Follicular Helper T Cell Markers
Click on one of the helper T cell subsets shown in the buttons below to see the markers that are most commonly used to identify that cell type.
Overview
Follicular helper T (Tfh) cells are a subset of CD4+ helper T cells that is involved in the regulation and development of antigen-specific B cell immunity. Tfh cells are localized to the B cell follicle of secondary lymphoid organs, where they interact with antigen-specific, germinal center B cells. Through these interactions, Tfh cells provide signals that are essential for the survival and proliferation of germinal center B cells and selectively promote the propagation of B cells with the highest antigen affinity. In mice, Tfh cells develop from activated, naïve CD4+ T cells in the presence of IL-6, IL-21, and ICOS ligand, while in humans, IL-21, IL-12, IL-23, TGF-beta, and ICOS ligand are required for their development. Both human and mice Tfh cells are most commonly identified as cells that express the cell surface markers CD4, CXCR5, ICOS, and PD-1, and secrete CXCL13, IL-4, and IL-21. Additionally, Tfh cells express high levels of IL-6 R alpha, and the transcription factors, STAT3 and Bcl-6, the latter of which is the master transcriptional regulator required for Tfh cell development. Bcl-6 is a transcriptional repressor involved in indirectly regulating the early expression of CXCR5, migration of the early Tfh cell to the B cell follicle, Tfh cell differentiation, and germinal center formation. Furthermore, Bcl-6 suppresses the expression of factors that promote the differentiation of other CD4+ T helper cell subsets.
Data Examples
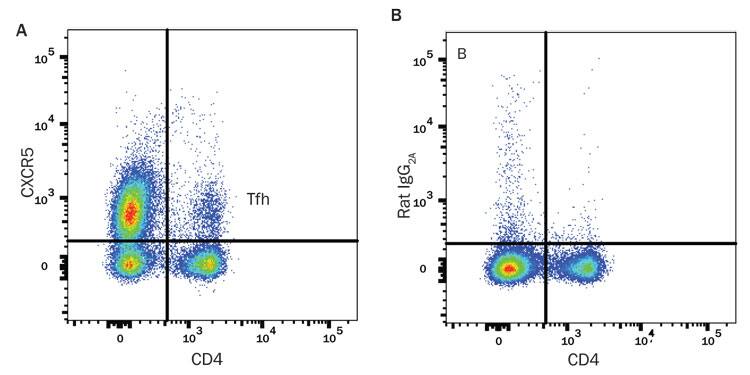
Detection of Follicular Helper T (Tfh) Cells in Mouse Splenocytes. (A) Immunized Balb/c mouse splenocytes were stained an Alexa Fluor® 405-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB554V) and either (A) an APC-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse CXCR5 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB6198A) or (B) an APC-conjugated Rat IgG2A Isotype Control (R&D Systems, Catalog # IC006A).