Mouse Siglec-F Antibody Summary
Asp18-Thr437
Accession # Q920G3
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
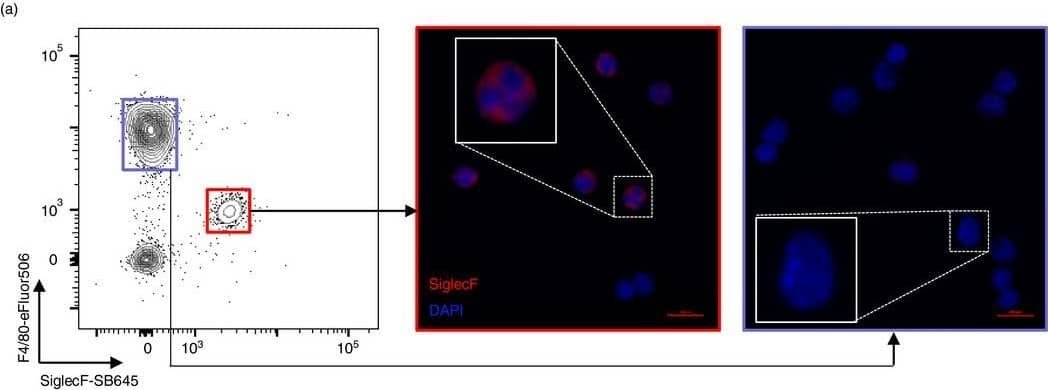
 View Larger
View Larger
Cell Adhesion Mediated by Siglec‑F and Neutralization by Mouse Siglec‑F Antibody. Recombinant Mouse Siglec-F Fc Chimera (Catalog # 1706-SF), immobilized onto a microplate, supports the adhesion of human red blood cells in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Adhesion elicited by Recombinant Mouse Siglec-F Fc Chimera (5 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Siglec-F Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB17061). The ND50 is typically 0.1-0.5 µg/mL.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Siglec-F
Siglecs (1) (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectins) are I-type (Ig-type) lectins (2) belonging to the Ig superfamily. They are characterized by an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain which mediates sialic acid binding (3), followed by varying numbers of Ig-like C2-type domains (1, 4). Eleven human Siglecs have been cloned and characterized (1, 4). They are sialoadhesin/CD169/Siglec-1, CD22/Siglec-2, CD33/Siglec-3, Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein (MAG/Siglec-4a) and Siglec 5 to 11 (4‑6). To date, no Siglec has been shown to recognized any cell surface ligand other than sialic acids, suggesting that interactions with glycans containing this carbohydrate are important in mediating the biological functions of Siglecs. Siglec 5 to 11 share a high degree of sequence similarity with CD33/Siglec-3 both in their extracellular and intracellular regions. They are collectively referred to as CD33-related Siglecs. One remarkable feature of the CD33-related Siglecs is their differential expression pattern within the hematopoietic system (4, 5). This fact, together with the presence of two conserved immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasmic tails, suggests that CD33-related Siglecs are involved in the regulation of cellular activation within the immune system.
Mouse Siglec-F cDNA encodes a 569 amino acid polypeptide with a hydrophobic signal peptide, an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, three Ig-like C2-type domains, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail (7). The expression of Siglec-F is restricted to the cells of myelomonocytic lineage. Mouse Siglec-F is likely an ortholog of human Siglec-5. Unlike many human CD33-related Siglecs, which show similar binding to both alpha 2,3- and alpha 2,6-linked sialic acids, mouse Siglec-F preferentially recognize alpha 2,3-linked sialic acid.
- Crocker, P.R. et al. (1998) Glycobiology 8:v.
- Powell, L.D. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:14243.
- May, A.R. et al. (1998) Mol. Cell 1998. 1:719.
- Crocker, P.R. and A. Varki (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:337.
- Crocker, P.R. et al. (2001) Immunology 103:137.
- Angata, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol Chem. 277:24466.
- Angata, T. et al. (2001) J. Biol Chem. 276:45128.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
8
Citations: Showing 1 - 8
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The impact of Charcot-Leyden Crystal protein on mesothelioma chemotherapy: targeting eosinophils for enhanced chemosensitivity
Authors: Willems, M;Hamaidia, M;Fontaine, A;Grégoire, M;Halkin, L;Vilanova Mañá, L;Terres, R;Jamakhani, M;Deshayes, S;Brostaux, Y;Heinen, V;Louis, R;Duysinx, B;Jean, D;Wasielewski, E;Scherpereel, A;Blanquart, C;Willems, L;
EBioMedicine
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Neonatal LTbetaR signaling is required for the accumulation of eosinophils in the inflamed adult mesenteric lymph node
Authors: C Li, LA Ward, A Nguyen, E Lam, D Dasoveanu, M Ahmed, K Haniuda, MB Buechler, HH He, B Ludewig, KM McNagny, JL Gommerman
Mucosal Immunology, 2022-02-18;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Il4ra-independent vaginal eosinophil accumulation following helminth infection exacerbates epithelial ulcerative pathology of HSV-2 infection
Authors: Alisha Chetty, Matthew G. Darby, Pia M. Vornewald, Mara Martín-Alonso, Anna Filz, Manuel Ritter et al.
Cell Host & Microbe
-
Fibroblast-derived IL-33 facilitates breast cancer metastasis by modifying the immune microenvironment and driving type-2 immunity
Authors: Ophir Shani, Tatiana Vorobyov, Lea Monteran, Dor Lavie, Noam Cohen, Yael Raz et al.
Cancer Research
-
A role of eosinophils in mediating the anti-tumour effect of cryo-thermal treatment
Authors: S Jia, W Li, P Liu, LX Xu
Sci Rep, 2019-09-13;9(1):13214.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Role of Eosinophils and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Interleukin-25-Mediated Protection from Amebic Colitis
Authors: Z Noor, K Watanabe, MM Abhyankar, SL Burgess, EL Buonomo, CA Cowardin, WA Petri
MBio, 2017-02-28;8(1):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
IL-33-mediated protection against experimental cerebral malaria is linked to induction of type 2 innate lymphoid cells, M2 macrophages and regulatory T cells.
Authors: Besnard A, Guabiraba R, Niedbala W, Palomo J, Reverchon F, Shaw T, Couper K, Ryffel B, Liew F
PLoS Pathog, 2015-02-06;11(2):e1004607.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Bioassay -
Eosinophils promote generation and maintenance of immunoglobulin-A-expressing plasma cells and contribute to gut immune homeostasis.
Authors: Chu V, Beller A, Rausch S, Strandmark J, Zanker M, Arbach O, Kruglov A, Berek C
Immunity, 2014-04-17;40(4):582-93.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsIsotype Controls
Reconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse Siglec-F Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse Siglec-F Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image