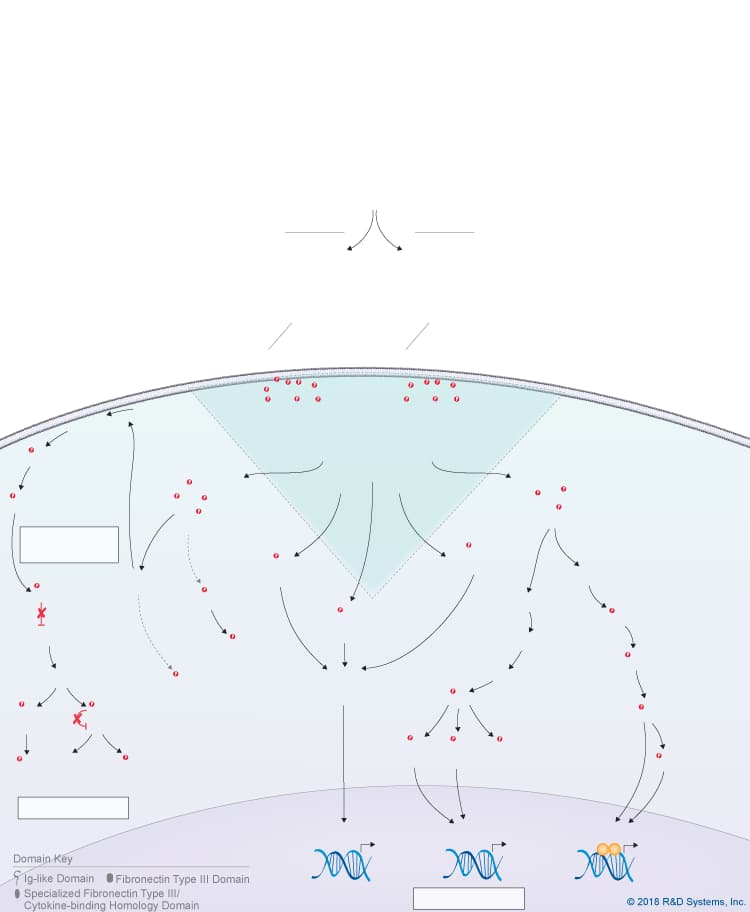
Oncostatin M Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Unknown)
(Unknown)

Overview of Oncostatin M (OSM) Signaling Pathways
Oncostatin M (OSM) is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, IL-31, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), and Neuropoietin. OSM is produced primarily by activated monocytes and macrophages, activated T cells, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and osteoblasts. Like other IL-6 family cytokines, OSM is a long chain four alpha-helix bundle cytokine with up-up-down-down topology, but it is unique in that it can signal through two different receptor complexes. The type I OSM receptor complex consists of LIF R and gp130, while the type II OSM receptor complex consists of OSM R and gp130. OSM initially binds with low affinity to gp130 and then recruits either LIF R or OSM R. LIF R, OSM R, and gp130 all associate with members of the Jak family of tyrosine kinases through their cytoplasmic domains, leading to the phosphorylation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of STAT family proteins, predominantly STAT3, STAT5, and STAT1. In addition, OSM signaling triggers activation of the Ras-MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt pathway, the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways, and PKC delta.
OSM was originally discovered as a cytokine capable of inhibiting the growth of melanoma cells and has subsequently been found to have a wide range of effects on different cell types. It has been shown to regulate the formation and maintenance of the bone marrow niche required for hematopoiesis, to suppress adipocyte differentiation and promote osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells, and to regulate inflammatory responses. OSM is capable of both promoting and inhibiting inflammation depending on the target cell and the other cytokines present in the microenvironment. In the liver, OSM was found to regulate the acute phase response, as well as hepatocyte proliferation and tissue remodeling during liver regeneration. Additionally, OSM has been shown to regulate the development of the central nervous system, induce the dedifferentiation of cardiomyocytes, regulate the production of other cytokines and growth factors by endothelial cells, and stimulate angiogenesis.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary OSM-Expressing Cells | Primary Biological Effects of OSM |
| Activated monocytes/macrophages | Regulates the formation and maintenance of the hematopoietic microenvironment |
| Activated T cells | Regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation; Suppresses adipocyte differentiation |
| Dendritic cells | Regulates hepatocyte proliferation and tissue remodeling during liver regeneration; Regulates the acute phase response |
| Neutrophils | Induces cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation |
| Osteoblasts | Regulates bone formation and resorption |
| Neuroregulatory | |
| Regulates the development of nociceptive neurons in the dorsal root ganglia | |
| Regulates inflammatory responses | |
| Regulates the production of other cytokines and growth factors by endothelial cells; Stimulates angiogenesis |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway