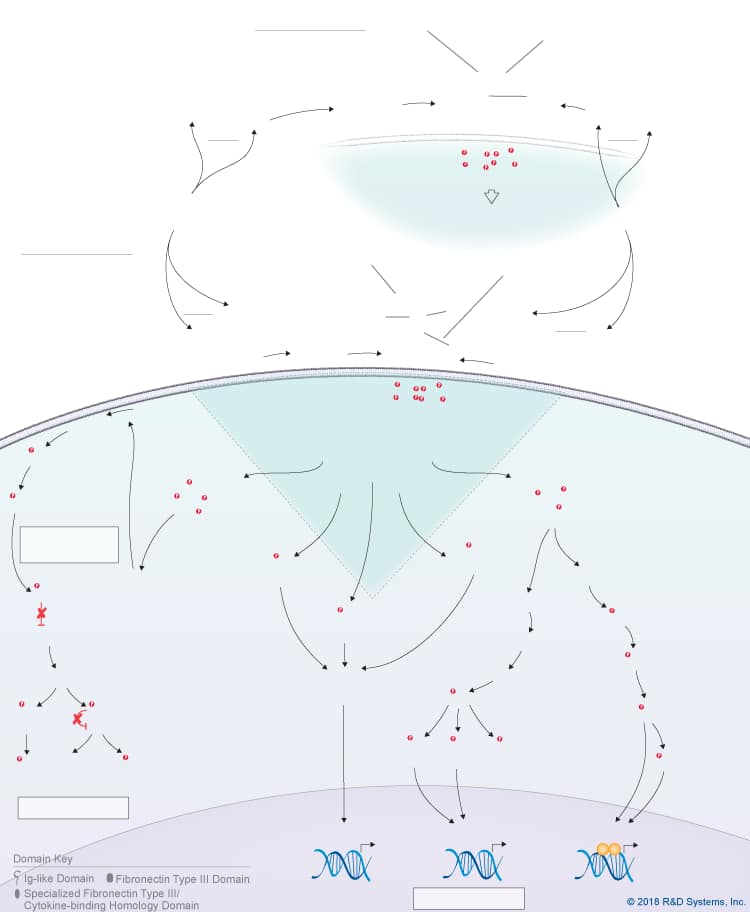
CNTF Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
sIL-6 R alpha
sIL-6 R alpha
sIL-6 R alpha
sIL-6 R alpha
IL-6 R alpha
IL-6 R alpha
IL-6 R alpha
IL-6 R alpha
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Unknown)
(Unknown)
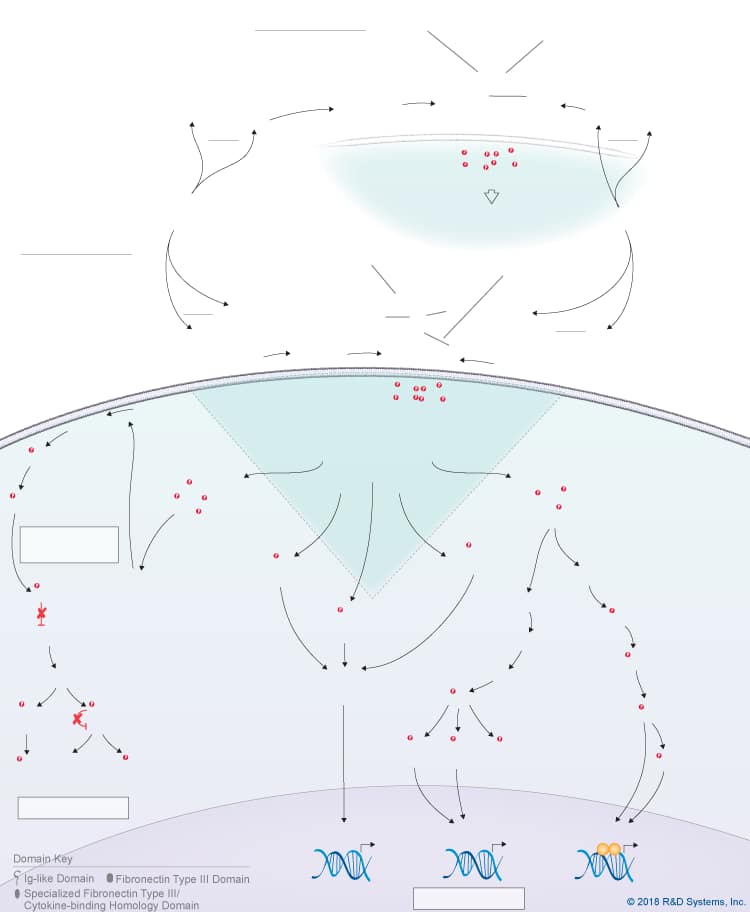
Overview of Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) Signaling Pathways
Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, IL-31, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Oncostatin M (OSM), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), and Neuropoietin. CNTF is a four-helix bundle cytokine that is expressed by Schwann cells, astrocytes, and T cells. It was identified as a trophic factor for embryonic chick ciliary neurons and subsequent studies have shown that it is a survival factor for dorsal root ganglion sensory neurons, sympathetic ganglion neurons, embryonic motor neurons, and hippocampal neurons. Additionally, CNTF has been shown to promote the survival and maturation of oligodendrocytes, to induce astrocyte differentiation of glial progenitors, to have neuroprotective effects following nervous system injury and in demyelinating neurological diseases, as well as protective and regenerative effects on denervated and intact skeletal muscle, and immunomodulatory effects. CNTF knockout mice have a mild phenotype characterized by the progressive loss of motor neurons, reduced bone length, and reduced muscular strength in adult mice, but no obvious developmental defects, suggesting that unlike CLC and CLF-1, CNTF is not required for normal physiological development.
Due to its lack of a signal peptide, CNTF is thought to be a cytoplasmic molecule that is released by damaged cells. Upon its release, CNTF binds to either a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored, non-signaling CNTF R alpha receptor subunit or a non-signaling IL-6 R alpha receptor subunit, which then recruits the signal-transducing receptor subunits, LIF R and gp130, to form a tripartite receptor complex. Assembly of the LIF R:gp130 heterodimer is enhanced by Sortilin, a member of the Vps10p domain family of type I transmembrane receptors, which binds to CNTF, CLC/CLF-1, and Neuropoietin with high affinity. In addition to the CNTF classic signaling pathway which occurs in cells expressing membrane-bound CNTF R alpha or IL-6 R alpha, LIF R, and gp130, CNTF can also initiate trans-signaling in cells expressing LIF R and gp130 by binding to a soluble form of CNTF R alpha or a soluble form of IL-6 R alpha. Soluble CNTF R alpha is generated following its release from the cell surface by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, while soluble IL-6 R alpha can be generated by either alternative splicing or proteolytic cleavage. CNTF bound to the soluble forms of CNTF R alpha or IL-6 R alpha promotes the heterodimerization of LIF R and gp130, allowing a wider range of cells to respond to CNTF. Formation of either the classic or trans-signaling CNTF receptor complex triggers the activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways including the Jak-STAT pathway, the Ras-MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt pathway, and the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways, which mediate various biological effects in different cell types.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary CNTF-Expressing Cells | Primary Biological Effects of CNTF |
| Astrocytes | Supports the survival of a variety of neuronal cell types including sensory, sympathetic, ciliary, and motor neurons |
| Schwann cells | Promotes the differentiation of glial progenitors into astrocytes |
| T cells | Promotes the maturation and survival of oligodendrocytes |
| Protects neuronal and glial cells following nervous system injury | |
| Promotes the viability of muscle progenitor cells; Has protective and regenerative neuromuscular effects | |
| Regulates muscle strength in aging | |
| Regulates the production of IFN-gamma by CD4+ T cells | |
| Induces the acute phase response in the liver |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway