Mouse CXCR4 Antibody Summary
Met1-Ser359
Accession # P70658
Customers also Viewed
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
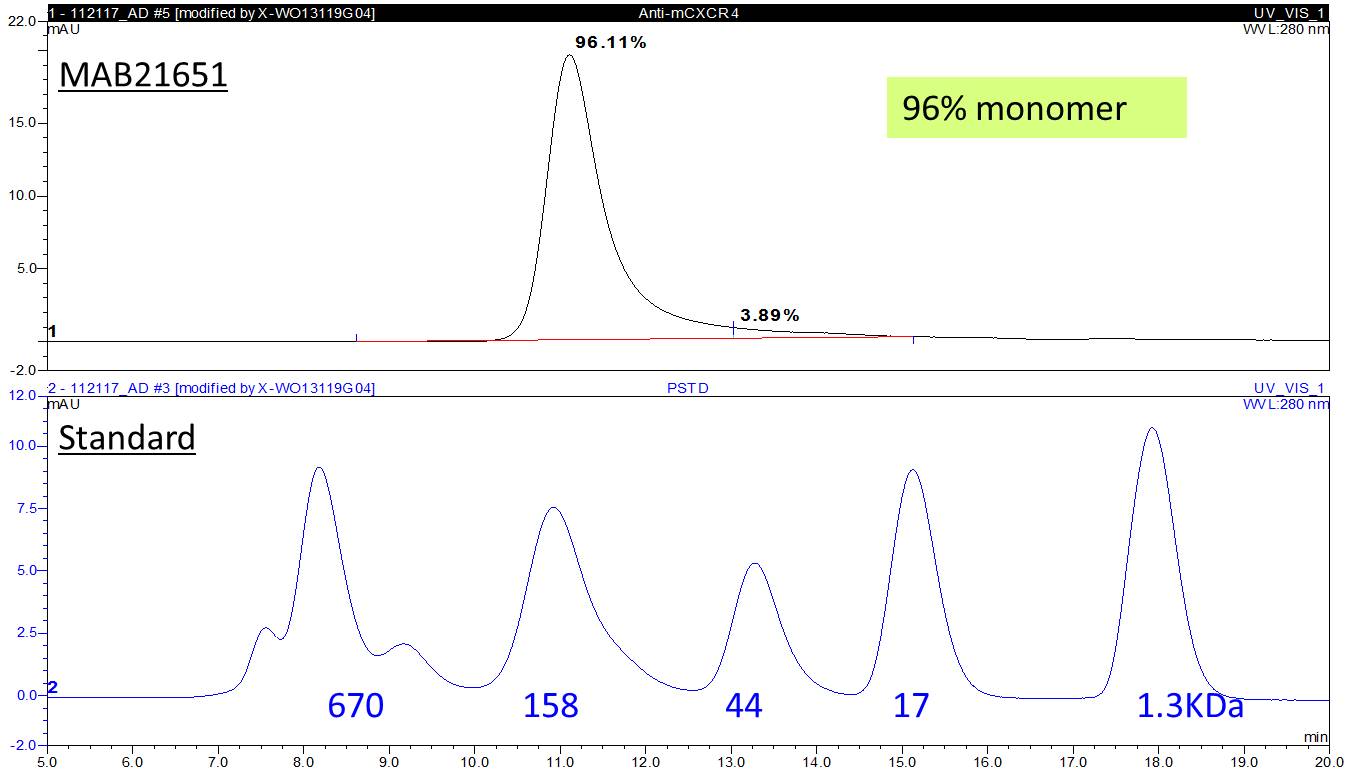
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
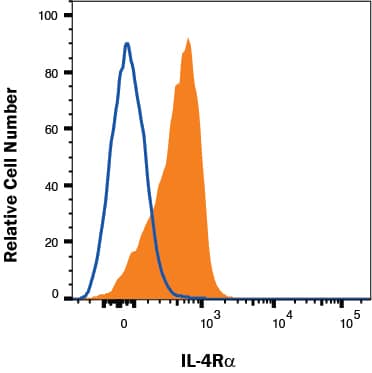
Detection of CXCR4 in Mouse Thymocytes by Flow Cytometry. Mouse thymocytes were stained with (A) Rat Anti-Mouse CXCR4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21651) or (B) Rat IgG2B isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB0061) followed by anti-Rat IgG PE-conjugated Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0105B) and Rat anti-Mouse CD8 alpha APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB116A). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
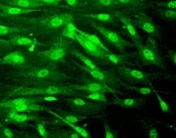
CXCR4 in Mouse Neural Progenitor Cells. CXCR4 was detected in immersion fixed mouse neural progenitor cells using 10 µg/mL Rat Anti-Mouse CXCR4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21651) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL013) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
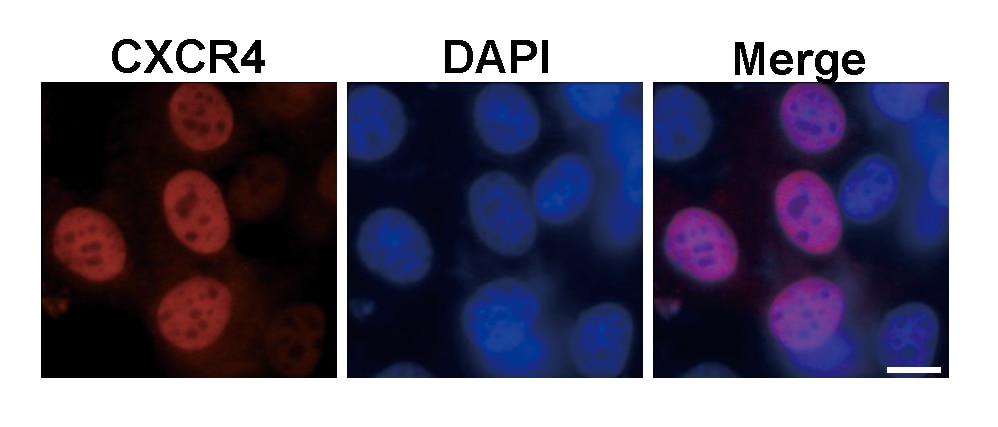
CXCR4 in Mouse Splenocytes. CXCR4 was detected in immersion fixed mouse splenocytes using 10 µg/mL Rat Anti-Mouse CXCR4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21651) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL013) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
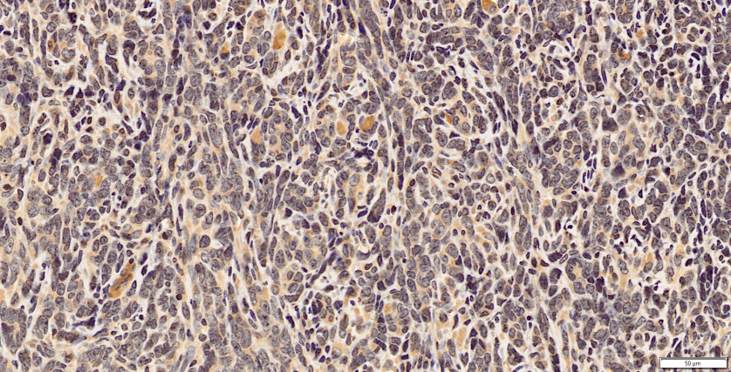
CXCR4 in Mouse Spleen. CXCR4 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse spleen using Rat Anti-Mouse CXCR4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21651) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS017) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Chemotaxis Induced by CXCL12/SDF‑1 alpha and Neutralization by Mouse CXCR4 Antibody. Recombinant Mouse CXCL12/SDF-1a (Catalog # 460-SD) chemo-attracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with mouse CXCR4 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (Catalog # AR002). Chemotaxis elicited by Recombinant Mouse CXCL12/ SDF-1a (10 ng/mL) is neutral-ized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Rat Anti-Mouse CXCR4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB21651). The ND50 is typically 8-40 µg/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CXCR4 by Western Blot Effects of SDF-1-CXCR4/CXCR7 pathway on MSC chemotaxis in vitro.(A) The chemotaxis in response to SDF-1 alpha (10 ng/ml for 12 h) was performed in the NP-MSCs and HP-MSCs treated with a neutralizing anti-CXCR4 antibody, an anti-CXCR7 antibody, and the respective isotype-matched control antibodies. *P<0.05, vs NP-MSCs; †P<0.05, vs the respective isotype-matched control antibodies. (B) NP-MSCs were transiently overexpressed with CXCR4 using pORF9-mCXCR4 vector or with CXCR7 using pORF9-mCXCR7 vector (n = 6). A negative control empty (pORF9-MCS) vector was used. (C) The transfected cells were subjected to chemotaxis in response to the indicated concentrations of SDF-1 alpha for 12 h. *P<0.05, vs the empty vector. (D and E) Western blot analysis (D) and FCM (E) were performed to determine the intracellular and extracellular expression of both CXCR4 and CXCR7 in the cells treated with or without SDF-1 alpha (50 ng/ml for 60 min). (F) The chemotaxis in response to SDF-1 alpha was performed in the cells treated with or without SDF-1 alpha. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22511954), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CXCR4 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Downregulation of Cxcr4, SSEA1 and expression of TRA98 after release from GoST induction.(A) Immunofluorescence of Cxcr4 (white) and SSEA1 (green) after release from GoST induction. Cxcr4 and SSEA1 were detected simultaneously. DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue). Cxcr4 and SSEA1 were expressed in ES, cES and GoST cells. Cxcr4 was downregulated at 4, 8 and 12 days after release from GoST induction, while SSEA1 remained expressed until 4 days after release from GoST induction and was downregulated afterwards at 8 and 12 days after release. Scalebar = 50 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence of TRA98 (white) and SSEA1 (green) after release from GoST induction. TRA98 and SSEA1 were detected simultaneously. DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue). TRA98 and SSEA1 were expressed in ES, cES and GoST cells. Expression of TRA98 slightly decreased but remained detectable in the nucleus at 4, 8 and 12 days after release from GoST induction, while SSEA1 remained expressed until 4 days after release from GoST induction and was downregulated afterwards at 8 and 12 days after release. Scalebar = 50 μm. See Fig. S6. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/srep25104), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CXCR4 by Functional CXCL12 induces CXCR4/CXCR7 and cell polarization in HUVECs. HUVECs were cultured on plastic Petri dishes (pretreated with PDL) with BSA stripes (the control group) and BSA plus CXCL12 stripes (CXCL12 group) for 5 min. HUVECs were fixed and stained with antibodies against CXCR4 (purple), CXCR7 (blue) and F-Actin (red). The micro stripes of fluorescein-conjugated BSA (A) or CXCL12 (H) are shown. CXCR4 (B), CXCR7 (C) and F-Actin (D) in HUVECs cultured on BSA stripes stayed in the resting state, while the polarization of CXCR4 (arrow: I), CXCR7 (arrow: J) and F-Actin (arrow: K) was observed in HUVECs cultured on CXCL12 stripes for 5 min. Moreover, the HUVECs in the BSA control group showed no morphological changes (E–G). The CXCL12 group HUVECs shows polarization towards the CXCL12 stripe (L–N). Scale bar: 10 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28811579), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human CXCR4 by Functional CXCL12 induces CXCR4/CXCR7 and cell polarization in HUVECs. HUVECs were cultured on plastic Petri dishes (pretreated with PDL) with BSA stripes (the control group) and BSA plus CXCL12 stripes (CXCL12 group) for 5 min. HUVECs were fixed and stained with antibodies against CXCR4 (purple), CXCR7 (blue) and F-Actin (red). The micro stripes of fluorescein-conjugated BSA (A) or CXCL12 (H) are shown. CXCR4 (B), CXCR7 (C) and F-Actin (D) in HUVECs cultured on BSA stripes stayed in the resting state, while the polarization of CXCR4 (arrow: I), CXCR7 (arrow: J) and F-Actin (arrow: K) was observed in HUVECs cultured on CXCL12 stripes for 5 min. Moreover, the HUVECs in the BSA control group showed no morphological changes (E–G). The CXCL12 group HUVECs shows polarization towards the CXCL12 stripe (L–N). Scale bar: 10 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28811579), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CXCR4 by Immunohistochemistry RhoA modulates the CXCR4-CXCL12 axis in breast tumors. (a) Representative immunohistochemical (IHC) staining images of breast primary tumor sections of mice orthotopically injected with 4T1 GFP-LUC cells carrying indicated lentiviral modifications, stained with antibodies for CD31 (top, left), F4/80 (middle, left) and alpha -SMA (bottom, left). CD31+ area (top, right), F4/80+ cells (middle, right) and alpha -SMA+ area (bottom, right) per tumor field of view (FOV) (mean ± SE) quantifications of IHC images. N = 4. (b) Representative IHC staining images of breast primary tumor sections of above mice stained with CXCL12 antibody (left). CXCL12+ area per tumor FOV (mean ± SE) quantification of IHC images. N = 4. (c) Representative immunofluorescent images of breast primary tumor sections of above mice co-stained with alpha -SMA, CXCL12 and DRAQ5 nuclear stain, showing the co-localization of alpha -SMA and CXCL12 signals. Scale bar: 50 µm. (d) Representative IHC staining images of breast primary tumor sections of above mice stained with CXCR4 antibody (left). CXCR4+ area per tumor FOV (mean ± SE) quantification of IHC images. N = 4. (e) Relative mCXCR4 mRNA levels normalized with mActin (mean ± SE), as quantified by qRT-PCR in primary breast tumors of above mice (top) and in 4T1 GFP-LUC cells carrying indicated lentiviral modifications (bottom). N = 4, ns- not significant *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test (two-tailed). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31705019), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CXCR4
CXCR4, also known as CD184, is a G-protein-linked seven transmembrane spanning receptor that binds stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1). CXCR4 acts as a co-factor for T-cell tropic HIV-1 and -2 viral entry into cells. While primarily a membrane protein, CXCR4 undergoes trafficking and internalization in response to stimulation with phorbol esters and ligand (1). Cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of CXCR4 has been observed in colorectal and renal carcinomas (2,3) and it has been used as the basis of prognosis and metastatic state (3,4,5).
- Orsini, M.J. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:31076.
- Zagzag, D. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65:6178.
- Speetjens, F.M. et al. (2009) Cancer Microenvironment 2:1.
- Wang, L. et al. (2009) Oncology Reports 22:1333.
- Amara, S. et al. (2015) Cancer Biomark. 15:869.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse CXCR4 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
46
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals a Dynamic Stromal Niche That Supports Tumor Growth
Authors: S Davidson, M Efremova, A Riedel, B Mahata, J Pramanik, J Huuhtanen, G Kar, R Vento-Torm, T Hagai, X Chen, MA Haniffa, JD Shields, SA Teichmann
Cell Rep, 2020-05-19;31(7):107628.
-
Novel characterization of CXCR4 expressing cells in uninfected and herpes simplex virus-1 infected corneas
Authors: PK Suvas, M Setia, M Rana, A Chakrabort, S Suvas
The ocular surface, 2023-02-20;28(0):99-107.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Novel characterization of CXCR4 expressing cells in uninfected and herpes simplex virus-1 infected corneas
Authors: PK Suvas, M Setia, M Rana, A Chakrabort, S Suvas
The ocular surface, 2023;28(0):99-107.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Selected renal cells harbor nephrogenic potential
Authors: Prakash Narayan, Andrew T. Bruce, Elias A. Rivera, Timothy A. Bertram, Deepak Jain
Frontiers in Medicine
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Immunocytochemistry -
CXCR4, CXCR5 and CD44 May Be Involved in Homing of Lymphoma Cells into the Eye in a Patient Derived Xenograft Homing Mouse Model for Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma
Authors: Neele Babst, Lisa K. Isbell, Felix Rommel, Aysegul Tura, Mahdy Ranjbar, Salvatore Grisanti et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
-
Tumor-infiltrated activated B cells suppress liver metastasis of colorectal cancers
Authors: Y Xu, Z Wei, M Feng, D Zhu, S Mei, Z Wu, Q Feng, W Chang, M Ji, C Liu, Y Zhu, L Shen, F Yang, Y Chen, Y Feng, J Xu, D Zhu
Cell Reports, 2022-08-30;40(9):111295.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Digit specific denervation does not inhibit mouse digit tip regeneration
Authors: Connor P. Dolan, Felisha Imholt, Mingquan Yan, Tae-Jung Yang, Joshua Gregory, Osama Qureshi et al.
Developmental Biology
-
Dual role for CXCL12 signaling in semilunar valve development
Authors: LA Ridge, D Kewbank, D Schütz, R Stumm, PJ Scambler, S Ivins
Cell Reports, 2021-08-24;36(8):109610.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates brain angiogenesis and independently decreases mouse survival under hypoxia
Authors: Drew R. Seeger, Svetlana A. Golovko, Bryon D. Grove, Mikhail Y. Golovko
Journal of Neurochemistry
-
CXCR4 Regulates Temporal Differentiation via PRC1 Complex in Organogenesis of Epithelial Glands
Authors: J Kim, SW Lee, K Park
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021-01-10;22(2):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Coexpression of CCR7 and CXCR4 During B Cell Development Controls CXCR4 Responsiveness and Bone Marrow Homing
Authors: Saria Mcheik, Nils Van Eeckhout, Cédric De Poorter, Céline Galés, Marc Parmentier, Jean-Yves Springael
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Reduced RhoA expression enhances breast cancer metastasis with a concomitant increase in CCR5 and CXCR4 chemokines signaling
Authors: G Kalpana, C Figy, M Yeung, KC Yeung
Sci Rep, 2019-11-08;9(1):16351.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Secreted nuclear protein DEK regulates hematopoiesis through CXCR2 signaling
Authors: ML Capitano, N Mor-Vaknin, AK Saha, S Cooper, M Legendre, H Guo, R Contreras-, F Kappes, MA Sartor, CT Lee, X Huang, DM Markovitz, HE Broxmeyer
J. Clin. Invest., 2019-05-20;130(0):2555-2570.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Inhibition of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis prevents peri-urethral collagen accumulation and lower urinary tract dysfunction in vivo
Authors: Jill A. Macoska, Zunyi Wang, Johanna Virta, Nicholas Zacharias, Dale E. Bjorling
The Prostate
-
The Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Mediates Recruitment of CD11c+ Conventional Dendritic Cells Into the Inflamed Murine Cornea
Authors: MJ Lopez, Y Seyed-Raza, A Jamali, DL Harris, P Hamrah
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 2018-11-01;59(13):5671-5681.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC -
Blastema formation and periosteal ossification in the regenerating adult mouse digit
Authors: Lindsay A. Dawson, Paula P. Schanes, Patrick Kim, Felisha M. Imholt, Osama Qureshi, Connor P. Dolan et al.
Wound Repair and Regeneration
-
CXCR4 signaling contributes to alveolar bone resorption in Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced periodontitis in mice
Authors: H Nagashima, M Shinoda, K Honda, N Kamio, A Hasuike, N Sugano, Y Arai, S Sato, K Iwata
J Oral Sci, 2017-10-31;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
The periosteal requirement and temporal dynamics of BMP2‐induced middle phalanx regeneration in the adult mouse
Authors: Lindsay A. Dawson, Ling Yu, Mingquan Yan, Luis Marrero, Paula P. Schanes, Connor Dolan et al.
Regeneration (Oxf)
-
CXCL12 enhances angiogenesis through CXCR7 activation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Authors: M Zhang, L Qiu, Y Zhang, D Xu, JC Zheng, L Jiang
Sci Rep, 2017-08-15;7(1):8289.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Proinflammatory CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 signaling axis drives Myc-induced prostate cancer in obese mice
Authors: A Saha, S Ahn, J Blando, F Su, MG Kolonin, J DiGiovanni
Cancer Res., 2017-07-07;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Natural amines inhibit activation of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells through CXCR4 engagement
Authors: N Smith, N Pietrancos, S Davidson, J Dutrieux, L Chauveau, P Cutolo, M Dy, D Scott-Alga, B Manoury, O Zirafi, I McCort-Tra, T Durroux, F Bachelerie, O Schwartz, J Münch, A Wack, S Nisole, JP Herbeuval
Nat Commun, 2017-02-09;8(0):14253.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Loss of Ranbp2 in motor neurons causes the disruption of nucleocytoplasmic and chemokine signaling and proteostasis of hnRNPH3 and Mmp28, and the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-like syndromes
Authors: KI Cho, D Yoon, S Qiu, Z Danziger, WM Grill, WC Wetsel, PA Ferreira
Dis Model Mech, 2017-01-18;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
CXCR4 signaling in macrophages contributes to periodontal mechanical hypersensitivity in Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced periodontitis in mice
Authors: H Nagashima, M Shinoda, K Honda, N Kamio, M Watanabe, T Suzuki, N Sugano, S Sato, K Iwata
Mol Pain, 2017-01-01;13(0):1744806916689.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr, Neutralization -
A gonogenic stimulated transition of mouse embryonic stem cells with enhanced control of diverse differentiation pathways
Sci Rep, 2016-05-09;6(0):25104.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
Predicted molecular signaling guiding photoreceptor cell migration following transplantation into damaged retina
Authors: Uchenna John Unachukwu, Alice Warren, Ze Li, Shawn Mishra, Jing Zhou, Moira Sauane et al.
Scientific Reports
-
CXCR7 Mediates Neural Progenitor Cells Migration to CXCL12 Independent of CXCR4.
Authors: Chen Q, Zhang M, Li Y, Xu D, Wang Y, Song A, Zhu B, Huang Y, Zheng J
Stem Cells, 2015-05-13;33(8):2574-85.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
NKG2D ligand overexpression in lupus nephritis correlates with increased NK cell activity and differentiation in kidneys but not in the periphery.
Authors: Spada R, Rojas J, Perez-Yague S, Mulens V, Cannata-Ortiz P, Bragado R, Barber D
J Leukoc Biol, 2015-01-12;97(3):583-98.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Protein z exerts pro-angiogenic effects and upregulates CXCR4.
Authors: Butschkau, Antje, Wagner, Nana-Mar, Genz, Berit, Vollmar, Brigitte
PLoS ONE, 2014-12-04;9(12):e113554.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Nuclear factor kappa-B signaling is integral to ocular neovascularization in ischemia-independent microenvironment.
Authors: DeNiro M, Al-Mohanna F
PLoS ONE, 2014-07-22;9(7):e101602.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
An important role of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in chronic skin inflammation.
Authors: Zgraggen, Silvana, Huggenberger, Reto, Kerl, Katrin, Detmar, Michael
PLoS ONE, 2014-04-02;9(4):e93665.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Systemic neutralization of IL-17A significantly reduces breast cancer associated metastasis in arthritic mice by reducing CXCL12/SDF-1 expression in the metastatic niches.
Authors: Roy, Lopamudr, Sahraei, Mahnaz, Schettini, Jorge L, Gruber, Helen E, Besmer, Dahlia M, Mukherjee, Pinku
BMC Cancer, 2014-03-27;14(0):225.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Mechanisms of adhesion and subsequent actions of a haematopoietic stem cell line, HPC-7, in the injured murine intestinal microcirculation in vivo.
Authors: Kavanagh D, Yemm A, Zhao Y, Frampton J, Kalia N
PLoS ONE, 2013-03-12;8(3):e59150.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling is required for the maintenance of mouse spermatogonial stem cells.
Authors: Yang, Qi-En, Kim, Dongwon, Kaucher, Amy, Oatley, Melissa, Oatley, Jon M
J Cell Sci, 2012-12-13;126(0):1009-20.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC -
Influence of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha on dendritic cell differentiation and migration.
Authors: Kohler T, Reizis B, Johnson RS, Weighardt H, Forster I
Eur. J. Immunol., 2012-05-01;42(5):1226-36.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
The role of SDF-1-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in the therapeutic effects of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Authors: Liu H, Liu S, Li Y, Wang X, Xue W, Ge G, Luo X
PLoS ONE, 2012-04-12;7(4):e34608.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
MicroRNA126 contributes to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization by reducing the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
Authors: Salvucci O, Jiang K, Gasperini P
Haematologica, 2012-01-22;97(6):818-26.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
IL-1alpha and IL-1beta recruit different myeloid cells and promote different stages of sterile inflammation.
Authors: Rider P, Carmi Y, Guttman O, Braiman A, Cohen I, Voronov E, White MR, Dinarello CA, Apte RN
J. Immunol., 2011-09-19;187(9):4835-43.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Hypoxic preconditioning advances CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression by activating HIF-1alpha in MSCs.
Authors: Liu H, Xue W, Ge G, Luo X, Li Y, Xiang H, Ding X, Tian P, Tian X
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2010-09-24;401(4):509-15.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Microarray analysis of retinal endothelial tip cells identifies CXCR4 as a mediator of tip cell morphology and branching.
Authors: Strasser GA, Kaminker JS, Tessier-Lavigne M
Blood, 2010-02-12;115(24):5102-10.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Paracrine modulation of CXCR4 by IGF-1 and VEGF: implications for choroidal neovascularization.
Authors: Sengupta N, Afzal A, Caballero S, Chang KH, Shaw LC, Pang JJ, Bond VC, Bhutto I, Baba T, Lutty GA, Grant MB
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 2009-12-10;51(5):2697-704.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
The angiogenic response is dictated by beta3 integrin on bone marrow-derived cells.
Authors: Feng W, McCabe NP, Mahabeleshwar GH, Somanath PR, Phillips DR, Byzova TV
J. Cell Biol., 2008-12-15;183(6):1145-57.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Rosuvastatin reduces atherosclerotic lesions and promotes progenitor cell mobilisation and recruitment in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.
Authors: Schroeter MR, Humboldt T, Schafer K, Konstantinides S
Atherosclerosis, 2008-11-25;205(1):63-73.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Regulation of CXCR4 by the Notch ligand delta-like 4 in endothelial cells.
Authors: Williams CK, Segarra M, Sierra Mde L, Sainson RC, Tosato G, Harris AL
Cancer Res., 2008-03-15;68(6):1889-95.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
CXCR4 receptor blockage reduces the contribution of tumor and stromal cells to the metastatic growth in the liver
Authors: A Benedicto, I Romayor, B Arteta
Oncol. Rep., 2018-02-08;0(0):.
-
Selected renal cells harbor nephrogenic potential
Authors: Prakash Narayan, Andrew T. Bruce, Elias A. Rivera, Timothy A. Bertram, Deepak Jain
Frontiers in Medicine
-
Cytotoxic T cells swarm by homotypic chemokine signalling
Authors: Jorge Luis Galeano Niño, Sophie V Pageon, Szun S Tay, Feyza Colakoglu, Daryan Kempe, Jack Hywood et al.
eLife
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsIsotype Controls
Reconstitution Buffers
Secondary Antibodies
Reviews for Mouse CXCR4 Antibody
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 4 Reviews)
Have you used Mouse CXCR4 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
1:75
Citrate buffer antigen retrieval