MAPK Signaling: Inflammatory Cytokines Pathway
Click on one of the boxes below to view other MAPK signaling pathways.
APRIL/TNFSF13
BAFF/BLyS/TNFSF13B
CD27 Ligand/TNFSF7
CD30 Ligand/TNFSF8
CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5
EDA/Ectodysplasin
EDA-A1/Ectodysplasin A1
EDA-A2/Ectodysplasin A2
Fas Ligand/TNFSF6
GITR Ligand/TNFSF18
LIGHT/TNFSF14
Lymphotoxin
Lymphotoxin beta/TNFSF3
OX40 Ligand/TNFSF4
TL1A/TNFSF15
TNF-alpha
Lymphotoxin-alpha/TNF-beta
TRAIL/TNFSF10
TRANCE/TNFSF11/RANK L
TWEAK/TNFSF12
APRIL/TNFSF13
BAFF/BLyS/TNFSF13B
CD27 Ligand/TNFSF7
CD30 Ligand/TNFSF8
CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5
EDA/Ectodysplasin
EDA-A1/Ectodysplasin A1
EDA-A2/Ectodysplasin A2
Fas Ligand/TNFSF6
GITR Ligand/TNFSF18
LIGHT/TNFSF14
Lymphotoxin
Lymphotoxin beta/TNFSF3
OX40 Ligand/TNFSF4
TL1A/TNFSF15
TNF-alpha
Lymphotoxin-alpha/TNF-beta
TRAIL/TNFSF10
TRANCE/TNFSF11/RANK L
TWEAK/TNFSF12
BAFF R/TNFRSF13C
BCMA/TNFRSF17
CD27/TNFRSF7
CD30/TNFRSF8
CD40/TNFRSF5
DcR3/TNFRSF6B
DcTRAIL R1/TNFRSF23
DcTRAIL R2/TNFRSF22
DR3/TNFRSF25
DR6/TNFRSF21
EDA2R/TNFRSF27/XEDAR
Fas/TNFRSF6/CD95
GITR/TNFRSF18
HVEM/TNFRSF14
Lymphotoxin beta R/TNFRSF3
NGF R/TNFRSF16
Osteoprotegerin/TNFRSF11B
OX40/TNFRSF4
RANK/TNFRSF11A
RELT/TNFRSF19L
TACI/TNFRSF13B
TNFRH3/TNFRSF26
TNF RI/TNFRSF1A
TNF RII/TNFRSF1B
TRAIL R1/TNFRSF10A
TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B
TRAIL R3/TNFRSF10C
TRAIL R4/TNFRSF10D
TROY/TNFRSF19
TWEAK R/TNFRSF12
BAFF R/TNFRSF13C
BCMA/TNFRSF17
CD27/TNFRSF7
CD30/TNFRSF8
CD40/TNFRSF5
DcR3/TNFRSF6B
DcTRAIL R1/TNFRSF23
DcTRAIL R2/TNFRSF22
DR3/TNFRSF25
DR6/TNFRSF21
EDA2R/TNFRSF27/XEDAR
Fas/TNFRSF6/CD95
GITR/TNFRSF18
HVEM/TNFRSF14
Lymphotoxin beta R/TNFRSF3
NGF R/TNFRSF16
Osteoprotegerin/TNFRSF11B
OX40/TNFRSF4
RANK/TNFRSF11A
RELT/TNFRSF19L
TACI/TNFRSF13B
TNFRH3/TNFRSF26
TNF RI/TNFRSF1A
TNF RII/TNFRSF1B
TRAIL R1/TNFRSF10A
TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B
TRAIL R3/TNFRSF10C
TRAIL R4/TNFRSF10D
TROY/TNFRSF19
TWEAK R/TNFRSF12
Proteasome
Proteasome
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Inflammation
Inflammation
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Gene mRNA
Gene mRNA
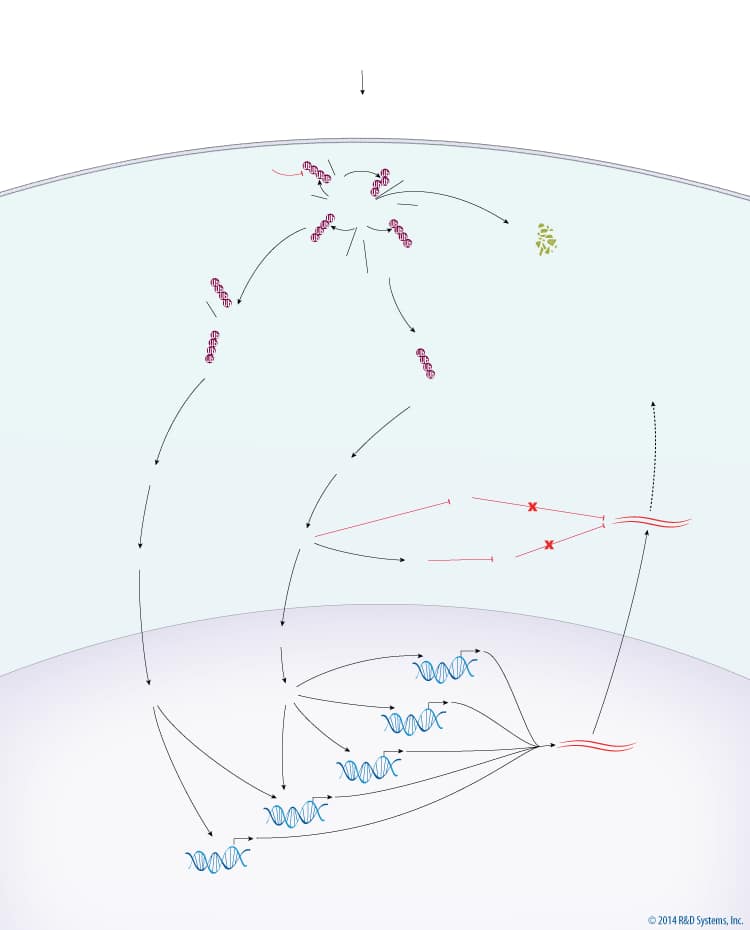
Overview of Inflammatory Cytokine MAPK Signaling
The major output of MAPK signaling downstream of inflammatory cytokines is a proinflammatory response. TNF Receptor (TNFR) activation by TNF superfamily ligands leads to recruitment of TRAF-2, TRAF-3, TRAF-6, and IKK gamma to the TNFR complex. TRAF-2 and TRAF-6 are subsequently auto-polyubiquitinated with Lys63-linked chains in a Ubc13-Uev1a-dependent manner. Ubiquitinated TRAF-2 and TRAF-6 recruit MEKK1 and TAK1, respectively, with TAK1 being recruited via TAB2. TRAF-3 inhibits the activation of MEKK1 and TAK1 at the TNFR complex. cIAP1/2 is then recruited to the TNFR complex and polyubiquitinated with Lys63-linked chains by the Ubc13-Uev1a complex. Ubiquitinated cIAP1/2 then promotes the polyubiquitination of TRAF-3 with Lys48-linked chains, which leads to the degradation of TRAF-3 via the 26S Proteasome. Degradation of TRAF-3 releases the MEKK1 and TAK1 complexes, leading to the activation of MEKK1 and TAK1. MEKK1 and TAK1 subsequently phosphorylate and activate MKK4/7 and MKK3/6, which then phosphorylate JNK and p38, respectively. Activated JNK and p38 translocate to the nucleus where they activate multiple transcription factors, via MSK1/2 in the case of p38, including AP-1, ATF2, CREB, ATF1, and NF-kappa B. The activation of these transcription factors results in the transcription of genes encoding proinflammatory cytokines. In the cytoplasm, the translation of proinflammatory gene mRNA is inhibited by KSRP and TTP, both of which bind to and promote the degradation of mRNA. p38 directly inhibits KSRP and indirectly inhibits TTP, via MAPKAPK2, to promote inflammation via the stabilization and translation of proinflammatory gene mRNA.
