Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Antibody Summary
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of TRA‑1‑60 in BG01V Human Cells by Flow Cytometry BG01V human embryonic stem cells were stained with Mouse Anti-Human TRA-1-60 Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB4770, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgM Secondary Antibody (F0116).
 View Larger
View Larger
TRA‑1‑60 in BG01V Human Stem Cells. TRA-1-60 was detected in immersion fixed BG01V human embryonic stem cells using Mouse Anti-Human TRA-1-60 Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB4770) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgM Secondary Antibody (yellow; NL019) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
TRA‑1‑60(R) in ADLF1 and FAB2 Stem Cell Lines. TRA-1-60(R) was detected in immersion fixed ADLF1 (top panel) and FAB2 (bottom panel) induced pluripotent stem cell lines using Mouse Anti-Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB4770) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of TRA‑1‑60(R) in iPSC cells by Flow Cytometry. iPSC cells were stained with Mouse Anti-Human TRA‑1‑60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB4770, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody Mouse IgM (open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgM Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0116). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine TRA-1-60(R) by Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry. Comparison of cell surface proteins CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34, CD45, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81 on primary cultures of BM-MSCs (A, C) and AT-MSCs (B, D). Solid histograms show nonspecific staining and open histograms show specific staining for the indicated marker. Three different donor MSC populations from each tissue type were analyzed and representative samples are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1746-6148-8-150), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine TRA-1-60(R) by Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry. Comparison of cell surface proteins CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34, CD45, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81 on primary cultures of BM-MSCs (A, C) and AT-MSCs (B, D). Solid histograms show nonspecific staining and open histograms show specific staining for the indicated marker. Three different donor MSC populations from each tissue type were analyzed and representative samples are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1746-6148-8-150), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
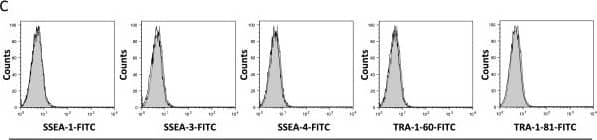
Detection of Canine Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Antibody by Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry. Comparison of cell surface proteins CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34, CD45, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81 on primary cultures of BM-MSCs (A, C) and AT-MSCs (B, D). Solid histograms show nonspecific staining and open histograms show specific staining for the indicated marker. Three different donor MSC populations from each tissue type were analyzed and representative samples are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22937862), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Antibody by Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry. Comparison of cell surface proteins CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34, CD45, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81 on primary cultures of BM-MSCs (A, C) and AT-MSCs (B, D). Solid histograms show nonspecific staining and open histograms show specific staining for the indicated marker. Three different donor MSC populations from each tissue type were analyzed and representative samples are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22937862), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
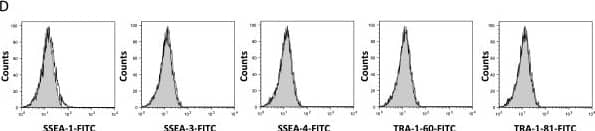
Detection of Canine TRA-1-60(R) by Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry. Comparison of cell surface proteins CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34, CD45, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81 on primary cultures of BM-MSCs (A, C) and AT-MSCs (B, D). Solid histograms show nonspecific staining and open histograms show specific staining for the indicated marker. Three different donor MSC populations from each tissue type were analyzed and representative samples are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22937862), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Canine TRA-1-60(R) by Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry. Comparison of cell surface proteins CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34, CD45, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81 on primary cultures of BM-MSCs (A, C) and AT-MSCs (B, D). Solid histograms show nonspecific staining and open histograms show specific staining for the indicated marker. Three different donor MSC populations from each tissue type were analyzed and representative samples are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22937862), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: TRA-1-60(R)
TRA-1-60 is a monoclonal antibody raised against a cell surface antigen of human embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells (1). The TRA-1-60 epitope is also found on human embryonic stem (ES) cells and primordial germ cells, and TRA-1-60 serves as a serum marker in patients with germ cell tumors (2‑4). Investigation into the identity of the TRA-1-60 epitope demonstrated that it is a carbohydrate carried by a cell surface, sialylated, keratan sulfate proteoglycan (5). Subsequent evidence implicated podocalyxin as a carrier for the TRA-1-60 epitope (6).
- Andrews, P. et al. (1984) Hybridoma 3:347.
- Thomson, J. et al. (1998) Science 282:1145.
- Giwercman, A. et al. (1993) Cancer 72:1308.
- Marrink, J. et al. (1991) Int. J. Cancer 49:368.
- Badcock, G. et al. (1999) Cancer Res. 59:4715.
- Schopperle, W. and W. DeWolf (2007) Stem Cells 25:723.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
13
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Functional defects in hiPSCs-derived cardiomyocytes from patients with a PLEKHM2-mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy and left ventricular non-compaction
Authors: Korover N, Etzion S, Cherniak A et al.
Biological research
-
Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line GZHMCi008-A derived from a patient with SRY-positive 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development
Authors: Y Luo, Y Chen, M Zhang, X Ma, D Zhu, Y Chen
Stem Cell Research, 2021-10-22;57(0):102583.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC -
Induced pluripotent stem cells from subjects with Lesch-Nyhan disease
Authors: DJ Sutcliffe, AR Dinasarapu, JE Visser, JD Hoed, F Seifar, P Joshi, I Ceballos-P, T Sardar, EJ Hess, YV Sun, Z Wen, ME Zwick, HA Jinnah
Scientific Reports, 2021-04-19;11(1):8523.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
A simplified approach for derivation of induced pluripotent stem cells from Epstein-Barr virus immortalized B-lymphoblastoid cell lines
Authors: SJ Walker, AL Wagoner, D Leavitt, DL Mack
Heliyon, 2021-04-03;7(4):e06617.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Glycan Epitopes on 201B7 Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using R-10G and R-17F Marker Antibodies
Authors: Y Nagai, H Nakao, A Kojima, Y Komatsubar, Y Ohta, N Kawasaki, N Kawasaki, H Toyoda, T Kawasaki
Biomolecules, 2021-03-29;11(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Transcriptional signatures of participant-derived neural progenitor cells and neurons implicate altered Wnt signaling in Phelan-McDermid syndrome and autism
Authors: MS Breen, A Browne, GE Hoffman, S Stathopoul, K Brennand, JD Buxbaum, E Drapeau
Mol Autism, 2020-06-19;11(1):53.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Labeling -
The Role of FGF9 in the Production of Neural Retina and RPE in a Pluripotent Stem Cell Model of Early Human Retinal Development
Authors: David M. Gamm, Eric Clark, Elizabeth E. Capowski, Ruchira Singh
American Journal of Ophthalmology
-
Generation of three induced pluripotent stem cell lines from postmortem tissue derived following sudden death of a young patient with STXBP1 mutation
Authors: T Yamamoto, M Otsu, T Okumura, Y Horie, Y Ueno, H Taniguchi, M Ohtaka, M Nakanishi, Y Abe, T Murase, T Umehara, K Ikematsu
Stem Cell Res, 2019-06-18;39(0):101485.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC -
Generation of kisspeptin-responsive GnRH neurons from human pluripotent stem cells
Authors: Ariel Poliandri, Duncan Miller, Sasha Howard, Muriel Nobles, Gerard Ruiz-Babot, Stephen Harmer et al.
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology
-
Rapid establishment of the European Bank for induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (EBiSC) - the Hot Start experience
Authors: PA De Sousa, R Steeg, E Wachter, K Bruce, J King, M Hoeve, S Khadun, G McConnachi, J Holder, A Kurtz, S Seltmann, J Dewender, S Reimann, G Stacey, O O'Shea, C Chapman, L Healy, H Zimmermann, B Bolton, T Rawat, I Atkin, A Veiga, B Kuebler, BM Serano, T Saric, J Hescheler, O Brüstle, M Peitz, C Thiele, N Geijsen, B Holst, C Clausen, M Lako, L Armstrong, SK Gupta, AJ Kvist, R Hicks, A Jonebring, G Brolén, A Ebneth, A Cabrera-So, P Foerch, M Geraerts, TC Stummann, S Harmon, C George, I Streeter, L Clarke, H Parkinson, PW Harrison, A Faulconbri, L Cherubin, T Burdett, C Trigueros, MJ Patel, C Lucas, B Hardy, R Predan, J Dokler, M Brajnik, O Keminer, O Pless, P Gribbon, C Claussen, A Ringwald, B Kreisel, A Courtney, TE Allsopp
Stem Cell Res, 2017-03-07;20(0):105-114.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Comparison of bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived canine mesenchymal stem cells.
BMC Vet Res, 2012-08-31;8(0):150.
Species: Canine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Blood-Derived Human iPS Cells Generate Optic Vesicle–Like Structures with the Capacity to Form Retinal Laminae and Develop Synapses
Authors: M. Joseph Phillips, Kyle A. Wallace, Sarah J. Dickerson, Michael J. Miller, Amelia D. Verhoeven, Jessica M. Martin et al.
Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science
-
Comparative proteomic analysis of human somatic cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, and embryonic stem cells.
Authors: Kim SY, Kim MJ, Jung H
Stem Cells Dev., 2011-08-29;21(8):1272-86.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human TRA-1-60(R) Neuraminidase Resistant Epitope Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
The cells were stained with 1 µg of TRA-1-60 antibody in 100 µl FACS buffer at 4C for 30 min. After washing, the cells were incubated with anti-IgM-AF488 antibody at 4C for 20 min.