Recombinant Active Human Hepsin His-tag Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Arg45 to Leu417 (Asp161Glu, Arg162Lys) with a C-terminal 10-His tag
The proform was activated.
Analysis
Customers also Viewed
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
11416-SE
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris and NaCl. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM Tris, 0.05% Brij-35, pH 9.0
- Recombinant Active Human HepsinHis-tag (rhHepsin) (Catalog # 11416-SE)
- Substrate: Boc-QRR-AMC, 5 mM stock in DMSO
- Black 96-well Plate
- Plate Reader with Fluorescence Read Capability
- Dilute rhHepsin, active to 0.01 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute Substrate to 400 µM in Assay Buffer.
- Load in a plate 50 μL of 0.01 µg/mL rhHepsin, active, and start the reaction by adding 50 μL of 400 μM Substrate. Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 μL of 400 μM Substrate and 50 μL of Assay Buffer.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 380 nm and 460 nm (top read), respectively, in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
- Calculate specific activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Vmax* (RFU/min) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| amount of enzyme (µg) |
- rhHepsin, active: 0.0005 μg
- Substrate: 200 µM
Scientific Data
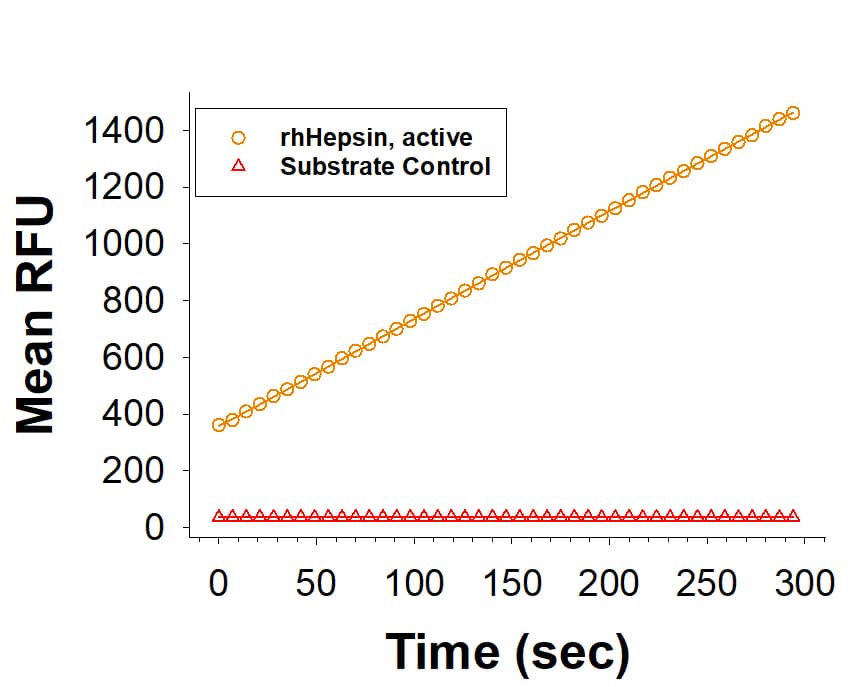 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Active Human Hepsin His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11416-SE) is measured by its ability to cleave tert-butoxycarbonyl-Gln-Arg-Arg-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (Boc-QRR-AMC).
Background: Hepsin
Hepsin, also known as TMPRSS1, is part of a family of type II transmembrane serine proteases (TTSPs) (1) that cleaves critical target proteins including Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), uromodulin (UMOD), uPA, and macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) at specific cleavage sites following basic residues with a strong preference for arginine residues (2-5). Hepsin is a 417 amino acid polypeptide that is activated to a two-chain disulfide-linked form. Hepsin, like other proteases in this family, contains an N-terminal cytoplasmic tail and transmembrane domain, and an extracellular stem region with an SRCR domain and C-terminal serine protease domain with a conserved activation site (1, 6). It is most highly expressed in liver, but is also present in many other tissues, notably lung, kidney, and skeletal muscle (7) and is found at high levels in several cancers including prostate, breast, and ovarian (2, 5, 8-10). In the liver, hepsin functions to regulate glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism through proteolytic conversion of pro-HGF to HGF, a potent ligand for Met signaling and dysregulation (11). Involvement in cancers has made hepsin a target of interest using either small molecule inhibitors or antibodies to neutralize their proteolytic activity, for example for prostate cancer and metastasis (12-14). Hepsin is also of interest for its potential role in osteoarthritis (15) and its ability to cleave surface proteins of respiratory viruses making it a therapeutic target for respiratory viral diseases (13). Recombinant Human Hepsin was expressed as a secreted, soluble protein lacking its cytosolic and transmembrane domains and activated.
- Li. S. et al. (2021) FEBS J. 288:5252.
- Herter, S. et al. (2005) Biochem. J. 390:125.
- Ganesan, R. et al. (2011) Mol. Cancer Res. 9:1175.
- Brunati, M. et al. (2015) Elife 4:e08887.
- Tanabe, L.M. and K. List (2017) FEBS J. 284:1421.
- Somoza, J.R. et al. (2003) Structure 11:1123.
- Tsuji, A. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:16948.
- Dhanasekaran, S.M. et al. (2001) Nature 412:822.
- Miao, J. et al. (2008) Int. J. Cancer 123:2041.
- Xing, P. et. al. (2011) J. Investig. Med. 59:803.
- Li, S. et al. (2020) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117:12359.
- Damalanka, V.C. et al. (2019) J. Med. Chem. 62:480.
- Murza, A. et al. (2020) Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 30:807.
- Wu, Q. and Parry, G. (2007) Front. Biosci. 12:5052.
- Wilkinson, D.J. et al. (2017) Sci. Rep. 7:16693.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Active Human Hepsin His-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Active Human Hepsin His-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Active Human Hepsin His-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image