Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF Summary
Learn more about Avi-tag Biotinylated Proteins- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein (AVI1968)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
| Human Siglec-2/CD22 (Asp20-Arg687) Accession # CAA42006.1 | IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI1968
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
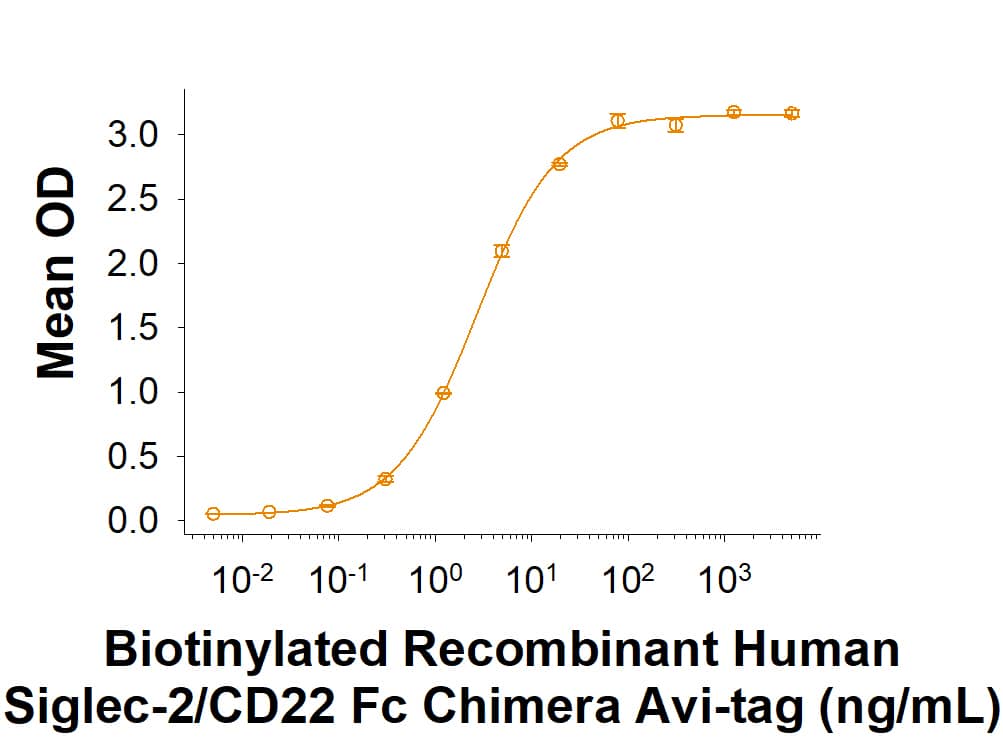 View Larger
View Larger
In a functional ELISA, Biotinylated Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI1968) binds to Human Siglec-2/CD22 Antibody (MAB19681) with an ED50 of 1.50-18.0 ng/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein (AVI1968) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 120-140 kDa and 240-280 kDa, respectively.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Siglec-2/CD22
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 2 (Siglec-2), also known as B-cell receptor CD22 or B-lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule (BL-CAM), is a I-type (Ig-type) lectin belonging to the sialoadhesin subclass of the immunoglobulin superfamily (1). Fourteen human and nine mouse Siglecs have been characterized and are divided into 2 families: CD33 related and evolutionarily conserved (2, 3). The extracellular domain (ECD) of Siglecs are characterized by an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, which mediates sialic acid binding, followed by varying numbers of Ig-like C2-type domains (1-3). The predominant form of human Siglec-2 contains a N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, six Ig-like C2-type domains, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail with six tyrosine residues and four immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) (1-3). A variant form of Siglec-2 missing two Ig-like C2-type domains along with a truncated cytoplasmic tail has also been identified (4). The mature ECD of human Siglec-2 shares 59% and 58% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat Siglec-2, respectively. Siglec-2 is an adhesion molecule that preferentially binds alpha 2,6- linked sialic acid on the same (cis) or adjacent (trans) cells (5). Besides its role as an adhesion molecule, Siglec-2 is a coreceptor that physically interacts with B-cell receptor (BCR), negatively regulating BCR signals by recruiting tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to its ITIMs. Phosphorylated Siglec-2 can also interact with other intracellular effector proteins such as Syk, PLC gamma, PI3 kinase and Grb-2, suggesting it may play a role in positive signaling (2). Another function of Siglec-2 is that it mediates the anti-phagocytic effect of alpha 2,6-linked sialic acid, and inhibition of Siglec-2 promotes the clearance of myelin debris, amyloid-beta oligomers and alpha -synuclein fibrils in vivo (6). Siglec-2 also plays a role in autoimmunity and has great potential for Siglec-2-based immunotherapeutics for the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (7). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated Recombinant Human Siglec-2 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Sato, S. et al. (1996) Immunity. 5:551.
- Crocker, P.R. and A. Varki (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:337.
- Macauley, M.S. et al. (2014) Nature Rev Imm. 14:653.
- Stamenkovic, I. and B. Seed (1990) Nature 345:74.
- Collins, B.E. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101:6104.
- Pluvinage, JV. et al. (2019) Nature. 568:7751.
- Clark, E.A. et al. (2018) Front Immunol. 9:2235.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human Siglec-2/CD22 Fc Avi-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

