Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein, CF
Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Phe26-Met208, with an N-terminal Met
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
1886-EL/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: IL-6
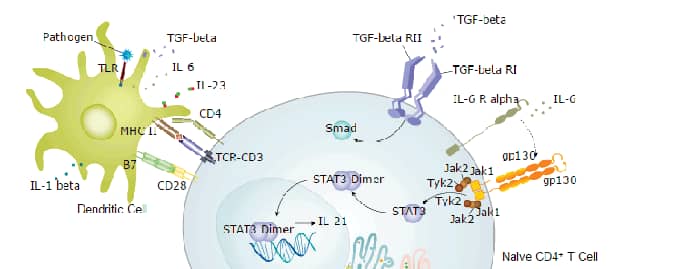
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic, alpha -helical, 22-28 kDa phosphorylated and variably glycosylated cytokine that plays important roles in the acute phase reaction, inflammation, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression (1-5). Mature equine IL-6 is 181 amino acids (aa) in length and shares 59%, 39%, and 40% aa sequence identity with human, mouse, and rat IL-6, respectively IL-6 (6). IL-6 induces signaling through a cell surface heterodimeric receptor complex composed of a ligand binding subunit (IL-6 R alpha) and a signal transducing subunit (gp130). IL-6 binds to IL-6 R alpha, triggering IL-6 R alpha association with gp130 and gp130 dimerization (7). gp130 is also a component of the receptors for CLC, CNTF, CT-1, IL-11, IL-27, LIF, and OSM (8). Soluble forms of IL-6 R alpha are generated by both alternative splicing and proteolytic cleavage (5). In a mechanism known as trans-signaling, complexes of soluble IL-6 and IL-6 R alpha elicit responses from gp130-expressing cells that lack cell surface IL-6 R alpha (5). Trans-signaling enables a wider range of cell types to respond to IL-6, as the expression of gp130 is ubiquitous, while that of IL-6 R alpha is predominantly restricted to hepatocytes, monocytes, and resting lymphocytes (2, 5). Soluble splice forms of gp130 block trans-signaling from IL-6/IL-6 R alpha but not from other cytokines that use gp130 as a co-receptor (5, 9). IL-6, along with TNF-alpha and IL-1, drives the acute inflammatory response and the transition from acute inflammation to either acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory disease (1-5). When dysregulated, it contributes to chronic inflammation in obesity, insulin resistance, inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, sepsis, and atherosclerosis (1, 2, 5). IL-6 can also function as an anti-inflammatory molecule, as in skeletal muscle where it is secreted in response to exercise (2). In addition, it enhances hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and the differentiation of Th17 cells, memory B cells, and plasma cells (1, 10).
- Mansell, A. and B.J. Jenkins (2013) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:249.
- Schuett, H. et al. (2009) Thromb. Haemost. 102:215.
- Erta, M. et al. (2012) Int. J. Biol. Sci. 8:1254.
- Garbers, C. et al. (2012) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 23:85.
- Mihara, M. et al. (2012) Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 122:143.
- Swiderski, C.E. et al. (2000) Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 77:213.
- Murakami, M. et al. (1993) Science 260:1808.
- Muller-Newen, G. (2003) Sci. STKE 2003:PE40.
- Mitsuyama, K. et al. (2006) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 143:125.
- Cerutti, A. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 160:2145.
Citations for Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Equine Arteritis Virus in Monocytic Cells Suppresses Differentiation and Function of Dendritic Cells
Authors: NA Moyo, D Westcott, R Simmonds, F Steinbach
Viruses, 2023-01-16;15(1):.
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Infection of monocytes with European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV-1) strain Lena is significantly enhanced by dexamethasone and IL-10
Authors: H Singleton, SP Graham, JP Frossard, KB Bodman-Smi, F Steinbach
Virology, 2018-03-02;0(0):.
Species: Porcine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Effects of priming with cytokines on intracellular survival and replication of Rhodococcus equi in equine macrophages
Authors: LJ Berghaus, S Giguère, AI Bordin, ND Cohen
Cytokine, 2017-12-12;102(0):7-11.
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Effects of high mobility group box protein-1, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-6 on cartilage matrix metabolism in three-dimensional equine chondrocyte cultures.
Authors: Ley C, Svala E, Nilton A, Lindahl A, Eloranta ML, Ekman S, Skioldebrand E
Connect. Tissue Res., 2010-11-30;52(4):290-300.
Species: Equine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Equine IL-6 Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image