Recombinant Zebrafish FGF-2 (bFGF), Animal-Free Protein
Recombinant Zebrafish FGF-2 (bFGF), Animal-Free Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Qk002
| Formulation | Lyophilized from Tris/NaCl/CyS/mannitol |
| Reconstitution | Resuspend in water at >100 µg/ml, prepare single use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped lyophilized at ambient temperture, on ice blocks or dry ice. Shipping at ambient temperture does not affect the bioactivity or stability of the protein. Upon reciept, store immediately at the conditions stated below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Store lyophilized protein between -20 and -80 °C until the date of expiry. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Zebrafish FGF2 activity is determined using the Promega serum response element luciferase reporter assay (*) in transfected HEK293T cells.Cells are treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of FGF2 for 6 hours. Firefly luciferase activity is measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. EC50 = 0.42 ng/ml (24.7 pM).*Promega pGL4.33[luc2P/SRE/Hygro] #E1340
 View Larger
View Larger
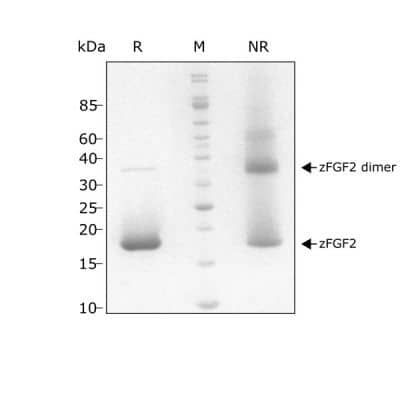
FGF2 migrates as major band at 17 kDa in non-reducing (-beta ME) conditions and upon reduction (+ beta ME). The higher molecular mass band at 35 kDa is a dimer that we always see in our highly purified zebrafish FGF2 protein, the presence of this does not affect biological activity. Purified recombinant protein (7 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+ beta -mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced conditions (NR) and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF
FGF basic (also known as FGF-2 and HBGF-2) is an 18-34 kDa, heparin-binding member of the FGF superfamily of molecules (1-3). Superfamily members are characterized by the presence of a centrally placed beta -trefoil structure. FGF acidic (FGF-1) and FGF basic (FGF-2) were the first two identified FGFs, and the designations acidic and basic refer to their relative isoelectric points. Human FGF basic is 288 amino acids (aa) in length. There are multiple start sites, four of which utilize atypical CUG codons, and one that initiates at an AUG start site (4-6). The four CUG start sites generate high molecular weight (HMW) FGF basic. There is a 34 kDa, 288 aa form, a 24 kDa, 210 aa form, a 22.5 kDa, 201 aa form, and a 22 kDa, 196 aa form. All are retained intracellularly, undergo extensive methylation, and possess one or more nuclear localization signals (NLS) (7-9). The AUG initiating form is 18 kDa and 155 aa in length. There is no signal sequence (ss). It is, however, secreted directly through the plasma membrane via a mechanism that appears to be dependent upon tertiary structure (10). In place of a ss, there is purportedly a 9 aa N-terminal prosegment that precedes a 146 aa mature segment (11). Early isolations of 18 kDa bovine FGF basic yielded 146 aa molecules, an effect attributed to the presence of acid proteases (12). The molecule contains a heparin-binding site (aa residues 128-144), and undergoes phosphorylation at Ser117 (13). There is also an ill-defined C-terminal NLS that may be more “functional” (or 3-dimensional) than structural (7). Human 146 aa FGF basic is 97% aa identical to mouse FGF basic (14).
- Sorenson, V. et al. (2006) BioEssays 28:504.
- Kardami, E. et al. (2004) Cardiovasc. Res. 63:458.
- Nugent, M.A. and R.V. Lozzo (2000) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 32:115.
- Abraham, J.A. et al. (1986) EMBO J. 5:2523.
- Prats, H. et al. (1989) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1836.
- Arnaud, E. et al. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:505.
- Foletti, A. et al. (2003) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60:2254.
- Arese, M. et al. (1999) Mol. Biol. Cell 10:1429.
- Pintucci, G. et al. (1996) Mol. Biol. Cell 7:1249.
- Nickel, W. (2005) Traffic 6:607.
- SwissProt # P09038.
- Klagsbrun, M. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:1839.
- Bailly, K. et al. (2000) FASEB J. 14:333.
- Hebert, J.M. et al. (1990) Dev. Biol. 138:454.
Product Specific Notices
The above product was manufactured, tested and released by R&D System's contract manufacturer, Qkine Ltd, at 1 Murdoch House, Cambridge, UK, CB5 8HW. The product is for research use only and not for the diagnostic or theraputic use.FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Zebrafish FGF-2 (bFGF), Animal-Free Protein
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Zebrafish FGF-2 (bFGF), Animal-Free Protein and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Zebrafish FGF-2 (bFGF), Animal-Free Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image



