Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 Antibody Summary
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Applications
Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
CCL2/JE/MCP‑1 in Human Crohn's Disease Intestine. CCL2/JE/MCP-1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human Crohn's disease intestine using Mouse Anti-Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB679) at 15 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membranes and cytoplasm. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Chemotaxis Induced by CCL2/MCP-1 and Neutralization by Human CCL2/MCP‑1 Antibody. Recombinant Human CCL2/MCP-1 (279-MC) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CCR2A in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (AR002). Chemotaxis elicited by Recombinant Human CCL2/MCP-1 (75 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Human CCL2/MCP-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB679). The ND50 is typically 0.5-2.0 µg/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by Immunohistochemistry Expression patterns of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in healthy individuals and breast cancer patients. Representative examples of the expression of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in the different groups of patients included in the study, in biopsies obtained at the time of diagnosis. (a1-a4) Patients diagnosed with benign breast disorders. The pictures demonstrate the lack of staining of the four factors in the normal breast epithelial cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (b1-b4) DCIS patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the malignant lesions, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (c1-c4) IDC-no-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (d1-d4) IDC-with-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (a1, b1, c1, d1) CCL2 staining; (a2, b2, c2, d2) CCL5 staining; (a3, b3, c3, d3) TNF alpha staining; (a4, b4, c4, d4) IL-1 beta staining. The expression of the proteins was determined by IHC using specific antibodies, whose specificity in IHC was verified. The values of photo magnification are indicated in the left bottom corner of each of the pictures. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21486440), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by Immunohistochemistry Expression patterns of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in healthy individuals and breast cancer patients. Representative examples of the expression of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in the different groups of patients included in the study, in biopsies obtained at the time of diagnosis. (a1-a4) Patients diagnosed with benign breast disorders. The pictures demonstrate the lack of staining of the four factors in the normal breast epithelial cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (b1-b4) DCIS patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the malignant lesions, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (c1-c4) IDC-no-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (d1-d4) IDC-with-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (a1, b1, c1, d1) CCL2 staining; (a2, b2, c2, d2) CCL5 staining; (a3, b3, c3, d3) TNF alpha staining; (a4, b4, c4, d4) IL-1 beta staining. The expression of the proteins was determined by IHC using specific antibodies, whose specificity in IHC was verified. The values of photo magnification are indicated in the left bottom corner of each of the pictures. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21486440), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by Immunohistochemistry Expression patterns of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in healthy individuals and breast cancer patients. Representative examples of the expression of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in the different groups of patients included in the study, in biopsies obtained at the time of diagnosis. (a1-a4) Patients diagnosed with benign breast disorders. The pictures demonstrate the lack of staining of the four factors in the normal breast epithelial cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (b1-b4) DCIS patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the malignant lesions, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (c1-c4) IDC-no-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (d1-d4) IDC-with-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (a1, b1, c1, d1) CCL2 staining; (a2, b2, c2, d2) CCL5 staining; (a3, b3, c3, d3) TNF alpha staining; (a4, b4, c4, d4) IL-1 beta staining. The expression of the proteins was determined by IHC using specific antibodies, whose specificity in IHC was verified. The values of photo magnification are indicated in the left bottom corner of each of the pictures. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21486440), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by Immunohistochemistry Expression patterns of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in healthy individuals and breast cancer patients. Representative examples of the expression of CCL2, CCL5, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta in the different groups of patients included in the study, in biopsies obtained at the time of diagnosis. (a1-a4) Patients diagnosed with benign breast disorders. The pictures demonstrate the lack of staining of the four factors in the normal breast epithelial cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (b1-b4) DCIS patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the malignant lesions, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (c1-c4) IDC-no-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (d1-d4) IDC-with-relapse patients. The pictures demonstrate positive staining of the four factors in the tumor cells, as denoted in the majority of patients included in this group. (a1, b1, c1, d1) CCL2 staining; (a2, b2, c2, d2) CCL5 staining; (a3, b3, c3, d3) TNF alpha staining; (a4, b4, c4, d4) IL-1 beta staining. The expression of the proteins was determined by IHC using specific antibodies, whose specificity in IHC was verified. The values of photo magnification are indicated in the left bottom corner of each of the pictures. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21486440), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by ELISA Induction of CCL2 and CLXL8 in TNF alpha -stimulated MSCs is not mediated via the AP-1 pathway. (A) Human BM-derived MSCs were stimulated by TNF-alpha (50 ng/ml) for 5 and 10 minutes. Control cells were treated by the vehicle of TNF-alpha. c-Jun levels and phosphorylation were determined by western blot (WB) analyses. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as loading control. (B) Human BM-derived MSCs were transiently transfected by small interfering RNA (siRNA) to c-Jun or by control siRNA. (B1) c-Jun expression was determined by WB analyses. beta -Tubulin was used as loading control. (B2) Following siRNA transfection, the cells were stimulated by TNF-alpha (25 ng/ml; in this part of the study we used a suboptimal concentration of TNF-alpha in order to facilitate detection of inhibitory effects) for 24 hours. Expression levels of CCL2 and CXCL8 in the supernatants of the cells were determined by ELISA, in the linear range of absorbance. #siRNA to c-Jun has yielded minor increases or reductions in CCL2 and CXCL8 secretion in different experiments (see Results and discussion), and thus overall there was no significant effect on CCL2 and CXCL8 secretion. In all panels, the findings are representatives of n = 3 independent experiments that have shown similar results. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-015-0080-7), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by Western Blot NF-kappa B is essential in mediating TNF-alpha -induced release of chemokines by MSCs. (A) Human BM-derived MSCs were stimulated by TNF-alpha (50 ng/ml) for 15 minutes. The levels of I kappa B alpha (the negative regulator of the NF-kappa B pathway) were determined by WB analyses. GAPDH was used as a loading control throughout. (B) CAFs were generated by culturing MSCs with Tumor CM from MDA-MB-231 (MDA) or MCF-7 breast tumor cells over a prolonged period of time (~30 days). TNF-alpha (50 ng/ml) was added for the last 24 hours to MSCs + Tumor CM cells and I kappa B alpha levels were determined by WB analyses. (C) CAF #1 cells were stimulated for 48 hours by TNF-alpha (50 ng/ml). I kappa B alpha levels were determined by WB analyses. (D) Human BM-derived MSCs were stimulated with TNF-alpha (50 ng/ml) for 10 minutes. p65 phosphorylation was determined by WB analyses. (E) Human BM-derived MSCs were transiently transfected by siRNA to p65 or by control siRNA. (E1) p65 expression was determined by WB analyses. (E2) Following siRNA transfection, the cells were stimulated by TNF-alpha (25 ng/ml; a suboptimal concentration of TNF-alpha in order to facilitate detection of inhibitory effects) for 48 hours. Expression of CCL2 and CXCL8 in the supernatants of the cells was determined by ELISA, in the linear range of absorbance. In all panels, the findings are representatives of n = 3 independent experiments that have shown similar results. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-015-0080-7), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by ELISA Microparticle composition influences inflammatory cytokine production from activated monocytes.THP-1 cells (A) or CD14 sorted blood monocytes (B) were treated with control microparticles (grey bars) or PPAR gamma -overexpressing microparticles (black bars) or no microparticles (white bars) for 4 hours before activation with LPS or PAM3CSK4 for 24 hours. Supernatants were collected and pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-8 (top), MCP-1 (bottom) were measured by ELISA. Dotted line represents baseline cytokine production from unactivated cells with no microparticle exposure. Mean values with standard errors represent one of at least 3 experiments. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison post test was performed to determine statistical significance. * indicates (p<0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25426628), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 by ELISA Microparticle composition influences inflammatory cytokine production from activated monocytes.THP-1 cells (A) or CD14 sorted blood monocytes (B) were treated with control microparticles (grey bars) or PPAR gamma -overexpressing microparticles (black bars) or no microparticles (white bars) for 4 hours before activation with LPS or PAM3CSK4 for 24 hours. Supernatants were collected and pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-8 (top), MCP-1 (bottom) were measured by ELISA. Dotted line represents baseline cytokine production from unactivated cells with no microparticle exposure. Mean values with standard errors represent one of at least 3 experiments. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison post test was performed to determine statistical significance. * indicates (p<0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25426628), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
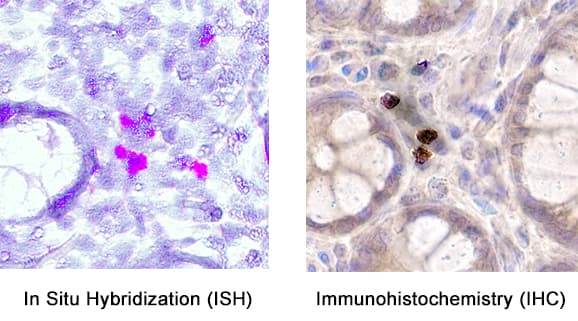
Detection of CCL2/JE/MCP‑1 in human Crohn's disease. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections of human Crohn’s Disease were probed for CCL2 mRNA (ACD RNAScope Probe, catalog # 423811; Fast Red chromogen, ACD catalog # 322360). Adjacent tissue section was processed for immunohistochemistry using mouse anti-human CCL2 monoclonal antibody (R&D Systems MAB679) at 20ug/mL with 1 hour incubation at room temperature followed by incubation with anti-mouse IgG VisUCyte HRP Polymer Antibody (VC001) and DAB chromogen (yellow-brown). Tissue was counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and membrane.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CCL2/JE/MCP-1
CCL2 is a beta -chemokine that is also known as monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1). It is produced by a variety of cell types and is chemotactic for monocytes.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
52
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Cervico-Vaginal Inflammatory Cytokine and Chemokine Responses to Two Different SIV Immunogens
Authors: Nikki P. L. Toledo, Hongzhao Li, Robert W. Omange, Tamara G. Dacoba, Jose Crecente-Campo, Dane Schalk et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Impact of heat therapy on recovery after eccentric exercise in humans
Authors: Kyoungrae Kim, Shihuan Kuang, Qifan Song, Timothy P. Gavin, Bruno T. Roseguini
Journal of Applied Physiology
-
Recruitment of IL‐1 beta ‐producing intermediate monocytes enhanced by C5a contributes to the development of malignant pleural effusion
Authors: Lisha Luo, Shuanglinzi Deng, Wei Tang, Xinyue Hu, Feifei Yin, Huan Ge et al.
Thoracic Cancer
-
Migration arrest and transendothelial trafficking of human pathogenic-like Th17 cells are mediated by differentially positioned chemokines
Authors: Parween, F;Singh, SP;Kathuria, N;Zhang, HH;Ashida, S;Otaizo-Carrasquero, FA;Shamsaddini, A;Gardina, PJ;Ganesan, S;Kabat, J;Lorenzi, HA;Riley, DJ;Myers, TG;Pittaluga, S;Bielekova, B;Farber, JM;
Nature communications
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 cardiovascular symptoms are associated with trace-level cytokines that affect cardiomyocyte function
Authors: Sinclair, JE;Vedelago, C;Ryan, FJ;Carney, M;Redd, MA;Lynn, MA;Grubor-Bauk, B;Cao, Y;Henders, AK;Chew, KY;Gilroy, D;Greaves, K;Labzin, L;Ziser, L;Ronacher, K;Wallace, LM;Zhang, Y;Macauslane, K;Ellis, DJ;Rao, S;Burr, L;Bain, A;Karawita, A;Schulz, BL;Li, J;Lynn, DJ;Palpant, N;Wuethrich, A;Trau, M;Short, KR;
Nature microbiology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: Bioassay -
Nanoparticles of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K8 Reduce Staphylococcus aureus Respiratory Infection and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha- and Interferon Gamma-Induced Lung Inflammation
Authors: Hong, J;Son, M;Sin, J;Kim, H;Chung, DK;
Nutrients
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Capture -
Effect of Flavonoids on MCP-1 Expression in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells and Impact on MCP-1-Dependent Migration of Human Monocytes
Authors: Brüser, L;Teichmann, E;Hinz, B;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by CTNNAL1 in Lung Cancer and Glioblastoma
Authors: Kahm, YJ;Jung, U;Kim, RK;
Biomedicines
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
The m6A methyltransferase METTL16 negatively regulates MCP1 expression in mesenchymal stem cells during monocyte recruitment
Authors: Zhaoqiang Zhang, Zhongyu Xie, Jiajie Lin, Zehang Sun, Zhikun Li, Wenhui Yu et al.
JCI Insight
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Dual-Enhanced Plasmonic Biosensing for Point-of-Care Sepsis Detection
Authors: Lip Ket Chin, Jun-Yeong Yang, Benjamin Chousterman, Sunghoon Jung, Do-Geun Kim, Dong-Ho Kim et al.
ACS Nano
-
Chemokine positioning determines mutually exclusive roles for their receptors in extravasation of pathogenic human T cells
Authors: F Parween, SP Singh, HH Zhang, N Kathuria, FA Otaizo-Car, A Shamsaddin, PJ Gardina, S Ganesan, J Kabat, HA Lorenzi, TG Myers, JM Farber
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2023-02-13;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Integrated DNA and RNA sequencing reveals early drivers involved in metastasis of gastric cancer
Authors: J Zhang, F Liu, Y Yang, N Yu, X Weng, Y Yang, Z Gong, S Huang, L Gan, S Sun, X Zhang, Y Gong, Y Liu, W Guo
Cell Death & Disease, 2022-04-21;13(4):392.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates, Cell Lysates
Applications: Neutralization, Western Blot -
Biological Characterization of Commercial Recombinantly Expressed Immunomodulating Proteins Contaminated with Bacterial Products in the Year 2020: The SAA3 Case
Authors: S Abouelasra, M De Bondt, N Berghmans, M Gouwy, VLS de Oliveir, SC Oliveira, FA Amaral, P Proost, J Van Damme, S Struyf, M De Buck
Mediators Inflamm., 2020-07-06;2020(0):6087109.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Su
Applications: ELISA -
Soft extracellular matrix enhances inflammatory activation of mesenchymal stromal cells to induce monocyte production and trafficking
Authors: SW Wong, S Lenzini, MH Cooper, DJ Mooney, JW Shin
Sci Adv, 2020-04-08;6(15):eaaw0158.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Functional Assay -
Induction of Chemokines by Hepatitis C Virus Proteins: Synergy of the Core Protein with Interleukin-1 beta and Interferon-gamma in Liver Bystander Cells
Authors: Sara Abouelasrar Salama, Mieke Gouwy, Alexandra De Zutter, Noëmie Pörtner, Lotte Vanbrabant, Nele Berghmans et al.
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research
-
MCP-1 promotes detrimental cardiac physiology, pulmonary edema, and death in the cpk model of polycystic kidney disease
Authors: Sally M. Salah, James D. Meisenheimer, Reena Rao, Jacqueline D. Peda, Darren P. Wallace, Dawson Foster et al.
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology
-
Comparison of three congruent patient-specific cell types for the modelling of a human genetic Schwann-cell disorder
Authors: Bipasha Mukherjee-Clavin, Ruifa Mi, Barbara Kern, In Young Choi, Hotae Lim, Yohan Oh et al.
Nature Biomedical Engineering
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
A Subset of Paracrine Factors as Efficient Biomarkers for Predicting Vascular Regenerative Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells
Authors: HK Kim, SG Lee, SW Lee, BJ Oh, JH Kim, JA Kim, G Lee, JD Jang, YA Joe
Stem Cells, 2018-10-08;0(0):.
-
Reactive astrocytic S1P3 signaling modulates the blood-tumor barrier in brain metastases
Authors: B Gril, AN Paranjape, S Woditschka, E Hua, EL Dolan, J Hanson, X Wu, W Kloc, E Izycka-Swi, R Duchnowska, R P?ksa, W Biernat, J Jassem, N Nayyar, PK Brastianos, OM Hall, CJ Peer, WD Figg, GT Pauly, C Robinson, S Difilippan, E Bialecki, P Metellus, JP Schneider, PS Steeg
Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2018-07-13;9(1):2705.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Protective effect of KLF15 on vascular endothelial dysfunction induced by TNF??.
Authors: Bing Liu, Lili Xu, Xinming Yu, Wei Li, Xiaozhi Sun, Shun Xiao, Mingjin Guo, Haofu Wang
Molecular Medicine Reports, 2018-06-20;0(0):1791-3004.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysate, Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
CCL2 influences the sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells to docetaxel
Authors: T Wang, Q Zhan, X Peng, Z Qiu, T Zhao
Oncol Lett, 2018-05-22;16(1):1267-1274.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: Western Blot -
Distinct CD40L receptors mediate inflammasome activation and secretion of IL-1? and MCP-1 in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Authors: ZM Bian, MG Field, SG Elner, JM Kahlenberg, VM Elner
Exp. Eye Res., 2018-02-16;170(0):29-39.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysate
Applications: Western Blot -
Involvement of Monocyte Subsets in the Immunopathology of Giant Cell Arteritis
Authors: Y van Sleen, Q Wang, KSM van der Ge, J Westra, WH Abdulahad, P Heeringa, AMH Boots, E Brouwer
Sci Rep, 2017-07-26;7(1):6553.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Caspase-8 Acts in a Non-enzymatic Role as a Scaffold for Assembly of a Pro-inflammatory FADDosome Complex upon TRAIL Stimulation
Authors: CM Henry, SJ Martin
Mol. Cell, 2017-02-16;65(4):715-729.e5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
CCL2 as a potential therapeutic target for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Cancer Med, 2016-09-26;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Evidence for chemokine synergy during neutrophil migration in ARDS
Thorax, 2016-08-05;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Association of MIF, but not type I interferon-induced chemokines, with increased disease activity in Asian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Sci Rep, 2016-07-25;6(0):29909.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Regulation of the inflammatory profile of stromal cells in human breast cancer: prominent roles for TNF-alpha and the NF-kappa B pathway
Authors: Christina Katanov, Shalom Lerrer, Yulia Liubomirski, Leonor Leider-Trejo, Tsipi Meshel, Jair Bar et al.
Stem Cell Research & Therapy
-
Chemokines CCL2, 3, 14 stimulate macrophage bone marrow homing, proliferation, and polarization in multiple myeloma
Authors: Yi Li, Yuhuan Zheng, Tianshu Li, Qiang Wang, Jianfei Qian, Yong Lu et al.
Oncotarget
-
Microparticles engineered to highly express peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma decreased inflammatory mediator production and increased adhesion of recipient monocytes.
Authors: Sahler J, Woeller C, Phipps R
PLoS ONE, 2014-11-26;9(11):e113189.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development (Capture) -
Statins Affect the Presentation of Endothelial Chemokines by Targeting to Multivesicular Bodies
Authors: Johanna Hol, Kari Otterdal, Unni M. Breland, Espen Stang, Turid M. Pedersen, Kathrine Hagelsteen et al.
PLoS ONE
-
RhoGDI2 suppresses lung metastasis in mice by reducing tumor versican expression and macrophage infiltration
Authors: Neveen Said, Marta Sanchez-Carbayo, Steven C. Smith, Dan Theodorescu
Journal of Clinical Investigation
-
Inflammatory mediators in breast cancer: Coordinated expression of TNF alpha & IL-1 beta with CCL2 & CCL5 and effects on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Authors: Gali Soria, Maya Ofri-Shahak, Ilana Haas, Neora Yaal-Hahoshen, Leonor Leider-Trejo, Tal Leibovich-Rivkin et al.
BMC Cancer
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Ocular Fibroblast Diversity: Implications for Inflammation and Ocular Wound Healing
Authors: Xia Xi, David H. McMillan, Geniece M. Lehmann, Patricia J. Sime, Richard T. Libby, Krystel R. Huxlin et al.
Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science
-
A multiplex immunoassay for human adipokine profiling.
Authors: Schipper HS, De Jager W, van Dijk ME, Meerding J, Zelissen PM, Adan RA, Prakken BJ, Kalkhoven E
Clin. Chem., 2010-06-08;56(0):1320.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: Luminex Development -
Resistance of human alveolar macrophages to Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin.
Authors: Wu W, Mehta H, Chakrabarty K, Booth JL, Duggan ES, Patel KB, Ballard JD, Coggeshall KM, Metcalf JP
J. Immunol., 2009-10-07;183(9):5799-806.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
Noninvasive detection of acute and chronic injuries in human renal transplant by elevation of multiple cytokines/chemokines in urine.
Authors: Hu H, Kwun J, Aizenstein BD, Knechtle SJ
Transplantation, 2009-06-27;87(12):1814-20.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Urine
Applications: Antibody Array Development -
Synergistic up-regulation of MCP-2/CCL8 activity is counteracted by chemokine cleavage, limiting its inflammatory and anti-tumoral effects.
Authors: Struyf S, Proost P, Vandercappellen J
Eur. J. Immunol., 2009-03-01;39(3):843-57.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
Fluorescence single-molecule counting assays for high-sensitivity detection of cytokines and chemokines.
Authors: Qui H, Ferrell EP, Nolan N, Phelps BH, Tabibiazar R, Whitney DH, Naelfski EA
Clin. Chem., 2007-11-01;53(11):2010-2.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: ELISA Development -
Effect of serum content and diluent selection on assay sensitivity and signal intensity in multiplex bead-based immunoassays.
Authors: Pfleger C, Schloot N, ter Veld F
J. Immunol. Methods, 2007-10-22;329(1):214-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
Applications: Luminex Development -
Ultrasensitive flow-based immunoassays using single-molecule counting.
Authors: Todd J, Freese B, Lu A, Held D, Morey J, Livingston R, Goix P
Clin. Chem., 2007-09-21;53(11):1990-5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: ELISA Development -
Borrelia burgdorferi-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production in vivo and in vitro.
Authors: Zhao Z, McCloud B, Fleming R, Klempner MS
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2007-05-02;358(2):528-33.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Platelet-derived LIGHT induces inflammatory responses in endothelial cells and monocytes.
Authors: Otterdal K, Smith C, Oie E, Pedersen TM, Yndestad A, Stang E, Endresen K, Solum NO, Aukrust P, Damas JK
Blood, 2006-08-01;108(3):928-35.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ELISA Development -
Cholinergic stimulation blocks endothelial cell activation and leukocyte recruitment during inflammation
Authors: Rubina W. Saeed, Santosh Varma, Tina Peng-Nemeroff, Barbara Sherry, David Balakhaneh, Jared Huston et al.
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
-
HIV-1 tat protein induces a migratory phenotype in human fetal microglia by a CCL2 (MCP-1)-dependent mechanism: possible role in NeuroAIDS.
Authors: Eugenin EA, Dyer G, Calderon TM, Berman JW
Glia, 2005-03-01;49(4):501-10.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
trans fatty acids and systemic inflammation in heart failure.
Authors: Mozaffarian D, Rimm EB, King IB, Lawler RL, McDonald GB, Levy WC
Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2004-12-01;80(6):1521-5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: ELISA Development -
Long-term effects of polymer-based, slow-release, sirolimus-eluting stents in a porcine coronary model.
Authors: Carter AJ, Aggarwal M, Kopia GA, Tio F, Tsao PS, Kolata R, Yeung AC, Llanos G, Dooley J, Falotico R
Cardiovasc. Res., 2004-09-01;63(4):617-24.
Species: Porcine
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Rapid chemokine secretion from endothelial cells originates from 2 distinct compartments.
Authors: Oynebraten I, Bakke O, Brandtzaeg P, Johansen FE, Haraldsen G
Blood, 2004-03-25;104(2):314-20.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Targeting AXL and RAGE to prevent geminin overexpression-induced triple-negative breast cancer metastasis
Authors: D Ryan, J Koziol, WM ElShamy
Sci Rep, 2019-12-16;9(1):19150.
-
MCP-1/CCR-2 axis in adipocytes and cancer cell respectively facilitates ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis
Authors: C Sun, X Li, E Guo, N Li, B Zhou, H Lu, J Huang, M Xia, W Shan, B Wang, K Li, D Weng, X Xu, Q Gao, S Wang, J Hu, Y Lu, GB Mills, G Chen
Oncogene, 2019-11-08;0(0):.
-
MCP-1 targeting: Shutting off an engine for tumor development
Authors: L Wang, J Lan, J Tang, N Luo
Oncology Letters, 2021-11-19;23(1):26.
-
JunB promotes cell invasion and angiogenesis in VHL-defective renal cell carcinoma.
Authors: Kanno T, Kamba T, Yamasaki T et al.
Oncogene.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 3 Reviews)
Have you used Human CCL2/JE/MCP-1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
After biotinylation, used as a capture reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Meso Scale Diagnostics LLC).
Paired with SulfoTag-modified AF-279-NA as a detection antibody. Calibration curves with Recombinant Human CCL2 (279-MC-010/CF) is shown (dynamic range 6-25,000 pg/ml)