Mouse CCL17/TARC Antibody Summary
Ala24-Pro93
Accession # Q9WUZ6
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
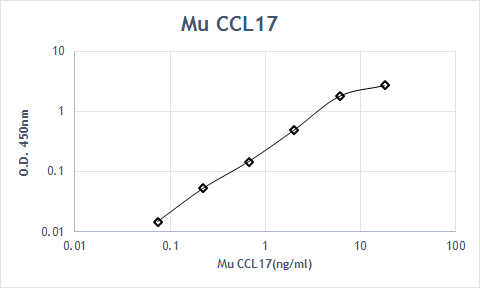
 View Larger
View Larger
Chemotaxis Induced by CCL17/TARC and Neutralization by Mouse CCL17/TARC Antibody. Recombinant Mouse CCL17/ TARC (Catalog # 529-TR) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CCR4 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (Catalog # AR002). Chemotaxis elicited by Recombinant Mouse CCL17/TARC (0.02 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Mouse CCL17/TARC Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF529). The ND50 is typically 0.2-0.6 µg/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CCL17/TARC by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Cd248 disruption reduced infiltration and pro-fibrotic phenotype switching of kidney macrophages during renal fibrosis. (a) Representative images of F4/80 immunostaining for macrophages in control and D14 UUO kidneys. F4/80+ staining was brown. Original magnification, × 100. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Quantification of F4/80+ areas on LPF images of kidney sections taken at 100 × magnification n = 10. (c). Representative images of green fluorescent protein (GFP)+ circulation-derived cells and F4/80+ (red) macrophages in control and day 3 (D3) UUO-kidneys of WT and Cd248–/– parabionts joined surgically to transgenic GFP (GFPTg) mice. Arrowhead indicates an F4/80+GFP+ macrophage. Original magnification, × 100. Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) Quantification of GFP+, F4/80+ and F4/80+GFP+ cells on LPF images of control (upper panel) and D3 UUO (lower panel) kidneys of WT and Cd248–/– parabionts. n = 3. (e) qPCR of genes encoding cytokines and enzymes in macrophages isolated from D7 UUO kidneys. n = 4. (f) qPCR of Nos2, Arg1 and Ccl17 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon gamma (IFN gamma )–primed RAW264.7 macrophages co-cultured with D7 UUO-kidney myofibroblasts isolated from WT or Cd248–/– mice in the Transwell system. RAW264.7 macrophages co-cultured with medium were used as control. n = 4. (g) qPCR of Ccl17 in WT bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs, Mϕ) co-cultured with medium only (control) or with WT or Cd248–/– UUO-kidney myofibroblasts (MF) in the same dish. Recombinant CD248 (rCD248) was included in the culture as indicated. n = 5. Data are expressed as means ± standard errors of the mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test in (b,g) and unpaired t-test in (d,e,f). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33033277), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CCL17/TARC by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Cd248 disruption reduced infiltration and pro-fibrotic phenotype switching of kidney macrophages during renal fibrosis. (a) Representative images of F4/80 immunostaining for macrophages in control and D14 UUO kidneys. F4/80+ staining was brown. Original magnification, × 100. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Quantification of F4/80+ areas on LPF images of kidney sections taken at 100 × magnification n = 10. (c). Representative images of green fluorescent protein (GFP)+ circulation-derived cells and F4/80+ (red) macrophages in control and day 3 (D3) UUO-kidneys of WT and Cd248–/– parabionts joined surgically to transgenic GFP (GFPTg) mice. Arrowhead indicates an F4/80+GFP+ macrophage. Original magnification, × 100. Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) Quantification of GFP+, F4/80+ and F4/80+GFP+ cells on LPF images of control (upper panel) and D3 UUO (lower panel) kidneys of WT and Cd248–/– parabionts. n = 3. (e) qPCR of genes encoding cytokines and enzymes in macrophages isolated from D7 UUO kidneys. n = 4. (f) qPCR of Nos2, Arg1 and Ccl17 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon gamma (IFN gamma )–primed RAW264.7 macrophages co-cultured with D7 UUO-kidney myofibroblasts isolated from WT or Cd248–/– mice in the Transwell system. RAW264.7 macrophages co-cultured with medium were used as control. n = 4. (g) qPCR of Ccl17 in WT bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs, Mϕ) co-cultured with medium only (control) or with WT or Cd248–/– UUO-kidney myofibroblasts (MF) in the same dish. Recombinant CD248 (rCD248) was included in the culture as indicated. n = 5. Data are expressed as means ± standard errors of the mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test in (b,g) and unpaired t-test in (d,e,f). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33033277), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CCL17/TARC
Human thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) also known as CCL17, is a novel CC chemokine identified using a signal sequence trap method. Mouse TARC was discovered as a dendritic cell (DC) specific gene by differentiation RNA display. Mouse TARC cDNA encodes a highly basic 93 amino acid (aa) residue precursor protein with a 23 aa residue putative signal peptide that is cleaved to generate the 70 aa residue mature secreted protein. Among CC chemokine family members, TARC has approximately 24 - 29% amino acid sequence identity with RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, MIP-1 beta, MCP-1, MCP-2, MCP-3 and I-309. The gene for human TARC has been mapped to chromosome 16q13 rather than chromosome 17 where the genes for many human CC chemokines are clustered. Mouse TARC is constitutively expressed in thymic DC, and at a lower level in lymph node DC in the lung. Recombinant TARC has been shown to be chemotactic for T cell lines and antigen-primed T helper cells. In humans, TARC was identified to be a specific functional ligand for CCR-4 and CCR-8, receptors that are selectively expressed on T cells.
- Imai, T. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:15036.
- Imai, T. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:21514.
- Nomiyama, H. et al. (1997) Genomics 40:211.
- Lieberam, I. et al. (1999) Eur. J. Immunol. 29:2684.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse CCL17/TARC Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
12
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
PGE2-EP2/EP4 signaling elicits immunosuppression by driving the mregDC-Treg axis in inflammatory tumor microenvironment
Authors: D Thumkeo, S Punyawatth, S Prasongtan, R Matsuura, K Arima, H Nie, R Yamamoto, N Aoyama, H Hamaguchi, S Sugahara, S Takeda, V Charoensaw, A Tanaka, S Sakaguchi, S Narumiya
Cell Reports, 2022-06-07;39(10):110914.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Single-cell RNA sequencing uncovers the individual alteration of intestinal mucosal immunocytes in Dusp6 knockout mice
Authors: Cherng-Shyang Chang, Wen-Hsuan Yu, Chang-Chao Su, Jhen-Wei Ruan, Chiao-Mei Lin, Chih-Ting Huang et al.
iScience
-
Prolactin enhances T regulatory cell promotion of breast cancer through the long form prolactin receptor
Authors: KE Chen, M Ghosh, L Rivera, S Lin, A Kumar, S Swaminatha, MY Lorenson, AM Walker
Translational Oncology, 2021-08-07;14(11):101195.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Targeting fibroblast CD248 attenuates CCL17-expressing macrophages and tissue fibrosis
Authors: CH Pai, SR Lin, CH Liu, SY Pan, H Hsu, YT Chen, CT Yen, IS Yu, HL Wu, SL Lin, SW Lin
Sci Rep, 2020-10-08;10(1):16772.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Neutralization -
Cross-talk between iNKT cells and CD8 T cells in the spleen requires the IL-4/CCL17 axis for the generation of short-lived effector cells
Authors: M Valente, Y Dölen, E van Dinthe, L Vimeux, M Fallet, V Feuillet, CG Figdor
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2019-12-03;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Confocal Microscopy -
Eosinophil recruitment is dynamically regulated by interplay among lung dendritic cell subsets after allergen challenge
Authors: S Yi, J Zhai, R Niu, G Zhu, M Wang, J Liu, H Huang, Y Wang, X Jing, L Kang, W Song, Y Shi, H Tang
Nat Commun, 2018-09-24;9(1):3879.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
IL-4/CCL22/CCR4 axis controls regulatory T-cell migration that suppresses inflammatory bone loss in murine experimental periodontitis.
Authors: Araujo-Pires A, Vieira A, Francisconi C, Biguetti C, Glowacki A, Yoshizawa S, Campanelli A, Trombone A, Sfeir C, Little S, Garlet G
J Bone Miner Res, 2015-03-01;30(3):412-22.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Defective immunoregulation in RSV vaccine-augmented viral lung disease restored by selective chemoattraction of regulatory T cells.
Authors: Loebbermann, Jens, Durant, Lydia, Thornton, Hannah, Johansson, Cecilia, Openshaw, Peter J
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013-02-04;110(8):2987-92.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Comprehensive assessment of chemokine expression profiles by flow cytometry.
Authors: Eberlein J, Nguyen TT, Victorino F, Golden-Mason L, Rosen HR, Homann D
J. Clin. Invest., 2010-02-08;120(3):907-23.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Allergic pulmonary inflammation in mice is dependent on eosinophil-induced recruitment of effector T cells.
Authors: Jacobsen EA, Ochkur SI, Pero RS, Taranova AG, Protheroe CA, Colbert DC, Lee NA, Lee JJ
J. Exp. Med., 2008-03-03;205(3):699-710.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
CCL17 transgenic mice show an enhanced Th2-type response to both allergic and non-allergic stimuli.
Authors: Tsunemi Y, Saeki H, Nakamura K, Nagakubo D, Nakayama T, Yoshie O, Kagami S, Shimazu K, Kadono T, Sugaya M, Komine M, Matsushima K, Tamaki K
Eur. J. Immunol., 2006-08-01;36(8):2116-27.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization, Western Blot -
Immunosuppressive effects of CCL17 on pulmonary antifungal responses during pulmonary invasive aspergillosis.
Authors: Carpenter KJ, Hogaboam CM
Infect. Immun., 2005-11-01;73(11):7198-207.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types:
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsIsotype Controls
Reconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Mouse CCL17/TARC Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Mouse CCL17/TARC Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Used as Detection in ELISA