Human Prolactin R Antibody Summary
Gln25-Asp234
Accession # P16471
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
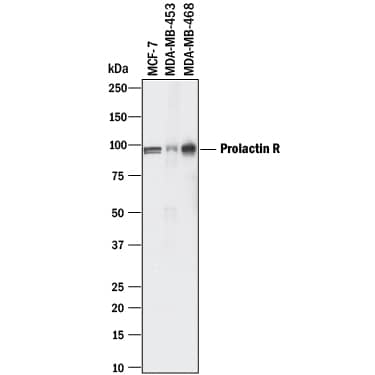 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Prolactin R by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-453 human breast cancer cell line, and MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human Prolactin R Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1167) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Prolactin R at approximately 95 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
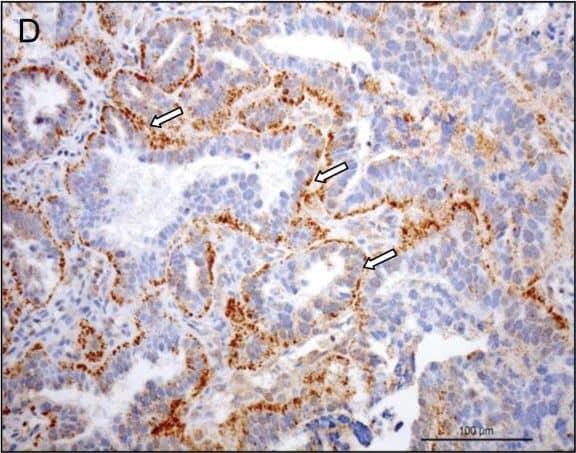 View Larger
View Larger
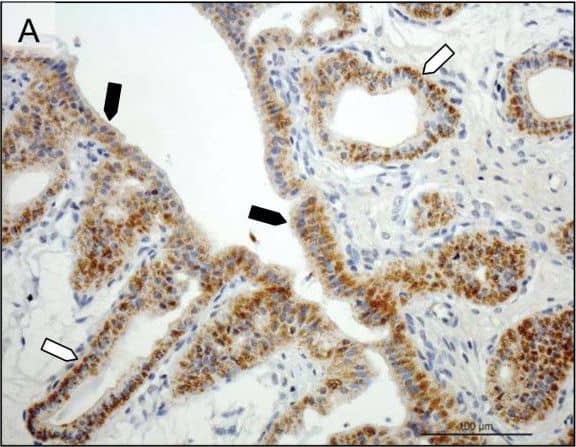
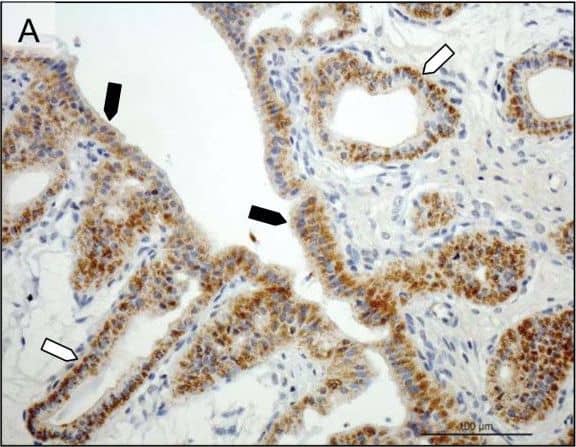
Detection of Canine Prolactin R by Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical (IHC) localization of PRLr in the uterus pre-implantation and in the utero/placental compartment. (A, B) IHC localization of PRLr in canine endometrium at the pre-implantation stage of pregnancy. (C, D) IHC localization of PRLr within the utero/placental compartment (mid-gestation). (E, F) Localization of PRLr-mRNA in utero/placental compartment by in situ hybridization (ISH).(A, B) Pre-implantation PRLr is localized to the endometrial surface epithelial cells (solid arrowheads) and glandular epithelial cells of the superficial (open arrowheads) and deep (solid arrows) uterine glands. (C, D) Within the utero/placental compartment signals are localized to the endometrial glands including the superficial glands (solid arrowheads) (the so-called glandular chambers) and to the fetal trophoblast cells (open arrows). (E, F) The same localization pattern was observed at the mRNA-level by ISH. Thus, strong signals are localized to the trophoblast cells (open arrows) including those strongly invading maternal blood vessels at the base of placental labyrinth (open arrows). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7827-9-109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
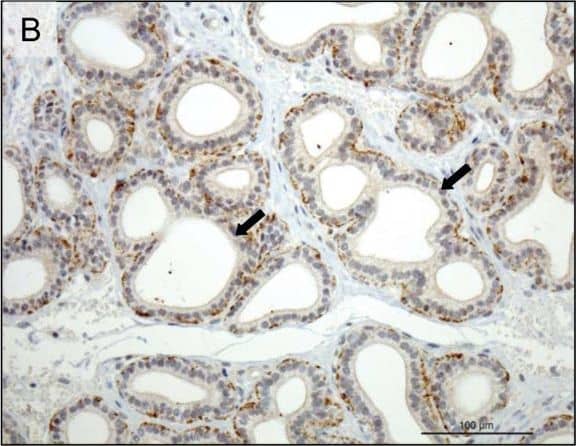 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine Prolactin R by Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical (IHC) localization of PRLr in the uterus pre-implantation and in the utero/placental compartment. (A, B) IHC localization of PRLr in canine endometrium at the pre-implantation stage of pregnancy. (C, D) IHC localization of PRLr within the utero/placental compartment (mid-gestation). (E, F) Localization of PRLr-mRNA in utero/placental compartment by in situ hybridization (ISH).(A, B) Pre-implantation PRLr is localized to the endometrial surface epithelial cells (solid arrowheads) and glandular epithelial cells of the superficial (open arrowheads) and deep (solid arrows) uterine glands. (C, D) Within the utero/placental compartment signals are localized to the endometrial glands including the superficial glands (solid arrowheads) (the so-called glandular chambers) and to the fetal trophoblast cells (open arrows). (E, F) The same localization pattern was observed at the mRNA-level by ISH. Thus, strong signals are localized to the trophoblast cells (open arrows) including those strongly invading maternal blood vessels at the base of placental labyrinth (open arrows). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7827-9-109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
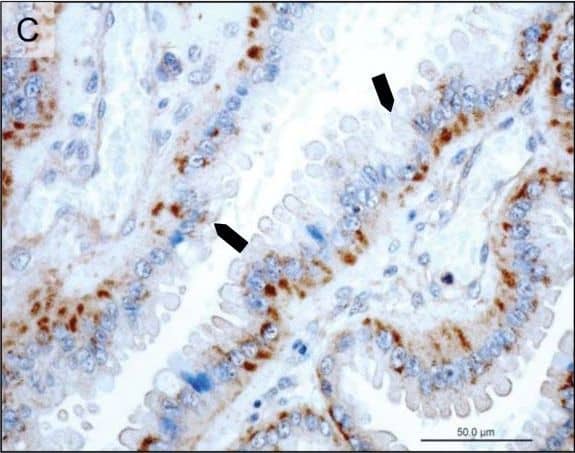 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine Prolactin R by Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical (IHC) localization of PRLr in the uterus pre-implantation and in the utero/placental compartment. (A, B) IHC localization of PRLr in canine endometrium at the pre-implantation stage of pregnancy. (C, D) IHC localization of PRLr within the utero/placental compartment (mid-gestation). (E, F) Localization of PRLr-mRNA in utero/placental compartment by in situ hybridization (ISH).(A, B) Pre-implantation PRLr is localized to the endometrial surface epithelial cells (solid arrowheads) and glandular epithelial cells of the superficial (open arrowheads) and deep (solid arrows) uterine glands. (C, D) Within the utero/placental compartment signals are localized to the endometrial glands including the superficial glands (solid arrowheads) (the so-called glandular chambers) and to the fetal trophoblast cells (open arrows). (E, F) The same localization pattern was observed at the mRNA-level by ISH. Thus, strong signals are localized to the trophoblast cells (open arrows) including those strongly invading maternal blood vessels at the base of placental labyrinth (open arrows). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7827-9-109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine Prolactin R by Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical (IHC) localization of PRLr in the uterus pre-implantation and in the utero/placental compartment. (A, B) IHC localization of PRLr in canine endometrium at the pre-implantation stage of pregnancy. (C, D) IHC localization of PRLr within the utero/placental compartment (mid-gestation). (E, F) Localization of PRLr-mRNA in utero/placental compartment by in situ hybridization (ISH).(A, B) Pre-implantation PRLr is localized to the endometrial surface epithelial cells (solid arrowheads) and glandular epithelial cells of the superficial (open arrowheads) and deep (solid arrows) uterine glands. (C, D) Within the utero/placental compartment signals are localized to the endometrial glands including the superficial glands (solid arrowheads) (the so-called glandular chambers) and to the fetal trophoblast cells (open arrows). (E, F) The same localization pattern was observed at the mRNA-level by ISH. Thus, strong signals are localized to the trophoblast cells (open arrows) including those strongly invading maternal blood vessels at the base of placental labyrinth (open arrows). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7827-9-109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine Prolactin R by Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical (IHC) localization of PRLr in the uterus pre-implantation and in the utero/placental compartment. (A, B) IHC localization of PRLr in canine endometrium at the pre-implantation stage of pregnancy. (C, D) IHC localization of PRLr within the utero/placental compartment (mid-gestation). (E, F) Localization of PRLr-mRNA in utero/placental compartment by in situ hybridization (ISH).(A, B) Pre-implantation PRLr is localized to the endometrial surface epithelial cells (solid arrowheads) and glandular epithelial cells of the superficial (open arrowheads) and deep (solid arrows) uterine glands. (C, D) Within the utero/placental compartment signals are localized to the endometrial glands including the superficial glands (solid arrowheads) (the so-called glandular chambers) and to the fetal trophoblast cells (open arrows). (E, F) The same localization pattern was observed at the mRNA-level by ISH. Thus, strong signals are localized to the trophoblast cells (open arrows) including those strongly invading maternal blood vessels at the base of placental labyrinth (open arrows). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7827-9-109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Prolactin R
The neuroendocrine pituitary hormone Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotrophin, mamotrophin, luteotropic hormone (LTH), or luteotropin, is a secreted hormone that affects reproduction and homeostasis in vertebrates. The functions of PRL can be placed in six broad categories: 1) reproduction and lactation; 2) growth and development; 3) endocrinology and metabolism; 4) brain and behavior; 5) immunomodulation; and 6) electrolyte balance (1, 2). PRL is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, mammary gland, placenta, brain, uterus, decidua, dermal fibroblasts, B cells, T cells, NK cells, and some breast cancer cell lines. Although the major form of PRL is a 23 kDa monomeric protein, splice variants of 14, 16, and 22 kDa have been identified. PRL has also been found to be glycosylated, phosphorylated, dimerized, and polymerized. Glycosylation, phosphorylation, dimerization, or polymerization of PRL result in lower activity (2).
Cell activation by PRL is mediated by a single chain membrane-bound protein belonging to the class 1 cytokine superfamily. The PRL receptor (PRL R) contains an extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domain. Transcriptional regulation of the PRL R gene results in several different species-dependent isoforms of PRL R being produced. Although the cytoplasmic domains of the different isoforms vary in length and composition, their extracellular domains are identical. In rats, three major PRL receptor isoforms have been described, a short (291 amino acid), an intermediate (393 amino acid), and a long (591 amino acid) (2). PRL receptors are found in mammary tissue, pituitary gland, brain, heart, lung thymus, spleen, liver, pancreas, kidney, adrenal gland, uterus, skeletal muscle, and skin (3). A soluble form of PRL-R containing the 206 NH2-terminal amino acids of the extracellular domain is secreted by mammary epithelial cells and is found in milk. Binding of the transmembrane PRL R results in ligand dimerization followed by binding and phosphorylation of Jak2. Jak2 then phosphorylates STAT and the long form of PRL R. C‑src, fyn, and the Ras/Raf/MAP kinase pathway have also been found to be activated upon PRL R ligand binding (2).
- Kelly, P.A. et al. (2001) Biochem. Society Transaction 29:48.
- Freeman, M.E. et al. (2000) Physiol. Rev. 80:1532.
- Nagano, M. and P.A. Kelly (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:13337.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Prolactin R Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Prolactin up-regulates female-predominant Cyp gene expressions and down-regulates male-predominant gene expressions in mice liver
Authors: Y Sato, Y Kaneko, T Cho, K Goto, T Otsuka, S Yamamoto, S Goto, H Maruyama, I Narita
Drug Metab. Dispos, 2017-03-22;0(0):.
-
Expression of prolactin receptors in normal canine mammary tissue, canine mammary adenomas and mammary adenocarcinomas.
Authors: Michel E, Feldmann S, Kowalewski M, Bley C, Boos A, Guscetti F, Reichler I
BMC Vet Res, 2012-05-30;8(0):72.
Species: Canine
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Luteal and placental function in the bitch: spatio-temporal changes in prolactin receptor (PRLr) expression at dioestrus, pregnancy and normal and induced parturition.
Authors: Kowalewski MP, Michel E, Gram A
Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol., 2011-08-03;9(0):109.
Species: Canine
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Immunoregulation of autocrine prolactin: suppressing the expression of costimulatory molecules and cytokines in T lymphocytes by prolactin receptor knockdown.
Authors: Xu D, Lin L, Lin X
Cell. Immunol., 2010-03-02;263(1):71-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsIsotype Controls
Reconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Human Prolactin R Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Prolactin R Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Prolactin R Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image










