MAPK Signaling Pathway: Mitogen Stimulation Pathway
Click on one of the boxes below to view other MAPK signaling pathways.
ErbB2/Her2
ErbB3/Her3
ErbB4/Her4
FGF R1-4
FGF R1 alpha
FGF R1 beta
FGF R2
FGF R2 alpha
FGF R2 beta
FGF R3
FGF R4
FGF R5/FGFRL1
HGF R/c-MET
IGF-I R
IGF-II R
Insulin and Insulin-like Receptor Inhibitors
Insulin R/CD220
INSRR
PDGF R alpha
PDGF R beta
Tie-1
Tie-2
TrkA
TrkB
TrkC
VEGF R1, R2, R3
VEGF R1/Flt-1
VEGF R2/KDR/Flk-1
VEGF R3/Flt-4
All RTK Products
ErbB2/Her2
ErbB3/Her3
ErbB4/Her4
FGF R1-4
FGF R1 alpha
FGF R1 beta
FGF R2
FGF R2 alpha
FGF R2 beta
FGF R3
FGF R4
FGF R5/FGFRL1
HGF R/c-MET
IGF-I R
IGF-II R
Insulin and Insulin-like Receptor Inhibitors
Insulin R/CD220
INSRR
PDGF R alpha
PDGF R beta
Tie-1
Tie-2
TrkA
TrkB
TrkC
VEGF R1, R2, R3
VEGF R1/Flt-1
VEGF R2/KDR/Flk-1
VEGF R3/Flt-4
All RTK Products
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
/SEF
/SEF
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Protein
Synthesis
Protein
Synthesis
ErbB2/Her2
ErbB3/Her3
ErbB4/Her4
FGF R1-4
FGF R1 alpha
FGF R1 beta
FGF R2
FGF R2 alpha
FGF R2 beta
FGF R3
FGF R4
FGF R5/FGFRL1
HGF R/c-MET
IGF-I R
IGF-II R
Insulin and Insulin-like Receptor Inhibitors
Insulin R/CD220
INSRR
PDGF R alpha
PDGF R beta
Tie-1
Tie-2
TrkA
TrkB
TrkC
VEGF R1, R2, R3
VEGF R1/Flt-1
VEGF R2/KDR/Flk-1
VEGF R3/Flt-4
All RTK Products
ErbB2/Her2
ErbB3/Her3
ErbB4/Her4
FGF R1-4
FGF R1 alpha
FGF R1 beta
FGF R2
FGF R2 alpha
FGF R2 beta
FGF R3
FGF R4
FGF R5/FGFRL1
HGF R/c-MET
IGF-I R
IGF-II R
Insulin and Insulin-like Receptor Inhibitors
Insulin R/CD220
INSRR
PDGF R alpha
PDGF R beta
Tie-1
Tie-2
TrkA
TrkB
TrkC
VEGF R1, R2, R3
VEGF R1/Flt-1
VEGF R2/KDR/Flk-1
VEGF R3/Flt-4
All RTK Products
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Growth and
Proliferation
Growth and
Proliferation
Phospholipids
Phospholipids
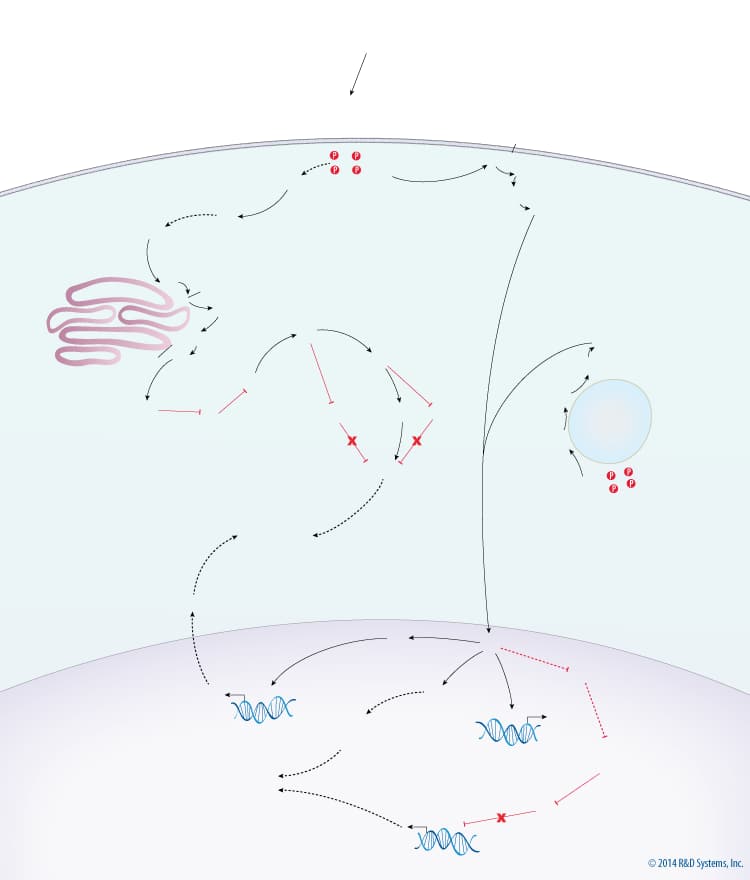
Overview of Mitogenic MAPK Signaling
Stimulation of the MAPK signaling pathway by mitogens ultimately leads to cellular growth and proliferation. One mechanism by which mitogens promote MAPK signaling is through the activation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Activated RTKs promote the phosphorylation and activation of ERK map kinase through the Ras/Raf/MEK signaling cascade. The activation of ERK by RTKs can occur at the plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, and endosomes via scaffold proteins, with different scaffold proteins being required depending on the cellular localization of Ras activation. More specifically, ERK activation requires KSR at the plasma membrane, MP1 at endosomes, and IL-17 RD/Sef at the Golgi. Once activated, ERK phosphorylates cytoplasmic targets and also translocates to the nucleus and phosphorylates nuclear targets. ERK activated at the Golgi is sequestered in the cytoplasm by Sef and can therefore only phosphorylate cytoplasmic targets. Alternatively, ERK activated at the plasma membrane and at endosomes is capable of translocating to the nucleus and can thus activate both cytoplasmic and nuclear targets. In the cytoplasm, ERK activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RSK), which indirectly activates TOR signaling by inhibiting TSC2. TOR signaling then promotes protein synthesis via activation of S6 kinase (S6K) and inhibition of 4EBP. ERK activity in the nucleus promotes growth and proliferation in multiple ways. ERK stimulates the synthesis of ribosomal (r)RNA via indirect activation of RNA Polymerase I. The synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides, the building blocks for RNA, DNA, and phospholipids, is increased through ERK-dependent activation of CAD, the enzyme that performs the rate limiting step of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis. ERK also indirectly activates E2F transcription factors, which upregulate many genes required for cell cycle entry and DNA synthesis, via activation of Myc.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway

