Human/Mouse Wnt-5a Antibody Summary
Gln38-Lys380
Accession # P22725
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
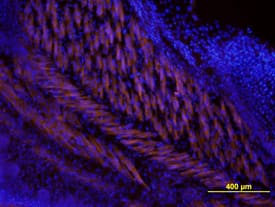
Wnt‑5a in Mouse Embryo. Wnt-5a was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo using Human/Mouse Wnt-5a Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB645) at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (orange; Catalog # NL013) and counter-stained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
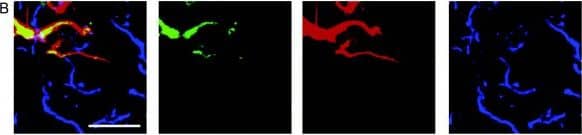
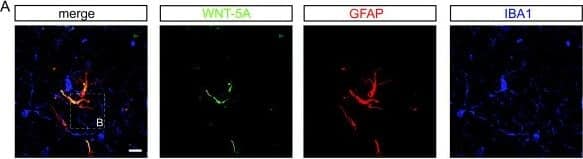
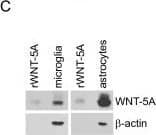
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence WNT-5A expression in mouse GFAP+astrocytes. (A) Immunohistochemistry was performed on adult mouse brain sections using an anti-WNT-5A antibody in combination with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein1 (IBA1) antibodies as astrocyte and microglia marker, respectively. Merge presents the overlay of IBA1, GFAP, WNT-5A. Size bar −2 μm. The images represent a maximum intensity projection of a Z-stack of 5 μm thickness. The white square marked ‘B’ indicates the area magnified in B: (B) Close up of a GFAP+ astrocyte reveals the expression of WNT-5A in this cell type. (C) shows immunoblot detection of recombinant WNT-5A (rWNT-5A; 375 ng/lane) in comparison to lysates from mouse primary microglia and mixed astrocyte cultures. beta -actin serves as a loading control. (D) The bar graph depicts expression levels of WNT-5A mRNA in mouse primary microglia and mixed astrocyte cultures measured by QPCR. Data are normalized to GAPDH expression and analyzed with a non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. n = 4 to 8. (E) shows indirect immunocytochemistry of mixed astrocyte cultures employing anti-GFAP as astrocyte and anti-CD11b as microglia markers. DAPI is used as nuclear counterstain. Image represents a maximum image projection of an 8 μm Z-stack. Size bar 20 μm. The frame shows 63 cells in total and 10 CD11b-positive microglia (arrows). Routinely 10% to 18% microglia were observed (n = 4). DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GADPH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; n, number. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22647544), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
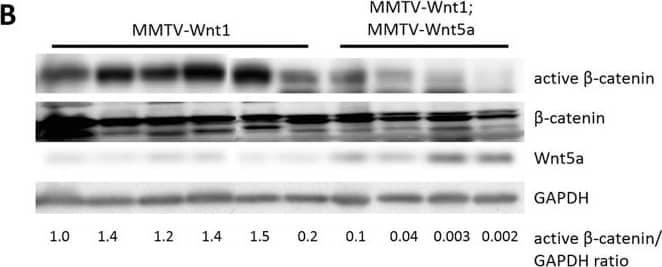
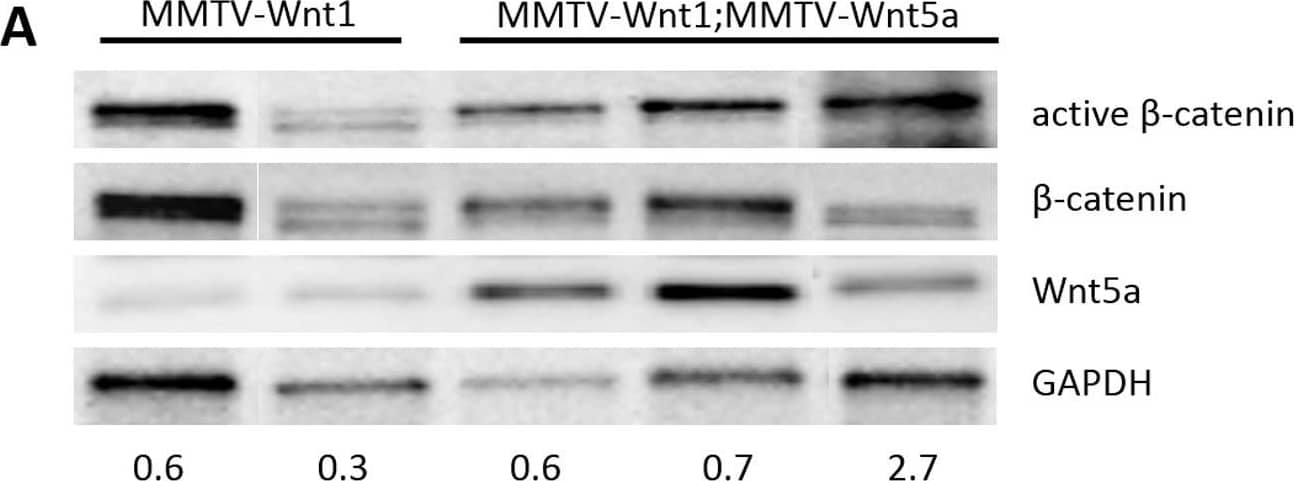
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Western Blot Wnt5a expressing tumors have less Wnt/ beta -catenin signaling than MMTV-Wnt1 tumors.(A) Quantitative RT-PCR of Wnt/ beta -catenin target genes. Expression of Axin2 mRNA in MMTV-Wnt1 versus MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a tumors as determined by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 5 MMTV-Wnt1, n = 5 MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a). Data are shown as tables obtained using REST software. Axin2 mRNA was significantly down-regulated in MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a tumors. (B) Western blot for beta -catenin protein. Protein lysates were prepared from MMTV-Wnt1 and MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a tumors. beta -catenin and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used as loading controls. The ratio of active beta -catenin to beta -catenin as determined by densitometic analysis is shown. MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a tumors displayed decreased levels of active beta -catenin compared to controls. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113247), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
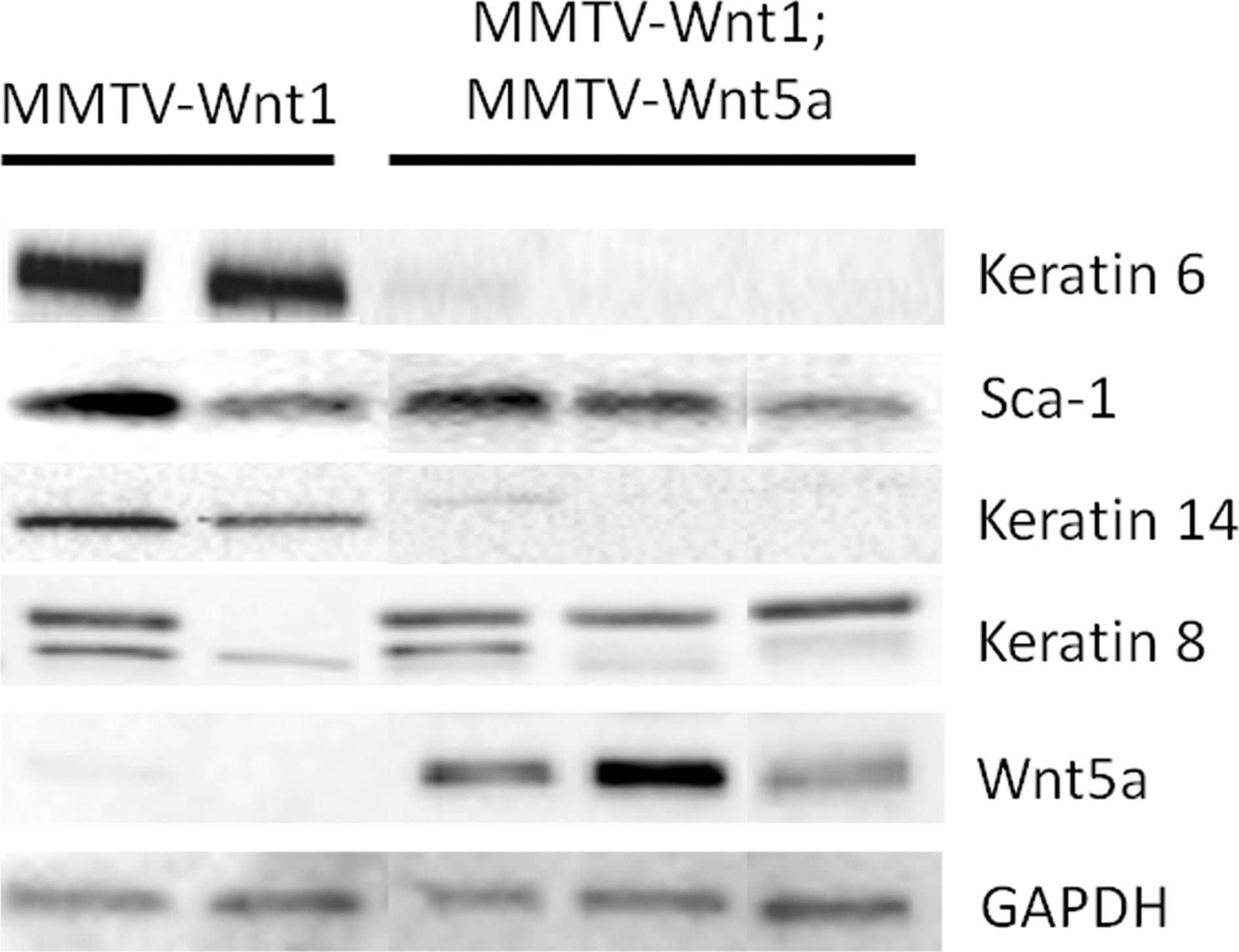
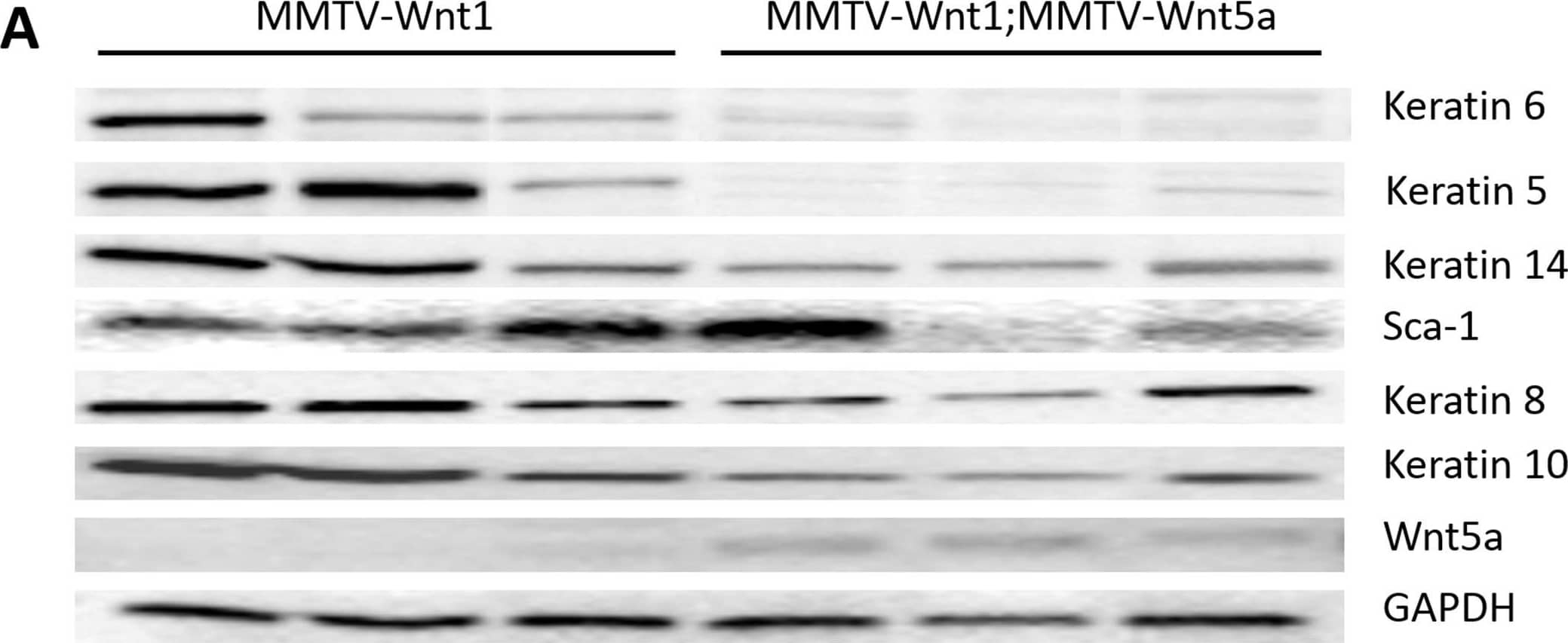
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Western Blot Ectopic expression of Wnt5a results in low expression of K6 and K14.Expression of molecular markers for basal and luminal progenitors in MMTV-Wnt1 and MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a mammary glands was compared by western blot. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control. Each lane contains protein isolated from a separate mouse. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113247), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence WNT-5A expression in mouse GFAP+astrocytes. (A) Immunohistochemistry was performed on adult mouse brain sections using an anti-WNT-5A antibody in combination with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein1 (IBA1) antibodies as astrocyte and microglia marker, respectively. Merge presents the overlay of IBA1, GFAP, WNT-5A. Size bar −2 μm. The images represent a maximum intensity projection of a Z-stack of 5 μm thickness. The white square marked ‘B’ indicates the area magnified in B: (B) Close up of a GFAP+ astrocyte reveals the expression of WNT-5A in this cell type. (C) shows immunoblot detection of recombinant WNT-5A (rWNT-5A; 375 ng/lane) in comparison to lysates from mouse primary microglia and mixed astrocyte cultures. beta -actin serves as a loading control. (D) The bar graph depicts expression levels of WNT-5A mRNA in mouse primary microglia and mixed astrocyte cultures measured by QPCR. Data are normalized to GAPDH expression and analyzed with a non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. n = 4 to 8. (E) shows indirect immunocytochemistry of mixed astrocyte cultures employing anti-GFAP as astrocyte and anti-CD11b as microglia markers. DAPI is used as nuclear counterstain. Image represents a maximum image projection of an 8 μm Z-stack. Size bar 20 μm. The frame shows 63 cells in total and 10 CD11b-positive microglia (arrows). Routinely 10% to 18% microglia were observed (n = 4). DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GADPH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; n, number. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22647544), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Western Blot WNT-5A expression in mouse GFAP+astrocytes. (A) Immunohistochemistry was performed on adult mouse brain sections using an anti-WNT-5A antibody in combination with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein1 (IBA1) antibodies as astrocyte and microglia marker, respectively. Merge presents the overlay of IBA1, GFAP, WNT-5A. Size bar −2 μm. The images represent a maximum intensity projection of a Z-stack of 5 μm thickness. The white square marked ‘B’ indicates the area magnified in B: (B) Close up of a GFAP+ astrocyte reveals the expression of WNT-5A in this cell type. (C) shows immunoblot detection of recombinant WNT-5A (rWNT-5A; 375 ng/lane) in comparison to lysates from mouse primary microglia and mixed astrocyte cultures. beta -actin serves as a loading control. (D) The bar graph depicts expression levels of WNT-5A mRNA in mouse primary microglia and mixed astrocyte cultures measured by QPCR. Data are normalized to GAPDH expression and analyzed with a non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. n = 4 to 8. (E) shows indirect immunocytochemistry of mixed astrocyte cultures employing anti-GFAP as astrocyte and anti-CD11b as microglia markers. DAPI is used as nuclear counterstain. Image represents a maximum image projection of an 8 μm Z-stack. Size bar 20 μm. The frame shows 63 cells in total and 10 CD11b-positive microglia (arrows). Routinely 10% to 18% microglia were observed (n = 4). DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GADPH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; n, number. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22647544), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Western Blot Wnt/ beta -catenin signaling is not down-regulated in Wnt5a expressing MMTV-Wnt1 glands.(A) Western blot analysis of beta -catenin protein in MMTV-Wnt1mammary gland. The level of active beta -catenin was compared in protein lysates from MMTV-Wnt1 and MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a mammary glands. Total beta -catenin and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used as loading controls. The ratio of active beta -catenin-to-beta -catenin is shown at the bottom on the gel. Each lane represents a sample from a different mouse. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of Axin2, a Wnt/ beta -catenin target gene, in unsorted primary mammary epithelial cells. Expression of Axin2 and hWnt5a mRNA in unsorted PMECs from MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a vs. MMTV-Wnt1 mammary glands was determined by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 12 MMTV-Wnt1, n = 11 MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a separate mice). Data are shown as tables obtained using REST analysis software. Expression = fold difference in MMTV-Wnt1;Wnt5a relative to MMTV-Wnt1 controls after normalization to Gapdh. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR of Axin2 in E-cadherin negative primary mammary epithelial cells. Expression of Axin2 and hWnt5a mRNA in E-cadherin (Ecad) negative PMECs from MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a vs. MMTV-Wnt1 mammary glands was determined by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 2 MMTV-Wnt1, n = 2 MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a separate mice). Data are shown as tables obtained using REST analysis software. Expression = fold difference in MMTV-Wnt1;Wnt5a relative to MMTV-Wnt1 controls after normalization to Gapdh. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113247), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Wnt-5a by Western Blot Wnt5a expressing tumors demonstrate a decrease in markers of the basal tumor subtype.(A) Western blot using protein lysates isolated from the epithelium of MMTV-Wnt1 and MMTV-1;MMTV-Wnt5a mammary tumors. The expression of molecular markers of basal and luminal tumor subtypes were compared. Keratin 6 and Keratin 5 were strongly down-regulated in Wnt5a expressing tumors. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control. (B–D) Immunostaining for K6. Sections from MMTV-Wnt1 (B) and MMTV-1;MMTV-Wnt5a (C) tumors were stained with anti-Keratin 6 antibody using immunofluorescence (K6 = green; nuclei = blue). The percentage of cells expressing K6 was determined and graphed (D). Values are means +/− standard error (n = 6 MMTV-Wnt1, 3 fields per tumor; n = 5 MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a, 3 fields per tumor). MMTV-Wnt1;MMTV-Wnt5a tumors demonstrated a significant decrease in K6-expressing cells as measured by T-test (* = p<0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113247), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Wnt-5a
Wnt proteins are secreted glycoproteins that contain a conserved pattern of 23‑24 cysteine residues. Wnts play critical roles in both carcinogenesis and embryonic development for a variety of organisms. Wnts bind to receptors of the Frizzled family, sometimes in conjunction with other membrane-associated proteins such as LRPs or proteoglycans. Downstream effects of Wnt signaling occur through different intracellular components, depending on which pathway is activated. Three pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt/ beta -catenin pathway, the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway, and the planar cell polarity (1‑2).
Wnt-5a is part of the subgroup of Wnts that are not axis-inducing in Xenopus embryos and do not transform C57MG mammary epithelial cells. This subgroup is also implicated in the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway, playing roles in cell movements and cell adhesion (3). This non-canonical Wnt pathway can inhibit canonical Wnt/ beta -catenin signaling. In Wnt-5a deficient mouse embryos, beta -catenin accumulates in the limb bud suggesting that Wnt-5a normally promotes degradation of beta -catenin (4). Likewise, in Xenopus embryos Wnt-5a antagonizes the ability of the canonical Wnt subgroup to induce a secondary axis (5). Wnt-5a is implicated in various types of cancer and has complex roles. It acts as a tumor suppressor for mammary, B-cell, colon, and uroepithelial cancer cells but is up-regulated in melanomas, where expression levels correlate with severity of metastasis (3). Furthermore, aberrant Wnt-5a signaling results in other diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (6). Like other developmental growth factors Wnt-5a has diverse roles in development. They are too numerous to enunciate here, as functions span from early anterior-posterior development and gastrulation movements to maintaining hematopoietic stem cell population, lung morphogenesis, and limb outgrowth. Mature Wnt-5a is a 49 kDa protein that shares 99% amino acid identity in mouse, rat and human.
- Miller, J.R. (2002) Genome Biol. 3:3001.
- Roelink, H. and R. Nusse (1991) Genes Dev. 5:381.
- Veeman, M.T. et al. (2003) Developmental Cell 5:367.
- Topol, L. et al. (2003) J. Cell Biol 162:899.
- Torres, M. et al. (1996) J. Cell Biol. 133:1123.
- Sen, M. et al. (2001) Arthritis & Rheumatism 44:772.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse Wnt-5a Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
48
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Cirmtuzumab blocks Wnt5a/ROR1 stimulation of NF-kappa B to repress autocrine STAT3 activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Authors: Yun Chen, Liguang Chen, Jian Yu, Emanuela M. Ghia, Michael Y. Choi, Ling Zhang et al.
Blood
-
Exogenous WNT5A and WNT11 proteins rescue CITED2 dysfunction in mouse embryonic stem cells and zebrafish morphants
Authors: João M. A. Santos, Leonardo Mendes-Silva, Vanessa Afonso, Gil Martins, Rui S. R. Machado, João A. Lopes et al.
Cell Death & Disease
-
A cellular and spatial map of the choroid plexus across brain ventricles and ages
Authors: Neil Dani, Rebecca H. Herbst, Cristin McCabe, Gilad S. Green, Karol Kaiser, Joshua P. Head et al.
Cell
-
Spatial regulation of cell cohesion by Wnt5a during second heart field progenitor deployment
Authors: Ding Li, Tanvi Sinha, Rieko Ajima, Hwa-Seon Seo, Terry P. Yamaguchi, Jianbo Wang
Developmental Biology
-
beta -catenin-independent WNT signaling and Ki67 in contrast to the estrogen receptor status are prognostic and associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer liver metastases
Authors: Annalen Bleckmann, Lena-Christin Conradi, Kerstin Menck, Nadine Annette Schmick, Antonia Schubert, Eva Rietkötter et al.
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis
-
Deletion of Wnt5a in osteoclasts results in bone loss through decreased bone formation
Authors: Roberts JL, Liu G, Paglia DN et al.
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
-
Partial Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Phenotypes by Placenta-Derived DBMSCs in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines, In Vitro
Authors: Basmaeil, Y;Subayyil, AA;Kulayb, HB;Kondkar, AA;Alrodayyan, M;Khatlani, T;
Cells
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
A fibronectin gradient remodels mixed-phase mesoderm
Authors: Zhu, M;Gu, B;Thomas, EC;Huang, Y;Kim, YK;Tao, H;Yung, TM;Chen, X;Zhang, K;Woolaver, EK;Nevin, MR;Huang, X;Winklbauer, R;Rossant, J;Sun, Y;Hopyan, S;
Science advances
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
The Lin28b/Wnt5a axis drives pancreas cancer through crosstalk between cancer associated fibroblasts and tumor epithelium
Authors: Shu, Z;Fan, M;Tu, B;Tang, Z;Wang, H;Li, H;Li, H;Yuan, M;Bai, J;Huo, S;Wang, L;Zhu, WG;Wang, W;Liu, X;Shu, S;Zhao, Y;
Nature communications
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Hyperglycemia increases SCO-spondin and Wnt5a secretion into the cerebrospinal fluid to regulate ependymal cell beating and glucose sensing
Authors: Nualart, F;Cifuentes, M;Ramírez, E;Martínez, F;Barahona, MJ;Ferrada, L;Saldivia, N;Bongarzone, ER;Thorens, B;Salazar, K;
PLoS biology
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Development of opioid-induced hyperalgesia depends on reactive astrocytes controlled by Wnt5a signaling
Authors: Liu X, Bae C, Liu B et al.
Molecular Psychiatry
-
Increased MARCKS Activity in BRAF Inhibitor-Resistant Melanoma Cells Is Essential for Their Enhanced Metastatic Behavior Independent of Elevated WNT5A and IL-6 Signaling
Authors: V Yadav, N Jobe, SR Satapathy, P Mohapatra, T Andersson
Cancers, 2022-12-10;14(24):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein Extracts
Applications: Western Blot -
YAP-dependent Wnt5a induction in hypertrophic adipocytes restrains adiposity
Authors: GJ Lee, YJ Kim, B Park, S Yim, C Park, H Roh, Y Moon, JK Seong, H Park
Cell Death & Disease, 2022-04-27;13(4):407.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
RNF43 inhibits WNT5A-driven signaling and suppresses melanoma invasion and resistance to the targeted therapy
Authors: T Radaszkiew, M Nosková, K Gömöryová, O Vondálová, KA Radaszkiew, M Picková, R Víchová, T Gybe?, K Kaiser, L Demková, L Ku?erová, T Bárta, D Pot?šil, Z Zdráhal, K Sou?ek, V Bryja
Elife, 2021-10-27;10(0):.
Species: Human, Xenograft
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates, Cell Lysates, Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
HDAC6 suppresses microRNA-199a transcription and augments HPV-positive cervical cancer progression through Wnt5a upregulation
Authors: Y Shao, F Zhu, S Zhu, L Bai
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 2021-04-29;0(0):106000.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are a Major Source of Wnt5A in the Melanoma Microenvironment and Depend on Wnt5A for Full Suppressive Activity
Authors: Douglass SM, Fane ME, Sanseviero E et al.
Cancer Research
-
Wnt5a and Wnt11 as acute respiratory distress syndrome biomarkers for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 patients
Authors: Eun Young Choi, Hee Ho Park, Hyelim Kim, Hong Nam Kim, Inyoung Kim, Soyoung Jeon et al.
European Respiratory Journal
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: ELISA Capture -
Deletion of Wnt5a in osteoclasts results in bone loss through decreased bone formation
Authors: Roberts JL, Liu G, Paglia DN et al.
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
-
Host Wnt5a Potentiates Microenvironmental Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Metastasis
Authors: M Asem, AM Young, C Oyama, AG Claure De, Y Liu, J Yang, TS Hilliard, J Johnson, EI Harper, I Guldner, S Zhang, TM Page-Maybe, WJ Kaliney, MS Stack
Cancer Res., 2020-01-13;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Exogenous WNT5A and WNT11 proteins rescue CITED2 dysfunction in mouse embryonic stem cells and zebrafish morphants
Authors: João M. A. Santos, Leonardo Mendes-Silva, Vanessa Afonso, Gil Martins, Rui S. R. Machado, João A. Lopes et al.
Cell Death & Disease
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot, Neutralization -
Wnt5a causes ROR1 to complex and activate cortactin to enhance migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.
Authors: Hasan M, Rassenti L, Widhopf G, Yu J, Kipps T
Leukemia, 2018-12-19;33(3):653-661.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Distinct roles and differential expression levels of Wnt5a mRNA isoforms in colorectal cancer cells
Authors: TC Huang, PT Lee, MH Wu, CC Huang, CY Ko, YC Lee, DY Lin, YW Cheng, KH Lee
PLoS ONE, 2017-08-31;12(8):e0181034.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
ABCB1 and ABCG2 drug transporters are differentially expressed in non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) and expression is modified by cisplatin treatment via altered Wnt signaling
Authors: M Vesel, J Rapp, D Feller, E Kiss, L Jaromi, M Meggyes, G Miskei, B Duga, G Smuk, T Laszlo, I Karner, JE Pongracz
Respir. Res, 2017-03-24;18(1):52.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Noncanonical WNT-5A signaling impairs endogenous lung repair in COPD
Authors: Hoeke A Baarsma
J. Exp. Med, 2016-12-15;0(0):.
Species: Human, Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Neutralization, Western Blot -
WNT5A signaling impairs breast cancer cell migration and invasion via mechanisms independent of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition
J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2016-09-13;35(1):144.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Wnt5a induces ROR1/ROR2 heterooligomerization to enhance leukemia chemotaxis and proliferation
Authors: Jian Yu, Liguang Chen, Bing Cui, George F. Widhopf, Zhouxin Shen, Rongrong Wu et al.
Journal of Clinical Investigation
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Noncanonical Wnt signaling promotes obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction independent of adipose tissue expansion.
Authors: Fuster J, Zuriaga M, Ngo D, Farb M, Aprahamian T, Yamaguchi T, Gokce N, Walsh K
Diabetes, 2014-10-28;64(4):1235-48.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Stage of breast cancer progression influences cellular response to activation of the WNT/planar cell polarity pathway.
Authors: MacMillan, Connor D, Leong, Hon S, Dales, David W, Robertson, Amy E, Lewis, John D, Chambers, Ann F, Tuck, Alan B
Sci Rep, 2014-09-10;4(0):6315.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Wnt5a promotes inflammatory responses via nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in human dental pulp cells.
Authors: Zhao Y, Wang C, Li R, Hui T, Su Y, Yuan Q, Zhou X, Ye L
J Biol Chem, 2014-07-25;289(30):21028-39.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Interleukin-6 drives melanoma cell motility through p38alpha-MAPK-dependent up-regulation of WNT5A expression.
Authors: Linnskog R, Jonsson G, Axelsson L, Prasad C, Andersson T
Mol Oncol, 2014-05-27;8(8):1365-78.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Wnt5a/beta-catenin signaling drives calcium-induced differentiation of human primary keratinocytes.
Authors: Popp T, Steinritz D, Breit A, Deppe J, Egea V, Schmidt A, Gudermann T, Weber C, Ries C
J Invest Dermatol, 2014-03-21;134(8):2183-91.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Oncogenic effects of WNT5A in Epstein-Barr virusassociated nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Authors: Yap L, Ahmad M, Zabidi M, Chu T, Chai S, Lee H, Lim P, Wei W, Dawson C, Teo S, Khoo A
Int J Oncol, 2014-03-13;44(5):1774-80.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
Diverse mechanisms for activation of Wnt signalling in the ovarian tumour microenvironment.
Authors: Barbolina MV, Burkhalter RJ, Stack MS
Biochem. J., 2011-07-01;437(1):1-12.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Ascites Fluid
Applications: Western Blot -
Wnt5A Signaling Blocks Progression of Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis
Authors: Shreyasi Maity, Arijit Chakraborty, Sushil Kumar Mahata, Syamal Roy, Anjan Kumar Das, Malini Sen
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Aberrantly expressed Wnt5a in nurse-like cells drives resistance to Venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Authors: Yao Guo, Hanzhong Pei, Bo Lu, Dengyang Zhang, Yuming Zhao, Fuqun Wu et al.
Cell Death Discovery
-
Development of opioid-induced hyperalgesia depends on reactive astrocytes controlled by Wnt5a signaling
Authors: Liu X, Bae C, Liu B et al.
Molecular Psychiatry
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are a Major Source of Wnt5A in the Melanoma Microenvironment and Depend on Wnt5A for Full Suppressive Activity
Authors: Douglass SM, Fane ME, Sanseviero E et al.
Cancer Research
-
Wnt5a induces ROR1/ROR2 heterooligomerization to enhance leukemia chemotaxis and proliferation
Authors: Jian Yu, Liguang Chen, Bing Cui, George F. Widhopf, Zhouxin Shen, Rongrong Wu et al.
Journal of Clinical Investigation
-
FOXC1-induced non-canonical WNT5A-MMP7 signaling regulates invasiveness in triple-negative breast cancer
Authors: B Han, B Zhou, Y Qu, B Gao, Y Xu, S Chung, H Tanaka, W Yang, AE Giuliano, X Cui
Oncogene, 2017-12-18;0(0):.
-
Increased Extracellular Vesicles Mediate WNT5A Signaling in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Authors: Aina Martin-Medina, Mareike Lehmann, Olivier Burgy, Sarah Hermann, Hoeke A. Baarsma, Darcy E. Wagner et al.
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
-
Characterisation of tumour-derived microvesicles in cancer patients’ blood and correlation with clinical outcome
Authors: Kerstin Menck, Annalen Bleckmann, Astrid Wachter, Bianca Hennies, Lena Ries, Matthias Schulz et al.
Journal of Extracellular Vesicles
-
Heterotrimeric G protein-dependent WNT-5A signaling to ERK1/2 mediates distinct aspects of microglia proinflammatory transformation
Authors: Carina Halleskog, Jacomijn Petronella Dijksterhuis, Michaela Brita Christina Kilander, Javier Becerril-Ortega, Juan Carlos Villaescusa, Eva Lindgren et al.
Journal of Neuroinflammation
-
Induction and transport of Wnt 5a during macrophage-induced malignant invasion is mediated by two types of extracellular vesicles
Authors: Kerstin Menck, Florian Klemm, Julia Christina Gross, Tobias Pukrop, Dirk Wenzel, Claudia Binder
Oncotarget
-
Wnt5a and Wnt11 as acute respiratory distress syndrome biomarkers for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 patients
Authors: Eun Young Choi, Hee Ho Park, Hyelim Kim, Hong Nam Kim, Inyoung Kim, Soyoung Jeon et al.
European Respiratory Journal
-
Wnt5a Suppresses Tumor Formation and Redirects Tumor Phenotype in MMTV-Wnt1 Tumors
Authors: Stephanie L. Easter, Elizabeth H. Mitchell, Sarah E. Baxley, Renee Desmond, Andra R. Frost, Rosa Serra
PLoS ONE
-
Expression profile and clinical significance of Wnt signaling in human gliomas
Authors: Hao Zhang, Yanhua Qi, Decheng Geng, Yi Shi, Xu Wang, Rutong Yu et al.
Oncology Letters
-
Noncanonical WNT Activation in Human Right Ventricular Heart Failure
Authors: Jonathan J. Edwards, Jeffrey Brandimarto, Dong-Qing Hu, Sunhye Jeong, Nora Yucel, Li Li et al.
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine
-
Naturally Occurring Variants in LRP1 (Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1) Affect HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Metabolism Through ABCA1 (ATP-Binding Cassette A1) and SR-B1 (Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1) in Humans
Authors: Oldoni F, van Capelleveen JC, Dalila N.
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse Wnt-5a Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human/Mouse Wnt-5a Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:




