM-B by Immunohistochemistry Subregion-specific expression of RGMs and Neogenin in the hippocampus.In situ hybridization (A–C, J–L) and immunohistochemistry (D–I, M–O) on coronal mouse brain sections at E16.5 (A–I) and P5 (J–O). Sections in D–I and M–O are counterstained in blue with fluorescent Nissl. (A–F) RGMa mRNA and protein are expressed in the ventricular zone (VZ), dentate gyrus (DG) and cornu ammonis (CA) region. Strong expression of RGMb mRNA and protein is detected in the pial surface lining the hippocampal fissure (HF). Neogenin transcripts and protein are widely expressed in the developing hippocampus (Hip). (G–I) Immunostaining with isotype matched controls. (J–L) In situ hybridization at P5 shows strong but differential expression patterns of RGMa, RGMb and Neogenin in the CA pyramidal cell layers (Pyr). In addition, strong expression of Neogenin is detected in the granular layer (GC) of the DG. (M–O) Immunohistochemistry reveals expression of RGMa and weak expression of RGMb in the stratum lacunosum moleculare (SLM) and fimbria (FIM). Neogenin strongly labels different hippocampal layers. CX, cortex; Hb, habenula; HC, hippocampal commissure; PO, polymorph layer; SO, stratum oriens; SR, stratum radiatum; Th, thalamus. Scale bar A–C: 400 µm, D–F: 300 µm, G–I: 300 µm, J–L: 500 µm and M–O: 400 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23457482), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
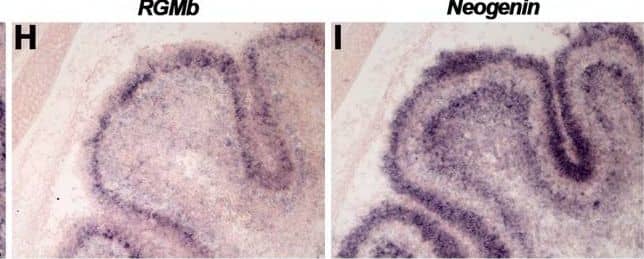
Detection of RGM-B by Immunohistochemistry Differential expression of RGMs and Neogenin in the cerebellum.In situ hybridization (A–C, G–I, M–O) and immunohistochemistry (D–F, J–L, P–R) on coronal mouse brain sections at E16.5 (A–F), P5 (G–L) and in the adult (M–R). (A–I, M–O) In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry reveals strong and broad expression of RGMa, RGMb and Neogenin in the cerebellum (CB). (J–L) Immunostaining shows expression of RGMa and Neogenin in all cerebellar layers at P5. RGMb is expressed in the internal granular layer (IGL), Purkinje cell layer (PCL) and external granular layer (EGL). (P–R) In the adult, RGMa, RGMb and Neogenin protein are expressed in Purkinje cells (PCs) and axons in the granular cell layer (GCL), PCL and molecular layer (ML). Neogenin strongly labels PC dendrites in the ML. DCN, deep cerebellar nuclei; WM, white matter; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bar A–C: 300 µm, D–F: 250 µm, G–I: 150 µm, J–L: 150 µm, M–O: 100 µm and P–R: 50 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23457482), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
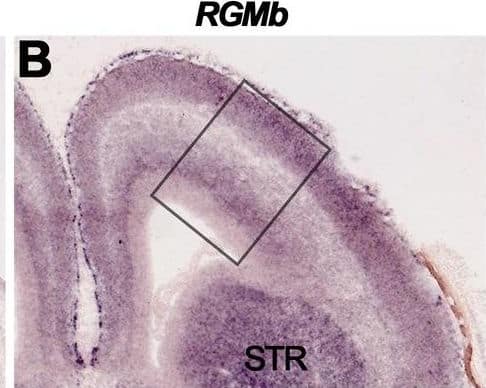
Detection of RGM-B by Immunohistochemistry RGMa, RGMb and Neogenin display partially complementary patterns of expression in the developing cortex and on cortical projections.In situ hybridization (A–C′) and immunohistochemistry (D–L) on coronal mouse brain sections at E16.5. Panels A′–C′ and D′–F′ show higher magnifications of the boxed areas in A–C and D–F, respectively. Sections in D–L are counterstained in blue with fluorescent Nissl. (A–C′) In situ hybridization reveals strong expression of RGMa and Neogenin, and moderate expression of RGMb, in the embryonic mouse cortex. Arrow in A indicates neurons of the lateral migratory stream. (D–I) RGMa and Neogenin protein are strongly expressed in the cortex and on various cortical axon projections. Strong staining for RGMb (E), and Neogenin (F), is detected in the corpus callosum (CC). The internal capsule (IC) stains strongly for RGMa (G). (J–L) Immunostaining with isotype-matched control antibodies did show significant staining. CP, cortical plate; FIM, fimbria; IZ, intermediate zone; LV, lateral ventricle; MZ, marginal zone; SP, subplate; STR, striatum; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bar A–C 400 µm, A′–C′ 200 µm, D–F 300 µm, D′–F′ 150 µm, G-I 300 µm and J-M 300 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23457482), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: RGM-B
RGM-B, also known as DRAGON, is a 40 kDa member of the repulsive guidance molecule (RGM) family of GPI-linked neuronal and muscle membrane proteins (1, 2). It is synthesized as a preproprotein that consists of a 48 amino acid (aa) signal sequence, a 367 aa mature region, and a 21 aa C-terminal prosegment (3). RGM-B contains two potential N-linked glycosylation sites and an abbreviated von Willebrand factor domain. Potential proteolytic cleavage within the VWF domain is supported by R&D Systems’ in house data (4). Within the region following the VWF domain, mouse RGM-B shares 49% and 43% aa sequence identity with RGM-A and RGM-C, respectively. It shares 90%, 79%, 92%, and 93% aa sequence identity with bovine, chicken, human, and rhesus macaque RGM-B, respectively. RGM-B is expressed in the developing and adult nervous system, particularly in the dorsal root ganglia and mantle layer of the spinal cord (3-5). In mouse, it shows a complementary, non-overlapping distribution with RGM-A (2-5). RGM-B is also expressed in fetal and adult enteric ganglia and in postnatal intestinal epithelium (6). RGM-B expression has been detected in neuronal cell bodies and proximal axonal segments (4) but is also present on the cell surface, where it interacts homophilically and mediates neuronal adhesion (3). RGM-B additionally functions as a BMP coreceptor. It directly binds BMP-2 and -4 but not other TGF-beta family proteins (7). RGM-B associates with BMP type I (ALK-2, -3, -6) and type II (Activin RIIA, Activin RIIB) receptors and enhances BMP signaling (7).
- Monnier, P.P. et al. (2002) Nature 419:392.
- Schmidtmer, J. and D. Engelkamp (2004) Gene Exp. Patterns 4:105.
- Samad, T.A. et al. (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:2027.
- Niederkofler, V. et al. (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:808.
- Oldekamp, J. et al. (2004) Gene Exp. Patterns 4:283.
- Metzger, M. et al. (2005) Dev. Dyn. 234:169.
- Samad, T.A. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:14122.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse RGM-B Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
5
Citations: Showing 1 - 5
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Dragon (RGMb) induces oxaliplatin resistance in colon cancer cells
Authors: Ying Shi, Xiao-Xiao Huang, Guo-Bin Chen, Ying Wang, Qiang Zhi, Yuan-Sheng Liu et al.
Oncotarget
-
Dragon (repulsive guidance molecule b, RGMb) is a novel gene that promotes colorectal cancer growth
Authors: Ying Shi, Guo-Bin Chen, Xiao-Xiao Huang, Chuan-Xing Xiao, Huan-Huan Wang, Ye-Sen Li et al.
Oncotarget
-
Simultaneous binding of Guidance Cues NET1 and RGM blocks extracellular NEO1 signaling
Authors: Ross A. Robinson, Samuel C. Griffiths, Lieke L. van de Haar, Tomas Malinauskas, Eljo Y. van Battum, Pavol Zelina et al.
Cell
-
RGMb is a novel binding partner for PD-L2 and its engagement with PD-L2 promotes respiratory tolerance.
Authors: Xiao, Yanping, Yu, Sanhong, Zhu, Baogong, Bedoret, Denis, Bu, Xia, Francisco, Loise M, Hua, Ping, Duke-Cohan, Jonathan, Umetsu, Dale T, Sharpe, Arlene H, DeKruyff, Rosemari, Freeman, Gordon J
J Exp Med, 2014-04-21;211(5):943-59.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Spatiotemporal Expression of Repulsive Guidance Molecules (RGMs) and Their Receptor Neogenin in the Mouse Brain
Authors: Dianne M. A. van den Heuvel, Anita J. C. G. M. Hellemons, R. Jeroen Pasterkamp
PLoS ONE
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsIsotype Controls
Reconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Mouse RGM-B Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse RGM-B Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse RGM-B Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image







